PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
Pakistan's Fintech Revolution to Promote Financial Inclusion
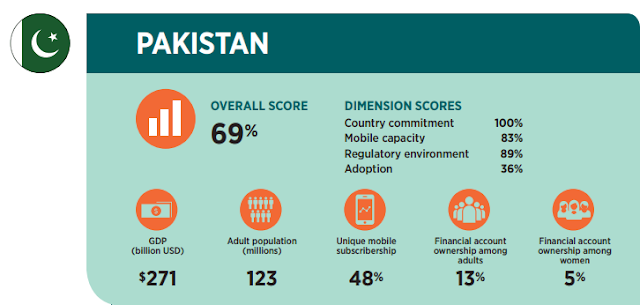 |
| Source: Brookings' Digital and Financial Inclusion Report 2017 |
Importance of Financial Inclusion:
Access to regulated financial services for all is essential in today's economy. It allows people to save, borrow and invest. Those who lack access to regulated banking services are often forced to resort to work with unscrupulous lenders who trap them in debt at unaffordable rates. Such loans in extreme cases leads to debt bondage in developing countries. Financial inclusion is good for the individuals as well as the national economies. It spurs economic growth and helps document more of the economy.
Easypaisa:
Fintech (financial technology) is bringing financial services to the unbanked population through non-bank institutions licensed by the State Bank of Pakistan, the top bank regulator in the country. One example of a non-bank is Telenor Pakistan, a leading mobile phone service operator, offering financial services via a large network of agents, currently over 70,000, far exceeding the total number of branches of all the banks in the country.
Easypaisa, a service operated by Telenor Pakistan, offers basic financial services like open a bank account, deposit or withdraw money, transfer funds, make mobile payments and pay utility bills.
Karandaaz:
Another important player promoting financial inclusion is Karandaaz Pakistan , a non-profit organization, set up by UK’s Department for International Development and Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. It is providing grants to a number of local initiatives to develop and promote financial technology solutions in Pakistan.
Karandaaz Pakistan is promoting Fintech startups in 5 areas of focus:
1) Access to Financial services
Credit Scoring Models, Formalize savings through need based products, Digital lending services, and Insurance
2) Payments
Retail payments solutions through QR code, Supply / Value Chain Digitization, Ideas around digitization of online payments and merchant payments
3) E-Commerce
Smoothening of on-boarding process, Enabling Escrow Accounts
for a retail merchant, Alternate payment modes other than COD
4) Interoperability
Innovative ideas to address the lack of interoperability among m-wallets
5) Early stage ideas related to:
M-Wallet Use cases, Education of Financial Services through technology, Customer Engagement / Experience, Micro Credit, Digital Savings
Finja's SimSim Mobile Payment:
Finja is a Pakistani fintech startup that recently introduced SimSim app for mobile payments. It's the first such application that has received approval of the State Bank of Pakistan. Finja has raised $1.5 million in venture funds so far. SimSim uses NADRA, a biometric citizen identity card that the Pakistan government has issued to almost its entire adult population, comprising around 60 percent of the total population of 207 million.
Private Credit Bureaus:
Credit data and scoring are essential to facilitate risk assessment and lending by financial institutions.
Under the Credit Bureaus Act, 2015, privately-run credit bureaus can collect and disseminate the credit data from both financial and non-financial institutions including retailers, insurance companies, utility providers and landlords, as notified by the federal government, according to Muhammad Akmal, Director of Banking Conduct and Consumer Protection Department at the State Bank of Pakistan. The bureaus can do credit scoring, consolidate credit data for analysis and research purposes.
Progress To Date:
According to the latest State Bank statistics on branchless banking (BB) sector, m-wallets grew by 87% , reaching 27.3 million by the end of June 2017. It has a lot of room for growth in a county where about 100 million adults lack access to regulated financial services.
Pakistan is ranked 16th among 26 nations ranked by Brookings Institution with an overall score of 69% in "The State of Financial and Digital Inclusion Project Report" for 2017.
Summary:
Pakistan is ranked 16th among 26 nations ranked by Brookings Institution with an overall score of 69% in "The State of Financial and Digital Inclusion Project Report" for 2017. Access to regulated financial services for all is essential in today's economy. It allows people to save, borrow and invest. Those who lack access to regulated banking services are often forced to resort to work with unscrupulous lenders who trap them in debt at unaffordable rates. Such debt in extreme cases leads to bondage in developing countries. Financial inclusion is good for the individuals as well as the national economies. It spurs economic growth and helps document more of the economy. The rapid growth of mobile phones and Internet access in Pakistan offers a unique opportunity to increase financial inclusion in the country. A number of players are working on financial technology to make its application a reality in Pakistan. Among these players are non-bank banks like Telenor and non-profits like Karandaaz.
Related Links:
Haq's Musings
Financial Services Sector in Pakistan
Pakistan Ranked Among Top 5 For Financial Inclusion Efforts
Pakistani Banks Post Strong Growth
Branchless Banking in Pakistan
Pakistan Ranks High in Microfinance
World's Largest Democracy Tops Slavery Charts
NADRA's Biometric Database
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 16, 2022 at 1:45pm
-
Meet the Investor Who Spots Opportunities for Jeffrey Katzenberg
Anthony Saleh oversees a growing venture-capital fund at the former Hollywood chief’s WndrCo, after its Quibi video app collapsed. He also works with the rapper Nas.
https://www.wsj.com/articles/meet-the-investor-who-spots-opportunit...
While working with Nas several years ago, Mr. Saleh cold-emailed Ben Horowitz, the co-founder of the venture-capital firm Andreessen Horowitz to discuss ideas, Mr. Horowitz said. The two men got to know one another, and in 2013, Mr. Saleh called Mr. Horowitz to say he and Nas were interested in bitcoin after seeing how many “unbanked” people in the world had no checking account but did have a cellphone—a dynamic he said could decentralize finance. When Mr. Horowitz later heard about Coinbase, the cryptocurrency exchange platform, he brought the duo into the investment.Last year, Coinbase Global Inc. was one of six investments in Mr. Saleh’s personal portfolio that ended in a public offering.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 19, 2022 at 7:31am
-
VEON Subsidiary Pushes Digital Inclusion in Pakistan
Tommy Clift | Reporter
https://www.sdxcentral.com/articles/news/veon-subsidiary-pushes-dig...
Mobilink Microfinance Bank (MMBL) launched a trio of initiatives to accelerate financial inclusion for farmers and female entrepreneurs in Pakistan. The move echoes another by its parent company VEON to promote digital access through its subsidiary Kyvistar.
The MMBL plans include an agriculture advisory service for Pakistani farmers, e-commerce services for female entrepreneurs, and 4G handsets. VEON CEO Kaan Terzioglu believes the initiatives will play a pivotal role in digitalizing the microfinance industry in Pakistan.
VEON noted in a statement that agriculture represents nearly 23% of Pakistan’s gross domestic product and employs approximately 37% of its workforce. Recent floods in the country destroyed 3.6 million acres of crops and killed 700,000 livestock, it added.
MMBL is partnering with Pakistan-based agricultural technology company BaKhabar Kissan to provide information and guidance on livestock management, weather monitoring, crop planting – including which are profitable, and boosting agricultural yields.
“We are aiming to build a digital infrastructure that will help further economic prosperity and financial empowerment among women business owners and small and medium-sized farmers in the country, two segments that have the potential to transform Pakistan’s economic future,” MMBL President and CEO Ghazanfar Azzam stated.
Their push to incentivize and advance female entrepreneurs comes with their collaboration with Pakistan e-commerce platforms Daraz and its flagship Women Inspirational Network (WIN) program. This is intend to promote a female-focused, “digital financial ecosystem” using their subscriber base – currently accounting for 53% of the 195 million cellular subscribers in Pakistan, according to VEON.
Women make up nearly half of the country’s population, but VEON notes “their financial inclusion figure stands at 7%.”
The new program will use the Digit 4G handsets to “drive participation in the digital economy among marginalized groups within the population.” The handsets will be discounted and targeted at female entrepreneurs, coming “pre-loaded with the digital banking application, MMBL DOST, which will enable customers to obtain quick financial assistance, pay bills, make money transfers, and use a vast array of digital banking services,” VEON explained.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 4, 2022 at 11:39am
-
Pakistan’s Digital Lending Revolution
Not only is increased digital lending the need of the hour, it is also a very attractive business proposition.
https://aurora.dawn.com/news/1144545/pakistans-digital-lending-revo...
The cruel spiral of poverty plagues generations once it takes grip. It takes money to make money. This is especially true of emerging and undocumented economies like ours. It takes money to educate one’s children, without which income prospects greatly diminish for the next generation. It also takes money for a small business owner to invest in stock or supplies. Without this, no income is generated from the business which feeds a disproportionate number of people downstream. Often, health issues can devastate families and their fortunes because a head of household was not able to afford medical treatment.
Poverty is not new. However, we have, for the first time in history, witnessed such a massive and rapid deliberate reduction in the world’s poverty. China systematically lifted 800 million people out of its poverty spiral over a relatively short 40-year period. There are many lessons in this for Pakistan, the biggest of which is that it is indeed possible to turn the corner for our people.
China relied heavily on digital technologies that financially included a significant portion of its population, and also connected them for commerce with each other. Mobile smartphone penetration, online connectivity, digital payments, and online commerce became key catalysts of income mobility. The ensuing digital footprints paved the way to provide credit to people who were previously undocumented and thus un-lendable. There is no debate now that access to credit is one of the most effective ways to reduce poverty. And today, digital access to credit can reduce poverty at scales and speeds previously unimaginable.
Pakistan has recently undergone its digital revolution. Today 80% of adults in Pakistan have access to internet-connected smartphones. About a third have made digital payments. Seventy percent of new bank accounts over the last five years were contributed by mobile wallets. Our chowkidars, mazdoors and corner store owners are all on WhatsApp and avidly consuming TikToks. E-commerce, although still relatively small with a market size of about six billion dollars annually, has shown one of the fastest growths globally. Key catalysts of income mobility are now present for us to take advantage of.
So why do less than two percent of our population receive loans from formal financial institutions? Because formal financial institutions employ traditional ways of establishing creditworthiness, by collecting documents. The size of our undocumented economy is at least as large as our formal economy and comprises the vast majority of our population. With no signals of creditworthiness, money is not lent. With poor signals of creditworthiness, money is lent but de-risked by pledging tangible assets, which are uncommon among the poor.
The scarcity of credit given by banks to consumers and small businesses is further compounded by the fact that it is hard work to give small loans with cumbersome and expensive physical processes. There is little incentive to serve these key segments, especially compared to the easy, safe and large lending appetite of our government. Nearly three-quarters of all the money deposited across banks is given to the government in the form of loans or investments by banks. This voracious appetite and easy profit from the government has crowded out private sector needs.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 4, 2022 at 11:40am
-
Pakistan’s Digital Lending Revolution
Not only is increased digital lending the need of the hour, it is also a very attractive business proposition.
https://aurora.dawn.com/news/1144545/pakistans-digital-lending-revo...
The good news is that the recent influx of venture capital into start-ups has led to the emergence of many new innovative financial technology (fintech) companies to solve these problems. Signals such as salary information, sales receipts and supply purchase data are being digitised and leveraged to establish creditworthiness with great success. Pakistani innovators benefit from the learnings from other emerging markets that previously cracked these problems with great success, including China, Indonesia, Africa and others. It should be no surprise that digital lending has started to make great progress in Pakistan.
For digital lending to truly take off in Pakistan, three key pieces of the ecosystem need to come together in a symbiotic manner: banks or money suppliers, fintechs and digital data-generating platforms. Banks are flush with cheap deposits from zero mark-up current accounts and therefore have the capital to lend. Fintechs, whose licences are governed under progressive lighter weight regulations, efficiently package small business and consume uncollateralised loans by acquiring and scoring them digitally. And finally, the platforms that collect the digital footprints of small businesses and consumers through transactional workflows, provide reliable signals for lending. They also embed financial services from fintechs into their platforms. The good news is that there are already several examples of all three stakeholders collaborating to lend in Pakistan with stellar results.
Pakistan’s five million micro and small businesses are stuck in a stagnant cash flow-starved hand-to-mouth status quo. Yet, they constitute 40% of our GDP and employ almost 80% of our non-agricultural workforce. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SME) lending data from fintechs shows that access to capital increases SME income by an average of 30%. Digital lending at scale to small businesses will have a tremendous impact on our economy, employment and standard of living. Similarly, less than 0.35% of people have received housing loans and consequently, home ownership remains dismally low. It is clearly in the country’s interest for responsible digital lending to take off.
Not only is increased digital lending the need of the hour, but it is also a very attractive business proposition. We have seen the entry of several well-funded foreign lending apps that have sprayed thousands of loans using sparse scoring data. As a result, their first cycle loan losses are exceptionally high, requiring expensive pricing to cover defaults. Many of these apps are unlicenced and engage in predatory practices. Customers are misled through claims of reasonably priced loans while hidden fees result in expensive triple-digit markup rates. Furthermore, the address books of customers are often harvested and their contacts are harassed if loans are not repaid on time. Most people who take loans from these apps are first-time borrowers with little financial literacy and can easily become over-indebted. Access to affordable credit with dignity is an important measure of a society’s evolution.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 4, 2022 at 11:40am
-
Pakistan’s Digital Lending Revolution
Not only is increased digital lending the need of the hour, it is also a very attractive business proposition.
https://aurora.dawn.com/news/1144545/pakistans-digital-lending-revo...
Clearly, increased regulatory oversight is urgently needed to keep pace with the innovations in digital lending that we are seeing in the field. Informal players like these loan apps and your local electronics store do not share loan repayment behaviour with credit bureaus. This results in financial institutions approving loans that are unlikely to be repaid, ruining future credit access to a vulnerable segment that can benefit most from them. This must be carefully monitored and regulators must encourage lenders to utilise high-quality data to minimise defaults and keep loans affordable for greater impact. For example, low default rates of working capital loans that leverage actual business transactional data through embedded digital workflows allow small businesses to negotiate better rates. These digital loans scored using rich data give power back to small business owners who can in turn profitably grow their businesses and hire more workers.
In addition, as data becomes more sought, stored, and potentially shared, our consumer data protection laws will be tested and likely need to be updated. We will inevitably hear about large-scale data breaches and their aftereffects. While data leaks must be prevented and privacy protected, platforms across the ecosystem must also integrate and share data responsibly. This must happen with consumer consent. Combined data sets will produce richer signals to unlock more opportunities. Seldom in human history have we had such powerful tools to uplift our population in such a short period. One hundred and ten million digitally connected and transacting Pakistanis will produce rich footprints to enable lending for themselves and their businesses. When regulated and executed responsibly, digital lending has the potential to uplift millions of Pakistanis out of poverty and significantly raise Pakistan’s GDP. Amid the doom and gloom, exciting times lie ahead.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 29, 2022 at 8:44am
-
Pakistan cracks down on sketchy digital lending
https://techcrunch.com/2022/12/28/pakistan-cracks-down-on-sketchy-d...
Pakistan’s markets regulator issued new guidelines for digital lending in the country, cracking down on several sketchy practices that it said have become prevalent in the South Asian market.
The Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan said Wednesday evening that non-banking finance companies that disburse loans through digital channels, including mobile apps, will be required to disclose key fact statements such as the credit amount they are granting to consumers, annual percentage rates, duration of the loan and “all fee and charges.”
The non-banking finance firms will be required to share these key facts with consumers through audio or video and emails and text messages in both English and Urdu languages. “Any fee not included in key fact statement will not be charged to the borrower,” the regulator said (PDF) in a press release.
These firms will also not be able to access borrower’s phone book or contacts lists or pictures on the device “even if the borrower has given consent in this regard,” the regulator said. (You can read the full guidelines here {PDF}.)
“The lender shall also not be allowed to contact the persons in the borrower’s contact list, other than those who have been specifically authorized by the borrower as guarantors and who have also provided their consent to the digital lender at the time of loan approval,” it added.
The move follows the regulator noticing a rise in mis-selling, breach of data privacy and “coercive” recovery practices of licensed digital lending companies” and to safeguard public interest, it said.
Neighboring nation India also introduced strict rules surrounding digital lending in a move that has toppled the local fintech industry.
https://www.secp.gov.pk/document/circular-no-15-of-2022-requirement...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on March 2, 2023 at 4:54pm
-
Financial inclusion in Pakistan increases to 30% - Profit by Pakistan Today
https://profit.pakistantoday.com.pk/2023/02/08/financial-inclusion-...
https://portal.karandaaz.com.pk/dataset/financial-digital-inclusion...
KARACHI: Financial inclusion in Pakistan has increased by 9 basis points from 2020 to 2022 and women’s access, specifically has hit a double-digit percentage for the first time, as recorded by a survey conducted by Karandaaz Pakistan.
As defined by the World Bank, “financial inclusion means that individuals and businesses have access to useful and affordable financial products and services that meet their needs – transactions, payments, savings, credit and insurance – delivered in a responsible and sustainable way.” This means conducting transactions through banks, mobile money and fintech.
The Karandaaz Financial Inclusion Survey (K-FIS) measures the percentage of adults above the age of 15 who report having at least one account in their name with an institution that offers a full range of financial services that is also documented by the government of Pakistan.
Following a significant jump in financial inclusion between 2017 and 2020, K-FIS recorded a substantial rise in the level of financial inclusion from 21% in 2020 to 30% of adults in 2022. Registered mobile money users more than doubled with an increase from 9% to 19%, while registered bank users also increased by 4 basis points over the same period.
By region, Islamabad Capital Territory (ICT) recorded the highest level of financial inclusion at 45%, followed by Gilgit Baltistan at 35% and Azad Jammu & Kashmir at 34%.
Looking at the division by gender, male registration accounted for the bulk of financial account registrations in 2022 with 47% having at least one registered financial account. Comparatively, only 13% of women are recorded to have at least one registered financial account. Although women’s percentage accounts for less than half of their male counterparts, the financial account registration for women has reached double digits for the first time.
Overall, the largest increase was seen in mobile money wallet users, as active usage increased from 8% in 2020 to 16% in 2022. Active usage also saw an increase in bank account holders, indicating an increase from 12% in 2020 to 14% in 2022.
Addressing the webinar held by Karandaaz Pakistan on February 7, 2023, Noor Ahmed, Director of the Agri Finance and Financial Inclusion Department of the State Bank of Pakistan (SBP) said, “Over the years, there has been significant progress on financial inclusion. Key initiatives such as RAAST have been transformative in furthering the inclusion of the marginalised.”
Karandaaz Pakistan is a not-for-profit special-purpose vehicle set up under Section 42 in August 2014. The company is the implementation partner of the Enterprise and Asset Growth Programme (EAGR) and Sustainable Energy and Economic Development (SEED) programme of the UK’s Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO).
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on March 8, 2023 at 10:14am
-
Pakistan approves blockchain-based national eKYC banking platform
https://www.kitco.com/news/2023-03-06/Iran-advances-its-digital-ria...
In other crypto-related developments out of the MENA region, the Pakistan Banks’ Association (PBA) has signed off on the development of a blockchain-based Know Your Customer (KYC) platform with the goal of strengthening the country’s Anti-Money Laundering (AML) capabilities in a bid to counter the financing of terrorism.
According to a report from the Daily Times, the PBA, which is comprised of 31 traditional banks operating in Pakistan, signed off on the project to develop Pakistan’s first blockchain-based national eKYC banking platform on Thursday at the behest of the State Bank of Pakistan (SBP), the country’s central bank.
Included in the list of member banks are multiple international behemoths such as the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, Citibank and Deutsche Bank.
The new blockchain-based eKYC platform – dubbed “Consonance” – will also reportedly improve operational efficiencies, which are primarily aimed at improving customer experience during onboarding.
Consonance will be developed by the Avanza Group, and the platform will be used by member banks to standardize and exchange customer data via a decentralized and self-regulated network.
Comment
- ‹ Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Next ›
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
US Deports Indian Illegal Immigrants in Handcuffs and Chains Aboard Military Aircraft
A US Air Force transport plane landed in India today with 104 illegal Indian immigrants in handcuffs and shackles, according to media reports. Speaking with reporters, a deportee said: “For 40 hours, we were handcuffed, our feet tied with chains and were not allowed to move an inch from our seats. After repeated requests, we were allowed to drag ourselves to the washroom. The crew would open the door of the lavatory and shove us in.”…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on February 6, 2025 at 9:30am — 2 Comments
Researchers of Chinese Origin Dominate the World's Top AI Talent
Recent launch of DeepSeek AI model has brought to light the large and growing AI talent in China. The researchers working for the Chinese startup have shown that human creativity and problem-solving skills can overcome limitations such as access to high-performance hardware. It confirms that the most important resource needed for breakthroughs in AI is the human resource.
The people of…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on February 2, 2025 at 5:30pm
© 2025 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network