PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
PEACE Cable: Pakistan's Highest Bandwidth Undersea Internet Connection to Africa and Europe
Pakistan and East Africa Connecting Europe (PEACE) is 96 Tbps (terabits per second), 15,000 km long, privately owned submarine cable that will originate in Karachi, Pakistan and run underwater all the way to Marseilles, France via multiple points in the continent of Africa. It is being built as part of Digital Silk Road sponsored by China. Cybernet and Jazz are the local landing and global connectivity partners of PEACE Cable System in Pakistan. It will enable high-speed access to a variety of content, cloud computing, gaming and video streaming platforms.
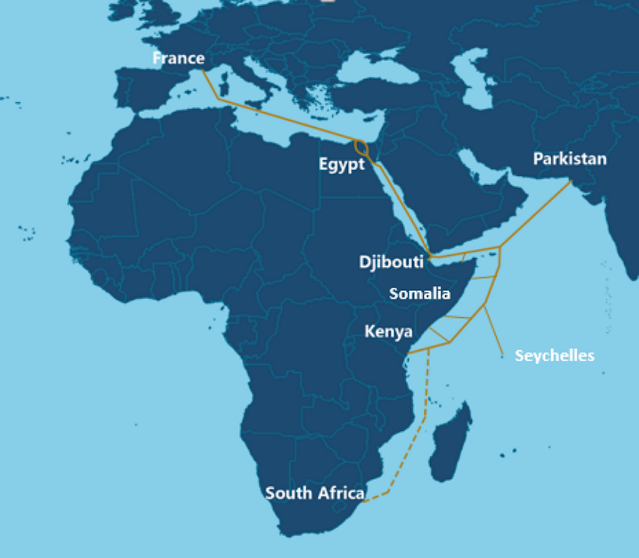 |
| PEACE Undersea Cable Route. Source: Submarine Cable Networks |
| Mobile Broadband Subscriptions & Data Growth in Pakistan |
 |
| Broadband Subscriptions Growth in Pakistan. Source: PTA |
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on March 27, 2023 at 8:52pm
-
OneWeb secures Pakistan distribution | Advanced Television
https://advanced-television.com/2021/11/08/oneweb-secures-pakistan-...
The newly formed OneWeb/NEOM Tech & Digital JV will bring high-speed satellite connectivity to NEOM, Saudi Arabia, the wider Middle East and neighbouring countries including Pakistan.
The OneWeb/NEOM Tech & Digital JV has exclusive rights to distribute OneWeb services in these regions for seven years, and is expected to commence operations in 2023.
The OneWeb/NEOM Tech & Digital JV is looking to transform businesses and communities, stimulating enterprise across the region, with gateways and Points of Presence (POPs) in the Middle East providing security, speed and low latency data to sectors such as finance and retail, as well as schools and hospitals.
The JV says it will offer a seamless solution to infrastructural hurdles in Pakistan, where mobile operators and local loop operators will be able to leverage the service to expand their coverage areas, offering dependable low-cost internet access.
Matthew Johnson, Interim CEO of the OneWeb/NEOM Tech & Digital JV, said: “LEO satellites not only mean we can reach absolutely everyone everywhere, but with reliable and rapid speeds – connectivity at 100 megabits per second and more without the need for techniques such as trenching or placement of 5G equipment and fiber optics. This partnership with REDtone highlights how this technology presents an incredible growth opportunity for the wider region.”
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on May 26, 2023 at 1:29pm
-
USF Approves Rs. 21 Billion for New Optical Fiber and Broadband Projects
https://propakistani.pk/2022/09/25/usf-approves-rs-21-billion-for-n...
The Universal Service Fund (USF) Board has approved the award of 10 contracts worth approximately Rs. 21 billion for the unserved and under-served communities of Baluchistan, Punjab, Sindh, and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP).
The high-speed mobile broadband projects, highways and motorways projects, and optical fiber cable projects will provide 4G LTE connectivity and backhaul connectivity to around 3.5 million people by connecting 187 Union Councils (UCs) with 1,554 kilometers (kms) of optical fiber cable and provide seamless connectivity to 622 km of unserved road segments on M-8 motorway and N-35 highway.
Additional Secretary (Incharge) IT & Telecommunication and Chairman USF Board Mohsin Mushtaq Chandna chaired the 83rd Board of Directors meeting of USF on Thursday.
While addressing the meeting, Chandna said that USF has delivered a record productive performance in the past 4 years by contracting 79 projects worth approximately Rs. 62.7 billion in subsidy. This is a testament to our absolute commitment to improving the lives and livelihoods of the unserved and underserved communities of Pakistan.
He also highlighted the importance of infrastructure, affordability, and accessibility of the internet and pledged to work with all stakeholders to achieve the vision of Digital Pakistan.
USF Chief Executive Officer Haaris Mahmood Chaudhary apprised the Board members of the progress of the current projects and the restoration of the flood-affected USF network. He said that these projects will empower around 3.3 million people living in far-flung and backward areas across Pakistan, enabling them to access e-services across various spheres, ranging from financial services like banking and loans to accessibility towards various government services and benefits.
According to the details, the Board approved the award of 5 high-speed mobile broadband contracts worth approximately Rs. 7.1 billion for providing 4G LTE services in the rural and remote districts of Punjab, Sindh, and Balochistan. These projects will benefit people living in 262 unserved muazas of Dera Ghazi Khan, Layyah, Muzaffargarh, Multan, and Rajanpur districts in Punjab, Jamshoro in Sindh, and Barkhan, Musakhel, Sherani, and Sibi in Balochistan covering an approximate unserved area of 12,784.91 sq. km.
Furthermore, the Board also approved the award of two high-speed mobile broadband projects for National Highways and Motorways worth Rs. 6 billion for providing 4G LTE services to commuters on unserved road segments of 622.68 km on M-8 motorway and N-35 highway respectively.
Similarly, the USF Board also approved the award of three optical fiber cable projects worth approximately Rs. 7.7 billion for providing backhaul connectivity to 187 Union Councils (UCs) of Punjab and KP. Under these projects, USF will deploy a total of 1,554 km of optical fiber cable that will benefit over 3.3 million people in the districts of Attock, Sheikhupura, and Nankana Sahib in Punjab and Bannu and Lakki Marwat in KP. These projects are designed to connect 684 educational institutions, 223 government offices, and 268 health institutions along with mandatory connectivity of 408 BTS towers.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 7, 2023 at 6:47pm
-
Super Fast Gigabit Fiber Internet is Coming to 11 Cities in Pakistan Soon
https://propakistani.pk/2023/06/07/super-fast-gigabit-fiber-interne...
Pakistan is about to get ultra-fast gigabit fiber internet in eleven cities soon, as per government documents available with ProPakistani.
This document highlights the Public Sector Development Project (PDSP) budget during the period of 2022-2024. It includes a summary of current ongoing projects, future projects, and more under the Ministry of Planning, Development, and Special Initiatives.
Under the Information Technology and Telecom Division, it highlights a new scheme for a project that will expand Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) Fiber to the Home (FTTH) services to eleven cities.
In simpler words, super fast gigabit internet is coming to more cities soon, as mentioned earlier. The project’s approval status is still “under process”, so it will probably be a while before it sees the light of day.
The government has approved a cost of Rs. 800 million and there is no foreign aid on this particular project. An additional Rs. 50 million will be allocated to this project during the course of 2023-2024.
Other Development Projects
The IT section of the document also highlights dozens of other projects the govt is working on at the moment, such as 4 more knowledge parks, a technology park development project, an online recruitment system for FPSC, smart offices for Federal Ministries and Departments, expansion of broadband services in Kashmir and Gilgit, and much more.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 25, 2023 at 1:45pm
-
Chinese firm starts to lay 16,000-km-long fibre-optic cable in Pakistan
https://www.thenews.com.pk/print/1072079-chinese-firm-starts-to-lay...
This was stated by Tony Lee, Chief Executive Officer of Sunwalk Pvt Limited, during a ceremony held in Islamabad. This Chinese company had already invested $5 million in Pakistan, and now planning to invest $100 million for laying optical fiber in other parts after getting Right of Way (ROW) from different public sector departments.
Tony Lee said Sunwalk is focusing on fast deployment and concentrating on quality according to the ITU-T Standards. “We are always committed to the best services in Pakistan”, he said.
Two months ago, Sunwalk Group Chairman Hou Xing Wang told Federal Minister for IT and Telecom Aminul Haque in a meeting Sunwalk Group will soon start laying fiber cable across the country with substantial investment.
According to an official statement about the project, Ms Afshaan Malik, Chief Business Officer of Sunwalk Group Pakistan, said keeping in view Pak-China long-term strategic relationships, Sunwalk has fulfilled its promise by initiating the national fiber backbone project. Sunwalk is committed to providing optic cable to the people of Pakistan, she said.
In this connection, groundbreaking of Phase-1 (Islamabad to Multan) to provide nationwide fiber backbone was done on Thursday. Afshaan further said Sunwalk is in the process of getting ROW from government departments. After getting that $100 million will be invested, she said.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 18, 2023 at 11:13am
-
China plans $500 million subsea internet cable to rival US-backed project | Reuters
https://www.reuters.com/world/china/china-plans-500-mln-subsea-inte...
Known as EMA (Europe-Middle East-Asia), the proposed cable would link Hong Kong to China’s island province of Hainan, before snaking its way to Singapore, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Egypt and France, the four people said. They asked not to be named because they were not allowed to discuss potential trade secrets.
The cable, which would cost approximately $500 million to complete, would be manufactured and laid by China’s HMN Technologies Co Ltd, a fast-growing cable firm whose predecessor company was majority-owned by Chinese telecom giant Huawei Technologies Co Ltd, the people said.
---------
SINGAPORE, April 6 (Reuters) - Chinese state-owned telecom firms are developing a $500 million undersea fiber-optic internet cable network that would link Asia, the Middle East and Europe to rival a similar U.S.-backed project, four people involved in the deal told Reuters. The plan is a sign that an intensifying tech war between Beijing and Washington risks tearing the fabric of the internet.
China's three main carriers – China Telecommunications Corporation (China Telecom), China Mobile Limited and China United Network Communications Group Co Ltd(China Unicom) – are mapping out one of the world’s most advanced and far-reaching subsea cable networks, according to the four people, who have direct knowledge of the plan.
-----------
They said HMN Tech, which is majority-owned by Shanghai-listed Hengtong Optic-Electric Co Ltd, would receive subsidies from the Chinese state to build the cable.
China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom, HMN Tech, and Hengtong did not respond to requests for comment.
The Chinese foreign ministry said in a statement to Reuters that it "has always encouraged Chinese enterprises to carry out foreign investment and cooperation" without commenting directly on the EMA cable project.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 18, 2023 at 11:14am
-
U.S. and China wage war beneath the waves - over internet cables
https://www.reuters.com/investigates/special-report/us-china-tech-c...
Subsea cables, which carry the world's data, are now central to the U.S.-China tech war. Washington, fearful of Beijing's spies, has thwarted Chinese projects abroad and choked Big Tech's cable routes to Hong Kong, Reuters has learned.
It started out as strictly business: a huge private contract for one of the world’s most advanced undersea fiber-optic cables. It became a trophy in a growing proxy war between the United States and China over technologies that could determine who achieves economic and military dominance for decades to come.
In February, American subsea cable company SubCom LLC began laying a $600-million cable to transport data from Asia to Europe, via Africa and the Middle East, at super-fast speeds over 12,000 miles of fiber running along the seafloor.
That cable is known as South East Asia–Middle East–Western Europe 6, or SeaMeWe-6 for short. It will connect a dozen countries as it snakes its way from Singapore to France, crossing three seas and the Indian Ocean on the way. It is slated to be finished in 2025.
It was a project that slipped through China’s fingers.
A Chinese company that has quickly emerged as a force in the subsea cable-building industry – HMN Technologies Co Ltd – was on the brink of snagging that contract three years ago. The client for the cable was a consortium of more than a dozen global firms. Three of China’s state-owned carriers – China Telecommunications Corporation (China Telecom), China Mobile Limited and China United Network Communications Group Co Ltd (China Unicom) – had committed funding as members of the consortium, which also included U.S.-based Microsoft Corp and French telecom firm Orange SA, according to six people involved in the deal.
HMN Tech, whose predecessor company was majority-owned by Chinese telecom giant Huawei Technologies Co Ltd, was selected in early 2020 to manufacture and lay the cable, the people said, due in part to hefty subsidies from Beijing that lowered the cost. HMN Tech’s bid of $500 million was roughly a third cheaper than the initial proposal submitted to the cable consortium by New Jersey-based SubCom, the people said.
The Singapore-to-France cable would have been HMN Tech’s biggest such project to date, cementing it as the world’s fastest-rising subsea cable builder, and extending the global reach of the three Chinese telecom firms that had intended to invest in it.
But the U.S. government, concerned about the potential for Chinese spying on these sensitive communications cables, ran a successful campaign to flip the contract to SubCom through incentives and pressure on consortium members.
Reuters has detailed that effort here for the first time. It’s one of at least six private undersea cable deals in the Asia-Pacific region over the past four years where the U.S. government either intervened to keep HMN Tech from winning that business, or forced the rerouting or abandonment of cables that would have directly linked U.S. and Chinese territories. The story of those interventions by Washington hasn’t been previously reported.
SubCom had no comment on the SeaMeWe-6 battle, and HMN Tech did not respond to requests for comment. In a statement last year about infrastructure projects, the White House briefly noted that the U.S. government helped SubCom to win the Singapore-to-France cable contract, without giving details. China’s foreign ministry did not respond to requests for comment. China Telecom, China Mobile, China Unicom and Orange did not respond to requests for comment. Microsoft declined to comment.
Undersea cables are central to U.S.-China technology competition.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 18, 2023 at 11:20am
-
U.S. and China wage war beneath the waves - over internet cables
https://www.reuters.com/investigates/special-report/us-china-tech-c...
Meanwhile, American diplomats cautioned participating foreign telecom carriers that Washington planned to impose crippling sanctions on HMN Tech, a development that could put their investment in the cable project at risk. The U.S. Commerce Department made good on that threat in December 2021, citing HMN Tech’s intention to acquire American technology to help modernize China’s People’s Liberation Army.
A senior U.S. State Department official confirmed that the department had advocated through its embassies to help SubCom win the contract, including warning other countries about the security risks posed by HMN Tech. Though the cable won’t come ashore in Chinese territory, the U.S. government believed HMN Tech could insert remote surveillance equipment inside the cable, the official said without providing evidence. The Commerce Department declined to comment.
Two months later, in February 2022, SubCom announced that the cable consortium had awarded it the contract to build the SeaMeWe-6 cable. China Telecom and China Mobile, which were due to own a combined 20% of the cable, pulled out because the Chinese government wouldn’t approve their involvement in the project with SubCom as the cable contractor, three people with knowledge of the matter told Reuters. China Unicom remained.
China’s foreign ministry and its defense ministry, which handles questions for the People’s Liberation Army, did not respond to Reuters’ questions.
On June 26, 2022, the White House published a fact sheet citing various upcoming infrastructure projects, including the SubCom undersea cable deal. The document said the U.S. government had “collectively helped secure” the award of that contract for SubCom.
The White House did not respond to a request for further comment.
U.S.-China relations are at the lowest they’ve been in decades. The two countries have clashed on a host of issues, including China’s tacit support for Russia’s invasion of democratic Ukraine, its crackdown on Hong Kong, and the future of Taiwan, which Chinese President Xi Jinping has pledged to bring under Beijing’s control. In February, the United States shot down a Chinese spy balloon that floated into American airspace. China has claimed it was a weather balloon that got blown off course and accused the Americans of overreacting.
President Joe Biden’s policies are increasingly isolating China’s high-tech sector with the aim of bringing some technology manufacturing back to America while keeping cutting-edge U.S. innovation out of Chinese hands.
Over the last year, the Biden administration has pushed through a landmark bill to provide $52.7 billion in subsidies for U.S. semiconductor production and research. The Commerce Department in December added dozens of Chinese firms producing technology such as drones and artificial intelligence chips to its so-called Entity List, which severely restricts their access to U.S. technology.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 18, 2023 at 11:23am
-
U.S. and China wage war beneath the waves - over internet cables
https://www.reuters.com/investigates/special-report/us-china-tech-c...
Chinese Foreign Minister Qin Gang, speaking in Beijing this month, said the two superpowers are destined for “conflict and confrontation” unless Washington abandons its policy of “containment and suppression” towards China.
Three companies have dominated the construction and laying of fiber-optic subsea cables for decades: America’s SubCom, Japan’s NEC Corporation and France’s Alcatel Submarine Networks, Inc.
But a seismic shift occurred in 2008 when Huawei Marine Networks Co Ltd entered the fray. Owned by Chinese telecom Huawei Technologies, the Tianjin-based company initially built small cable systems in underserved markets such as Papua New Guinea and the Caribbean.
Fast-forward 15 years and the firm, now known as HMN Tech, has become the world’s fastest-growing manufacturer and layer of subsea cables, according to TeleGeography data.
But the company’s short history has been shaped by deteriorating U.S.-China relations.
In 2019, Huawei Technologies came under fire from the administration of then-U.S. President Donald Trump. The Commerce Department banned Huawei and 70 affiliates from buying parts and components from U.S. companies without government approval.
That move was part of a global campaign by Washington and its allies to stop Huawei Technologies from building fifth-generation, or 5G, communications networks around the world due to concerns that host nations would be vulnerable to Chinese eavesdropping or cyberattacks, the details of which were revealed in a previous Reuters investigation.
Huawei Technologies said at the time that it was a private company that is not controlled by the Chinese government. Contacted for this story, Huawei Technologies said it fully divested its stake in Huawei Marine in 2020 and is no longer connected with the cable-laying company, which rebranded as HMN Tech under new Chinese ownership.
HMN Tech expanded its ambitions with the PEACE cable, which came online last year and connects Asia, Africa and Europe. The firm was poised to make another great leap with the Singapore-to-France project before SubCom snatched it away.
The following account of how that deal fell apart for the Chinese players is based on interviews with six people directly involved in the SeaMeWe-6 contract. They all asked not to be named as they were not authorized to discuss potential trade secrets or matters of national security.
Large undersea cables cost several hundreds of millions of dollars. They are usually paid for by a consortium of tech or telecom companies that can spread the cost and risks, as well as take responsibility for any cable landing that ends up in their countries.
In the case of SeaMeWe-6, there were more than a dozen companies funding the cable, and there was immediately a split in the group, which would need to reach a consensus to select a contractor for the project, the people said.
China Telecom, China Mobile and China Unicom were resolutely behind HMN Tech, which had come in with a bid of around $500 million. Microsoft, Orange and India’s Bharti Airtel expressed concerns about the risk of potential U.S. pushback on HMN Tech’s involvement. Still, it was hard to argue with the price. SubCom’s bid was closer to $750 million.
On a series of video calls in mid-2020, the consortium members verbally agreed that HMN Tech would build the cable. SubCom would be the reserve in case the Chinese firm pulled out or failed to deliver on the terms of its proposal.
But behind the scenes, SubCom and the U.S. government were sowing seeds of doubt about whether HMN Tech was the best company for the job.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 18, 2023 at 11:26am
-
U.S. and China wage war beneath the waves - over internet cables
https://www.reuters.com/investigates/special-report/us-china-tech-c...
SubCom had already successfully applied for loans from the federal Export-Import Bank of the United States to support its bid. It also secured advocacy assistance from the Department of Commerce, which quickly mobilized U.S. embassies around the world to lean on consortium members in their host nations.
U.S. ambassadors in at least six of those countries, including Singapore, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka, wrote letters to local telecom carriers participating in the deal, according to people involved. One of these letters, seen by Reuters, said picking SubCom is “an important opportunity to enhance commercial and security cooperation with the United States.”
Separately, ambassadors and senior diplomats met with executives at foreign telecom companies in at least five countries. The message: HMN Tech could be subject to U.S. sanctions in the near future. That in turn would make it difficult for the telecoms to sell bandwidth because their biggest likely customers – U.S. tech firms – wouldn’t be allowed to use the cable.
One senior Asian telecom executive recalled a meeting in mid-2020 with a top U.S. diplomat and an American digital trade attaché. The U.S. officials explained how sanctions on HMN Tech would render the cable virtually worthless, providing him a printed spreadsheet with an economic analysis showing just that.
“They said we’d go bankrupt. It was a persuasive argument,” the executive told Reuters.
Two other Asian telecom executives in the consortium told Reuters they met with both Chinese and U.S. diplomats, who urged them to back HMN Tech and SubCom, respectively.
By the end of 2020, several consortium members, including Bangladesh Submarine Cable Company Limited, India’s Bharti Airtel, Sri Lanka Telecom, France’s Orange and Telecom Egypt, told their partners they were having second thoughts about choosing HMN Tech as a supplier, mostly over the fear of sanctions.
None of these companies responded to requests for comment.
In February 2021, with the consortium partners at loggerheads, SubCom and HMN Tech were given a chance by the group to submit a “best and final offer.” SubCom lowered its bid to close to $600 million. But HMN Tech was now offering to build the cable for $475 million.
Several consortium members, including Microsoft, Singapore Telecommunications Limited (Singtel) and Orange, argued to the other participants that when the risk of sanctions was factored into the bids, SubCom was offering a better deal. The three state-owned Chinese companies strongly disagreed. The companies all declined comment.
On a tense final video call in late 2021, an executive from Singtel, the chair on the cable committee, urged the companies to vote on a final decision before the whole deal collapsed, two people who were on that call told Reuters.
China Telecom and China Mobile threatened to walk off the project, taking tens of millions of dollars of investment with them. But the majority of the consortium picked SubCom, and the two Chinese state-owned firms departed. Two new investors – Telekom Malaysia Berhad and PT Telekomunikasi Indonesia International (Telin) – joined the deal, and some of the original members raised their stakes to make up the shortfall, the people said.
Telekom Malaysia and Telin did not respond to requests for comment.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 18, 2023 at 11:28am
-
U.S. and China wage war beneath the waves - over internet cables
https://www.reuters.com/investigates/special-report/us-china-tech-c...
In addition to the successful campaign to freeze out HMT Tech from the Singapore-to-France cable, teams across the U.S. state and commerce departments and the Office of the U.S. Trade Representative once again coordinated with the White House to use diplomatic pressure to boot the Chinese firm from a project. This time it was a cable connecting the three Pacific island nations of Nauru, the Federated States of Micronesia and Kiribati, according to two sources involved in that deal.
The United States, Australia and Japan announced in December 2021 that they would jointly fund a cable on the same route, known as the East Micronesia Cable. In a joint statement this month, the three said they had met on March 8 to help “push forward” on this cable, without giving a time frame.
The U.S.-China backroom brawling over undersea cables is threatening to overwhelm the subsea cable industry, which has always relied on careful diplomatic collaboration to survive, said Paul McCann, a Sydney-based subsea cable consultant.
“I've never seen such geopolitical influence over subsea cables in the 40-odd years I’ve been involved in the business,” McCann told Reuters. “It's unprecedented.”
At the heart of Washington’s newly aggressive strategy is Team Telecom. That’s the informal name for an interagency committee set up through an Executive Order signed by Trump in April 2020. The mission: safeguarding U.S. telecommunication networks from spies and cyberattacks.
Team Telecom is run by the National Security Division of the Department of Justice (DOJ). That division is headed by Assistant Attorney General Matthew Olsen. Nominated to that position by Biden in May 2021, Olsen has worked in a string of intel posts. He served as director of the National Counterterrorism Center under former President Barack Obama from 2011 to 2014, and before that as general counsel for the National Security Agency, the U.S. spy nerve center.
The DOJ declined to make Olsen available for an interview.
While the State Department and its partners have helped to prevent China from obtaining new subsea contracts in foreign places of U.S. strategic interest, Team Telecom has focused on a purely domestic concern: stopping any cable from directly connecting U.S. territory with mainland China or Hong Kong due to worries about Chinese espionage.
To that end, the team makes cable licensing recommendations to the U.S. telecom regulator, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Since 2020, the team has been instrumental in the cancellation of four cables whose backers had wanted to link the United States with Hong Kong, Devin DeBacker, a DOJ official and senior member of Team Telecom, told Reuters in an interview.
Hong Kong, a former British colony that transitioned to self-rule and is dubbed a “special administrative region” by China, has long been the investment gateway to the communist mainland because of its well-developed financial sector, open economy and highly-educated workforce.
However, in 2019, Beijing launched a security crackdown and increased surveillance in Hong Kong, prompting mass demonstrations. As China tightened its grip, Washington became concerned that Chinese spy agencies would intercept data on the planned undersea cables if that equipment ultimately came ashore in Hong Kong, said DeBacker, the chief of the Foreign Investment Review Section of the DOJ’s National Security Division.
“That provides a physical access point in what is effectively Chinese territory,” DeBacker said. “Because of the way that China has eroded Hong Kong's autonomy, that enabled the Chinese government to have a direct, all-access path, effectively a collection platform on U.S. persons’ data and communications.”
“The risk is real. It has materialized in the past, and what we're trying to do is prevent it from materializing in the future”
Comment
- ‹ Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Next ›
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Russian Hackers Steal Indian Military Secrets From Pakistani Cyber Spies
Hackers linked to Russian intelligence have stolen Indian military data from cyber spies believed to be working on behalf of the Pakistani state, according to an assessment by Microsoft researchers. All those involved are part of what are known as "advanced persistent threat" (APT) organizations in their respective countries. TechTarget defines "Advanced Persistent Threat (APT)…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on December 8, 2024 at 8:00am
IDEAS 2024: Pakistan Defense Industry's New Drones, Missiles and Loitering Munitions
The recently concluded IDEAS 2024, Pakistan's Biennial International Arms Expo in Karachi, featured the latest products offered by Pakistan's defense industry. These new products reflect new capabilities required by the Pakistani military for modern war-fighting to deter external enemies. The event hosted 550 exhibitors, including 340 international defense companies, as well as 350 civilian and military officials from 55 countries.
Pakistani defense manufacturers…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on December 1, 2024 at 5:30pm — 3 Comments
© 2024 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()

You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network