PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
Pakistan Water Crisis: Facts and Myths
Pakistan is believed to be in the midst of a water crisis that is said to pose an existential threat to the country. These assertions raise a whole series of questions on the source of the crisis and possible solutions to deal with it. The New Water Policy adopted in April 2018 is a good start but it needs a lot more focus and continuing investments.
 |
| Indus Water System. Courtesy: The Friday Times |
Questions on Water Crisis:
How severe is Pakistan's water crisis? Is India contributing to this crisis? How many million acre feet (MAF) of water flows in Pakistan? What are its sources? Glaciers? Rain? Groundwater? How much of it is stored in dams and other reservoirs? What is the trend of per capita water availability in Pakistan? What sectors are the biggest consumers of water in Pakistan? Why does agriculture consume over 95% of all available water? How can Pakistan produce "more crop per drop"? What are Pakistan's options in dealing with the water crisis? Build more dams? Recharge groundwater? Use improved irrigation techniques like sprinklers and drip irrigation? Would metering water at the consumers and charging based on actual use create incentives to be more efficient in water use?
Water Availability:
Pakistan receives an average of 145 million acre feet (MAF) of water a year, according to the Indus River System Authority (IRSA) report. Water availability at various canal headworks is about 95 million acre feet (MAF). About 50%-90% comes from the glacial melt while the rest comes from monsoon rains. Additional 50 MAF of groundwater is extracted annually via tube wells.
Pakistan Water Availability. Source: Water Conference Presentation |
The total per capita water availability is about 900 cubic meters per person, putting Pakistan in the water-stressed category.
India Factor:
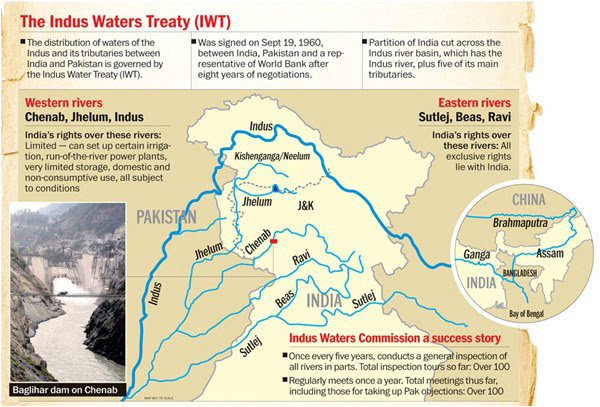
What is the impact of India's actions on water flow in Pakistan? Under the Indus Basin Water Treaty, India has the exclusive use of the water from two eastern rivers: Ravi and Sutlej. Pakistan has the right to use all of the water from the three western rivers: Chenab, Jhelum and Indus. However, India can build run of the river hydroelectric power plants with minimal water storage to generate electricity.
Currently, India is not using all of the water from the two eastern rivers. About 4.6 million acre feet (MAF) of water flows into Pakistan via Ravi and Sutlej. Water flow in Pakistan will be reduced if India decides to divert more water from Ravi and Sutlej for its own use.
Secondly, India can store water needed for run-of-the-river hydroelectric plants on the western rivers. When new hydroelectric projects are built on these rivers in India, Pakistan suffers from reduced water flows during the periods when these reservoirs are filled by India. This happened when Baglihar dam was filled by India as reported by Harvard Professor John Briscoe who was assigned by the World Bank to work on IWT compliance by both India and Pakistan.
Pakistan is also likely to suffer when India ensures its hydroelectric reservoirs are filled in periods of low water flow in the three western rivers.
Water Storage Capacity:
Pakistan's water storage capacity in its various dams and lakes is about 15 million acre feet (MAF), about 10% of all water flow. It's just enough water to cover a little over a month of water needed. There are several new dams in the works which will double Pakistan's water storage capacity when completed in the future.
Since 1970s, the only significant expansion in water storage capacity occurred on former President Musharraf's watch when Mangla Dam was raised 30 feet to increase its capacity by nearly 3 million acre feet (MAF). Musharraf increased water projects budget to Rs. 70 billion which was reduced to Rs. 51 billion by PPP government and further decreased to Rs. 36 billion by PMLN government. It was only the very last PMLN budget passed by Shahid Khaqan Abbasi's outgoing government that increased water development allocation to Rs. 65 billion, a far cry from Rs. 70 billion during Musharraf years given the dramatic drop in the value of the Pakistani rupee.
Water Consumption:
Domestic, business and industrial consumers use about 5 million acre feet while the rest is consumed by the agriculture sector to grow food. Just 5% improvement in irrigation efficiency can save Pakistan about 7.5 million acre feet , the same as the current storage capacity of the country's largest Tarbela dam.
Given the vast amount of water used to grow crops, there is a significant opportunity to save water and increase yields by modernizing the farm sector.
National Water Policy:
Pakistan's Common Council of Interests (CCI) with the prime minister and the provincial chief ministers recently adopted a National Water Policy (NWP) in April 2018. It is designed to deal with “the looming shortage of water” which poses “a grave threat to (the country’s) food, energy and water security” and constitutes “an existential threat…”as well as “the commitment and intent” of the federal and provincial governments to make efforts “ to avert the water crisis”.
The NWP supports significant increases in the public sector investment for the water sector by the Federal Government from 3.7% of the development budget in 2017-18 to at least 10% in 2018-19 and 20% by 2030; the establishment of an apex body to approve legislation, policies and strategies for water resource development and management, supported by a multi- sectoral Steering Committee of officials at the working level; and the creation of a Groundwater Authority in Islamabad and provincial water authorities in each of the provinces.
More Crop Per Drop:
"More crop per drop" program will focus on improving water use efficiency by promoting drip and sprinkler irrigation in agriculture.
The Punjab government started this effort with the World Bank with $250 million investment. The World Bank is now providing additional $130 million financing for the Punjab Irrigated Agriculture Productivity Improvement Program Phase-I.
The project is the Punjab Government's initiative called High-Efficiency Irrigation Systems (HEIS) to more than doubles the efficiency of water use. Under the project, drip irrigation systems have been installed on about 26,000 acres, and 5,000 laser leveling units have been provided. The additional financing will ensure completion of 120,000 acres with ponds in saline areas and for rainwater harvesting, and filtration systems for drinking water where possible, according to the World Bank.
Groundwater Depletion:
Pakistan, India, and the United States are responsible for two-thirds of the groundwater use globally, according to a report by University College London researcher Carole Dalin. Nearly half of this groundwater is used to grow wheat and rice crops for domestic consumption and exports. This puts Pakistan among the world's largest exporters of its rapidly depleting groundwater.
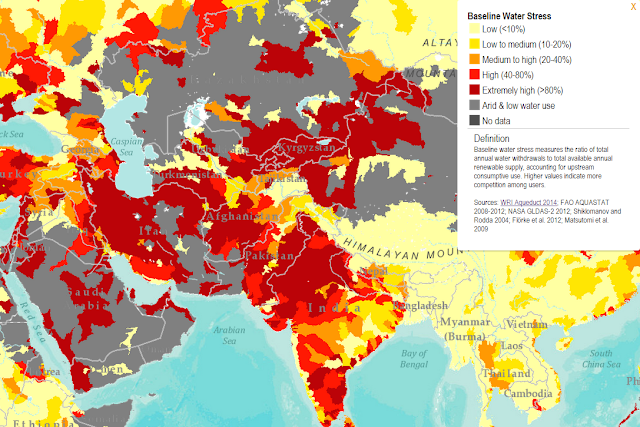
Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources is working with United States' National Air and Space Administration (NASA) to monitor groundwater resources in the country.
Water Stress Satellite Map Source: NASA |
NASA's water stress maps shows extreme water stress across most of Pakistan and northern, western and southern parts of India.
The US space agency uses Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) to measure earth's groundwater. GRACE’s pair of identical satellites, launched in 2002, map tiny variations in Earth's gravity. Since water has mass, it affects these measurements. Therefore, GRACE data can help scientists monitor where the water is and how it changes over time, according to NASA.
Aquifer Recharge:
Building large dams is only part of the solution to water stress in Pakistan. The other, more important part, is building structures to trap rain water for recharging aquifers across the country.
Typical Aquifer in Thar Desert |
Pakistan's highly water stressed Punjab province is beginning recognize the need for replacing groundwater. Punjab Government is currently in the process of planning a project to recharge aquifers for groundwater management in the Province by developing the economical and sustainable technology and to recharge aquifer naturally and artificially at the available site across the Punjab. It has allocated Rs. 582.249 million to execute this project over four years.
Summary:
Pakistan is in the midst of a severe water crisis that could pose an existential threat if nothing is done to deal with it. The total per capita water availability is about 900 cubic meters per person, putting the country in the water-stressed category. Agriculture sector uses about 95% of the available water. There are significant opportunities to achieve greater efficiency by using drop irrigation systems being introduced in Punjab. The New Water Policy is a good start but it requires continued attention with greater investments and focus to deal with all aspects of the crisis.
Here's a video discussion on the subject:
Related Links:
Groundwater Depletion in Pakistan
Cycles of Drought and Floods in Pakistan
Pakistan to Build Massive Dams
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on May 30, 2022 at 9:06pm
-
Balochistan water storage increases
https://tribune.com.pk/story/2351918/balochistan-water-storage-incr...
The water storage capacity of Balochistan has reached 68,939 acre feet which will enhance the irrigation network and address water scarcity issues of the drought-hit province.
Under the Public Sector Development Programme (PSDP), as many as 27 dams have been completed having storage capacity of 68,939 acre feet in various districts of Balochistan.
There are also ongoing small, medium, large and delayed action dams at various stages of implementation that will further add another 9.016 million acre feet (MAF) to the existing storage capacity.
After the construction of large reservoirs in the country, the storage capacity of water will increase several million-acre feet that will help store rain and floods water during monsoon.
An official of the Ministry of Water and Power told APP that the work was underway on various projects in Balochistan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Sindh to address the growing issue of water scarcity.
“The federal government is also providing funds for construction of various small, medium, large, and delay action and recharge dam projects in the country through Federal Public Sector Development Program (PSDP)”, he said.
These projects aimed at providing water for irrigation, agriculture, and drinking purposes which were being implemented by WAPDA and Irrigation Departments of four provinces besides the Public Health Engineering Department, Balochistan.
At present combined storage capacity of Mangla, Tarbela, and Chashma reservoirs is about 14.349 MAF. After the completion of ongoing projects i.e. Mohmand, Diamer Basha, and Nai Gaj Dams, the gross storage capacity will be increased to 23.988 MAF.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 18, 2022 at 10:55am
-
The World Bank’s Board of Executive Directors today approved $200 million in financing to support Pakistan in transforming the agricultural sector by adopting climate-smart technologies to improve water-use efficiency, build resilience to extreme weather events and increase incomes of small farmers.
https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2022/07/15/world-ba...
The agricultural sector in Punjab is central to the Pakistan’s economy and food security as it accounts for 73 percent of the country’s total food production. The Punjab Resilient and Inclusive Agriculture Transformation Project (PRIAT) will increase agricultural productivity through efficient and equitable access to water for small farms. It will support farmers at the community and household levels to adopt climate-smart farming practices and technologies that improve crop yields and conserve water resources in Punjab.
“In recent years Pakistan’s agriculture sector has suffered from losses in crop yields and livestock, damage to irrigation infrastructure, and food shortages due to climate change, particularly severe droughts in the Punjab province,” said Najy Benhassine, World Bank Country Director for Pakistan. “This project aligns with the Punjab Agriculture Policy 2018, which promotes massive expansion of water conservation efforts, enhancing sustainability and resilience in the wake of climate change, and private sector participation to help boost the productivity of the sector.”
PRIAT will support farmers implement innovative, climate-smart technologies to help the Punjab government achieve economies of scale to transform the agricultural sector. The project will engage the private sector in sourcing appropriate technologies and providing training tailored for water user associations and individual households to improve water conservation practices and agriculture productivity.
“The agriculture sector has a huge opportunity to both build climate resilience and improve economic conditions by generating access to domestic and international markets,” said Guo Li, Task Team Leader for the project. “PRIAT will help accelerate the government’s efforts to transform the agri-food system through market-oriented production activities that add value, increase competitiveness and generate higher incomes for farmers.”
The project will benefit about 190,000 small, family-owned farms and 1.4 million acres of irrigated land in rural communities in the province. It will also provide training to small- and medium-sized farm owners on water conservation and more sustainable, climate-resilient agricultural practices, including for women. About 74 percent of women in the province rely on agriculture as a source of livelihood.
The World Bank in Pakistan
Pakistan has been a member of the World Bank since 1950. Since then, the World Bank has provided $40 billion in assistance. The World Bank’s program in Pakistan is governed by the Country Partnership Strategy for FY2015-2020 with four priority areas of engagement: energy, private sector development, inclusion, and service delivery. The current portfolio has 60 projects and a total commitment of $14.2 billion.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 18, 2022 at 4:30pm
-
The Balochistan government has declared 10 districts of the province as calamity-hit areas in view of casualties and losses to businesses and infrastructure by recent torrential rains and floods.
https://www.dawn.com/news/1700021/10-districts-of-balochistan-decla...
An official notification issued by the office of the Relief Commissioner and Provincial Disaster Management Authority here on Saturday said that the 10 districts are Loralai, Kalat, Mastung, Kachhi, Sibi, Qila Saifullah, Barkhan, Duki, Panjgur and Lasbela.
Meanwhile, heavy rains continued in different districts of northern and central Balochistan, causing more damages and rendering the people homeless. A large number of villages in Sibi, Lasbela, Bolan, Qila Saifullah and Loralai districts were washed away or submerged due to floods and overflowing rivers.
Over 30 houses were damaged in villages located on the outskirts of Sibi on Friday night.
“Our rescue teams and Levies personnel were making all-out efforts to clear water from areas where flood and rainwater has accumulated,” Sibi Deputy Commissioner Mansoor Qazi told Dawn, adding that residents deprived of their homes were provided with shelter and relief goods.
“Though floodwater is reducing in the three main rivers, more flooding cannot be ruled out in view of more rains,” he said.
Lasbela district was also getting more rains in different areas which caused damages to homes in Winder, Kanraj and Bela areas where standing cotton and other crops were badly damaged. “A cotton field was completely destroyed in heavy rains and flash flood,” officials of the local administration said.
“Around a dozen people were stranded in a village in Lakhra area. They were rescued by the local administration with the help of Navy personnel,” Rohana Kakar, additional deputy commissioner, said, adding that the Hub dam was almost filled to capacity and its water level wa being continuously monitoring.
Meanwhile, the death toll of the rain-related incident in the province has reached 77. Over 1,000 houses were washed away and 500 heads of cattle were swept away in the floodwater.
The National Disaster Management Authority has sent 1,000 tents to Balochistan for the rain-stricken people.
Probe ordered into poor construction of breached dams
Balochistan Chief Minister Abdul Qudoos Bizenjo has ordered a probe into the alleged use of sub-standard construction material after at least 21 dams either gave way or were greatly damaged due to floods, especially in northern districts.
He has ordered inspection teams to survey these dams along with experts.
The irrigation department surveyed 503 big and small dams in 34 districts on the chief minister’s orders and found that most of them have been filled to capacity, including Hub, Mirani, Ankara Kur, Shadi Kur and Subakzai dams.
The report said the water storage level in the dams across the province had reached 1,208,872 acre-feet after rains compared to a capacity of 1,637,084 acre-feet.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 25, 2022 at 9:53am
-
Tarbela Dam is 96 feet away from touching its maximum level of 1550 feet as it has already attained level of 1494 feet on Friday against 1398 feet a day earlier, said sources from Pakistan Meteorological Department (PMD).
https://www.brecorder.com/news/40186234
They said the Dam had registered a gain of 96 feet in last 10 days. It may be noted that the Dam was at the level of 1405 feet on 1st of July when monsoon weather had hit the country. In other words, said the sources, the Dam was possessing one percent storage of its total capacity on 1st of May which has risen to 49.34 percent on Friday. The dam has been filled by half, they added.Mangla Dam, on the other hand, was carrying 4.57 percent storage of its capacity, which has reached 13.24 percent on Friday. So far as the water level is concerned, Mangla was at the level of 1098 feet, which has reached 1126.7 feet. The maximum conservation level of Mangla Dam is 1242 feet.
Director PMD Shahid Abbas confirmed the development, saying that Mangla has been filled by 13 percent and Tarbela by 49 percent. According to him, Tarbela could be filled to the maximum conservation level before 20th of July as there is no need of irrigation water for the agriculture of Sindh and Balochistan provinces due to heavy spells of rains.
At present, he said, 150,000 cusecs water is being released from the dam on daily basis, which is more than the agricultural need of the two provinces. The other purpose being met by this huge release of water is to generation of some 3000 plus megawatt electricity from the Dam, he added.
According to him, since the relevant authorities have no idea as how water is expected from the hilly sources, therefore, they are not in a hurry to fill it up. An early filling up of this dam may lead to heavy release of water in case of flood like situation after heavy rains in the hilly areas, he added. He said, another reason of releasing excessive water is the non-availability of storage capacity. He said the water being released at present is enough to fill another two dams of similar capacity in the country.
Meanwhile, the monsoon waves have proceeded to Sindh, particularly Karachi, to shower rain from Saturday night. Also, Director PMD said, the current monsoon waves would bring heavy downpour in Balochistan and lower parts of Southern Punjab for the next three days. The monsoon waves are likely to revert to the catchment areas of all the five rivers from 20th July until 22nd of July, including central Punjab and upper parts of the country.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on August 31, 2022 at 9:02pm
-
The groundwater system underneath Pakistan’s flowing rivers in the Indus plains has at least 400 million acre feet (MAF) of pristine water. This storage is so large that it is equivalent to more than three years of the mean annual flow of the Indus (or 1,000 days of storage, after excluding polluted areas). This should now be seriously considered in the mainstream planning of Pakistan’s water resources.
https://www.thethirdpole.net/en/climate/pakistans-riverine-aquifers-may-save-its-future/
More than a thousand years ago, Alberuni wrote, “India has once been a sea which by degrees has been filled up by the alluvium of the streams.” This view was later endorsed in the late 19th century by Austrian geologist Eduard Suess, who named the sea ‘Tethys Ocean’. Mike Searle, in his 2013 book Colliding Continents explains that the Himalayas resulted from collision of the Indian plate with the Eurasian plate 50 million years ago.
The Indus river and its Sutlej tributary both existed prior to this collision and drained into the Tethys Ocean. The collision gradually closed the sea and the remnants of the Tethys were filled by the material of eroding mountains deposited by the flowing rivers.
The Indus rivers have carried huge silt loads for millions of years, depositing them in the plains all the way to the delta. In their 1988 book, Irrigated Agriculture of Pakistan, Nazir Ahmad and Ghulam Rasul Chaudhry explained that high sediment loads in the Indus river system have created nearly 200,000 square kilometres of flatlands. These flatlands, to a considerable depth, are made up of unconsolidated and granular formations, capable of holding large volumes of water. “This reservoir of water is so vast, it ranks among the natural wonders of the world,” the authors write as they describe the groundwater resources of the Indus basin.
Aloys Arthur Michel, in his 1967 book, The Indus Rivers, describes these alluvial deposits as unconsolidated material, deeper than one mile, forming a large homogeneous groundwater reservoir with a capacity “at least ten times the annual runoff of the Indus rivers”.
This begs the question, that if we knew about this groundwater storage potential for decades, why has it never been discussed in the mainstream planning for sustainable exploitation to benefit the inhabitants of the Indus basin?
The reasons could have been many. The military dictatorship in place at the time of the signing of the Indus Water Treaty set a future discourse on the harnessing of surface waters only; a drift into debt economy and the lure of easy dollars in mega infrastructure projects for water; interest groups pushing large dams in the 1950s and 60s – an era when the whole world was going on a binge of building large dams; a lack of capacity at home to scrutinise proposals being advised by foreign ‘experts’ with vested interests; the obvious advantages of the visibility of big structures which can be loudly publicised in political arenas and so on. The result was that Pakistan chose the path of building mega-dams, river diversions and gravity-based flood irrigation systems. In doing so, we severely deteriorated our aquifers through waterlogging, salinity, unmanaged abstractions and indiscriminate pollution.
But that was the past. Is it possible to pursue a different path now?
Water quality
First, given the fact that this vast aquifer sits on top of a filled-up sea, its deeper formations are naturally saline. In the northern parts of the alluvial plains, the aquifer may hold sweet water up to a depth of a thousand feet or so, but as one moves south, the depth of sweet water gradually reduces.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on April 7, 2023 at 7:55am
-
Saudi Arabia signs $240m loan agreement to support Mohmand Dam
https://www.dawn.com/news/1746406/saudi-arabia-signs-240m-loan-agre...
The statement noted that the project is expected to enhance water and food security, and improve the standard of living for people in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, where almost 80 per cent of the population resides in rural areas, boosting the region’s socioeconomic development by creating employment opportunities and reducing poverty levels.
It added that by using renewable energy sources, the project will generate 800 MW of electricity production capacity, contributing to Pakistan’s energy security. In addition, the storage of 1.6 million cubic meters of water will support sustainable agricultural practices, enable irrigation of 6,773 hectares of new land, and increase the total cropping area from 1,517 hectares to 9,227 hectares in the province, facilitating agricultural activities.
Co-financed by the SFD, OPEC, Islamic Development Bank, and the Kuwait Fund for Arab Economic Development, the project aligns with SDG-2 (Food Security), SDG-6 (Clean Water), and SDG-7 (Clean Energy) and embodies SDG-17 (Partnerships for the Goals).
During the agreement signing ceremony, the CEO of SFD said this initiative is an extension of the fund’s continued support for development projects and programmes in Pakistan since its inception. He also highlighted the significance of joint cooperation between development funds, as evidenced by this project.
For his part, Dr Niaz expressed his sincere appreciation and gratitude to the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for its unwavering support towards the development sector in Pakistan through the SFD.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on April 10, 2023 at 12:49pm
-
Shrinking Indus Delta attracts UN’s attention
https://www.brecorder.com/news/40236204
The shrinking delta of Mighty River Indus of Pakistan has emerged on the United Nations radar after it accepted to create a global convention on all deltas of the world to ensure its protection against rising climate change impacts casting serious impact on its nature and habitat.
The development occurred after a strong international civil society nexus of experts, academicians, policy makers and stakeholders unanimously raised their voice for an international UN Convention for the Conservation River Delta (UN-CCRD) on the sequel of its UN Human Rights Declaration, UN Geneva Pact and many others to ensure that all the major deltas of the world were dying due to adverse impacts of climate change and environmental degradation namely sea intrusion, sea level rise, droughts, depleting water flows, shrinking creeks and others.
The African Centre for Climate Actions and Rural Development Initiative (ACCARD) in collaboration with the Nigeria’s Bayelsa State Government, the Institute for Environmental Diplomacy and Security at the University of Vermont, the Consortium for Capacity Building at the University of Colorado, Transboundary Water In-Cooperation Network (TWIN), Water Environment Forum-Pakistan, Center for the Advancement of Public Action (CAPA) Bennington College; Vietnam National University, Hanoi, Vietnam and Center for Environment and Sustainable Livelihood Projects (CESLP), among others hosted a side event at the UN Water conference titled “Integrative Highland to Ocean (H2O) Action for Disappearing Deltas: Towards a UN Convention on Conserving River Deltas.
Former Senator and federal minister for information and broadcasting and Chairman World Environment Forum, a civil society organization working to protect water resources and environment participated virtually to represent Pakistan in the sideline event whereas Freeman Elohor Oluowo of ACCARD and Prof. Dr. Asim Zia, Director, Institute for Environmental Diplomacy, Vermont physically participated in the session.
The global convention would help in achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to be achieved by 2030 namely SDG-6 demanding “Clean Water”, SDG-13 “Climate Action”, and SDG-14 “Conserving and sustainably using the oceans, seas and marine resources”.
The announcement has came after successful campaign of the above mentioned coalition of non-governmental and civil society organizations who started the drive for a global convention of UN to protect deltas.
The speakers, and experts discussed deltas starting from Nigerian Niger Delta, Indus Delta of Pakistan, Mekong River, Colorado, Nile and St. Lawrence transboundary river basins.
Each of these deltas possessed varying risks owing to spiking up sea level rise and salt water intrusion from the oceans, and rapidly melting glaciers, increasing dams and shifting rainfall patterns in the highlands.
The UN had accepted that all the world deltas were under threat and sea level rise and intrusion was causing damage to soil and water ecosystems. It is not only nature but rather the communities, the livelihood opportunities and human lives that were diminishing and demanded the world to respond for their protection.
There will be various activities in Delta countries towards achieving the UN Convention for the Conservation River Delta.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 11, 2023 at 4:22pm
-
SenatorSherryRehman
@sherryrehman
Good news for Pakistan! Our Recharge Pakistan project, which will be implemented over the next 7 years, has been approved today for funding of 77.8 M USD. These include GCF resources of 66 M USD and co-financing of around USD 11.8 M. This adaptation project aims to initiate ecosystem-based adaptation (EBA) interventions that will store flood water in wetlands, floodplains and depressions (green infrastructure) at several priority sites, build community resilience at these sites, and enable the Government of Pakistan, including all lead provinces and stakeholders to implement & replicate such nature-based solutions for climate resilience.
https://twitter.com/sherryrehman/status/1678625444176822275?s=20
--------
Funding of $77.8 million has been approved for Recharge Pakistan, a project that aims to build the country’s climate resilience and water security, Federal Minister for Climate Change Sherry Rehman announced on Tuesday.
https://www.brecorder.com/news/40252003/778mn-funding-secured-for-r...
“Good news for Pakistan! Our Recharge Pakistan project, which will be implemented over the next seven years, has been approved today for funding of $77.8mn,” said Rehman in a post on Twitter.
The minister highlighted that the funding includes $66 million from Green Climate Fund (GCF) resources and co-financing of around $11.8 million.
GCF was established in 2010 by 194 countries party to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change. It is designed as an operating entity of the Convention’s financial mechanism and is headquartered in South Korea.
“This adaptation project aims to initiate ecosystem-based adaptation interventions that will store flood water in wetlands, floodplains and depressions (green infrastructure) at several priority sites,” said Rehman.
Recharge Pakistan is a joint collaboration by GCF, World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the Government of Pakistan. As per information available on the WWF website, the project aims to build Pakistan’s climate resilience and water security through cost-effective ecosystem-based adaptation.
“The project will increase water storage and recharge through wetlands, floodplains, and hill-torrents management; promote climate-adapted community-based natural resource management and livelihoods; and forge a paradigm shift to scale up this approach,” read the website.
Last week, Rehman during a high-level meeting with a delegation led by Sultan Ahmed Al Jaber, President-designate of COP28 and UAE’s Minister of Industry and Advanced Technology, said a “critical gap” in resources for adaptation and mitigation has been identified by multilateral agencies -amounting to $348 billion or 10.7% of cumulative GDP by 2030.
Despite this, Pakistan is committed to a green energy transition, whereby it will transfer 60% of its energy needs to renewables by 2030 and reduce its projected emissions by 50% until 2030, Rehman said.
Pakistan is actively involved in transitioning the country towards the renewable energy sector and is seeking partnerships in the alternative and renewable energy sector, the minister added.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 28, 2023 at 9:41pm
-
Recharge Pakistan Project receives $77.8 million funding boost from the Green Climate Fund, United States Agency for International Development, The Coca-Cola Foundation and World Wildlife Fund | Press Releases | WWF
https://www.worldwildlife.org/press-releases/recharge-pakistan-proj...
The new 7-year project brings together a broad set of funders to help reduce the vulnerability of people and ecosystems in Pakistan to the impacts of climate change following the devastating floods of the past year—which submerged one-third of the country and displaced millions. In addition to the GCF funding, the project is supported through a further $12 million investment and technical support from, collectively, The Coca-Cola Foundation, The U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), and WWF-Pakistan.
The project represents a deep commitment to addressing climate impacts in vulnerable communities and will transform the country’s approach to flood and water resource management in local watershed sites in the Indus Basin river system. Further, by taking a nature-based approach to the problem, it will create benefits to communities beyond climate resilience.
“Recent years have brought an unprecedented series of climate disasters that touched every corner of the globe. The 2022 floods in Pakistan were among the most searing and severe. Our hearts go out to all who lost friends and loved ones,” said Carter Roberts, President and CEO of WWF-US. “The funding announced by the GCF alongside the commitments from The Coca-Cola Foundation and USAID marks a decisive step towards addressing the challenges faced by communities experiencing climate impacts first and worst. And while no intervention can fully protect against future climate disasters, the nature-based solutions funded through this investment will help local communities in Pakistan restore what was lost and build resilience to help withstand our shared climate future. WWF thanks the Government of Pakistan and looks forward to working with them and partners to implement this important initiative.”
Recharge Pakistan is a collaboration among: Pakistan’s Ministry of Climate Change (MoCC); the Federal Flood Commission (FFC) under the Ministry of Water Resources; local communities in DI Khan, the Ramak Watershed, and Manchar Lake; GCF; USAID; The Coca-Cola Foundation; and World Wildlife Fund (WWF). The program encompasses three vital components: demonstrating the effectiveness of ecosystem-based adaptation and green infrastructure, promoting its adoption via an improved enabling environment, and enhancing community resilience in Pakistan's Indus Basin. This will be achieved through:
Restoration and reforestation of 14,215 hectares of forests and wetlands
Rehabilitation 34 km of water flow paths and channels
Development of 127 recharge basins and retention areas
Strengthening the climate resilience of 7 local businesses in the agriculture and forests sectors
Together, project interventions will directly benefit more than 680,000 people and indirectly benefit more than 7 million people.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on May 25, 2025 at 8:34am
-
Rivers in Pakistan aren't drying yet. Here's why
Official data and satellite imagery processed by India Today's Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) team suggest rivers allocated to Pakistan under the IWT – the Indus, Chenab, and Jhelum (collectively called Western rivers) – continued to flow their normal course and speed as of April 30.
Subham Tiwari
New Delhi,UPDATED: May 1, 2025 22:37 IST
Posted By: Vivek Kumar
In Short
Rivers Indus, Chenab, Jhelum flow normally despite Treaty suspension
Hydrological data-sharing suspension affects Pakistan's irrigation
No significant change in river flow at Indian and Pakistani dams
https://www.indiatoday.in/india/story/rivers-in-pakistan-arent-dryi...
Geoanalytical expert Raj Bhagat puts the situation more succinctly: “At present, it’s impossible to stop waters of the Western rivers.” It will be difficult for us to do so even in the future, he tells India Today.
He says India practically has no instrument to control the flow of the Indus river at the moment. India has only a small dam on the river – that too hundreds of kilometers upstream at Nimoo Bazgo in Ladakh.
To regular waters of these rivers, the only feasible approach is to build big dams and canals to divert water to other areas within Indian territory for irrigation. As earlier analysis by India Today shows we need to build at least 22 dams equivalent to Bhakra Nangal to store the amount of water that flows in the three Western rivers in a year.
India didn’t have any “storage” dams that could store waters for longer periods because the IWT didn’t allow it to be built on the Western rivers – the Indus, Chenab, and Jhelum. Under-construction Pakal Dul is the sole hydropower project that is envisaged as a “storage” facility.
However, Bhagat says, “The topography of the region doesn’t allow big dams to be built The only river whose water can be diverted to an extent is Chenab that would need massive investments.”
Environmentalist Himanshu Thakkar says the risks of building dams on Chenab river are too high. “We already have the largest number of existing, under construction and planned projects in this very fragile, disaster-prone area. This is also a location where experts have warned about the major risks of landslides, floods, seismic activity and glacial lake outburst floods,” says Thakkar, the coordinator of non-profit South Asia Network on Dams, Rivers, and People (SANDRP).
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Pak-Saudi Joint Defense: Is Pakistan A Major Power or Bit Player in the Middle East?
The recently signed “Strategic Mutual Defense Agreement” between Saudi Arabia and Pakistan states that “any aggression against either country will be considered an aggression against both”. It is being seen by some geopolitical analysts as the beginning of an "Islamic NATO". Others, such as Indian-American analyst Shadanand Dhume, have dismissed Pakistan as no more than a "bit player"…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on September 27, 2025 at 5:30pm — 5 Comments
Silicon Valley Pakistani-Americans Among Top Donors to Mamdani Campaign
Omer Hasan and Mohammad Javed are the top donors to Zohran Mamdani’s mayoral campaign in New York City, according to media reports. Both are former executives of Silicon Valley technology firm AppLovin. Born and raised in Silicon Valley, Omer is the son of a Pakistani-American couple who are long-time residents of Silicon Valley, California. …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on September 19, 2025 at 9:00am
© 2025 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()


You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network