PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
India's Forex Reserves Fall As Foreign Investors Head For The Exits
India's foreign exchange reserves are falling rapidly as foreign investors flee and the country's trade and current account deficits widen. More than $267 billion worth of India's external debt of the total $621 billion is due for repayment in the next nine months. This repayment is equivalent to about 44% of India's foreign exchange reserves. This combination of investors' exodus, widening twin deficits and short-term debt repayments has caused the Indian rupee to hit new lows. Unlike China and other nations that have accumulated large reserves by running trade surpluses, India runs perennial trade and current account deficits. The top contributor to India's forex reserves is debt which accounts for 48%. Portfolio equity investments known as “hot” money or speculative money flows account for 23% of India's forex reserves, according to an analysis published by The Hindu BusinessLine.
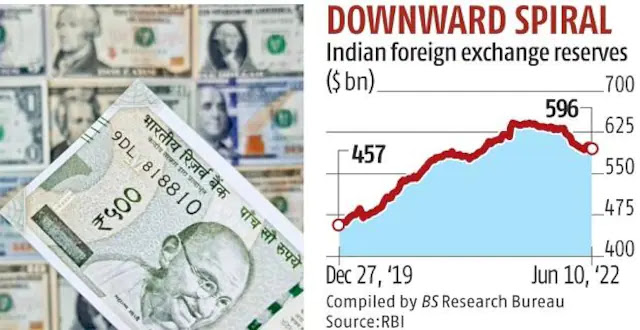 |
| India's Declining Forex Reserves. Source: Business Standard |
Investor Exodus:
Foreign portfolio investors have pulled out a whopping $33.5 billion from equity and $2.1 billion from debt segments of Indian financial markets, for a total net outflow of $35.6 billion from October 2021 to June 2022, according to data compiled by the National Securities Depository Limited. In the first half of this calendar year, the total net outflows were $29.7 billion.
It's not just the FPIs leaving India; a number of multinational companies are also pulling foreign direct investment (FDI) from India. Several big names including German retailer Metro AG, Swiss building-materials firm Holcim, US automaker Ford, UK banking major Royal Bank of Scotland, US motorcycle manufacturer Harley-Davidson and US banking behemoth Citibank have chosen to pull the plug on their operations in India or downsize their presence in recent years.
Widening Deficits:
India's finance ministry has warned of a growing twin deficit problem, with higher commodity prices and rising subsidy burden leading to an increase in both the fiscal and current account deficits. India's June trade deficit widened to a record high of $25.63 billion, mainly due to a rise in crude oil and coal imports, from $9.61 billion a year earlier. India's April-May fiscal deficit was $25.8 billion.
Summary:
India's current level of forex reserves is enough for less than 10 months of imports projected for 2022-23. But the country has had a structural current account deficit which has been funded by large capital inflows. The accumulation of forex reserves has been due to surplus in the capital account. Since late February, the foreign exchange reserves have declined by $36 billion. India still has large forex reserves but its economy is in the same boat as other emerging markets that run large and worsening trade and current account deficits. With declining forex reserves, India is likely to face headwinds as the US Federal Reserves raises interest rates to fight inflation.
Related Links:
Haq's Musings
South Asia Investor Review
India in Crisis: Unemployment and Hunger Persist After COVID waves
Food in Pakistan 2nd Cheapest in the World
Western Money Keeps Indian Economy Afloat
Pakistan to Become World's 6th Largest Cement Producer by 2030
How Has India Accumulated Large Forex Reserves Despite Perennial Tr...
Pakistan's Computer Services Exports Jump 26% Amid COVID19 Lockdown
Coronavirus, Lives and Livelihoods in Pakistan
Vast Majority of Pakistanis Support Imran Khan's Handling of Covid1...
Pakistani-American Woman Featured in Netflix Documentary "Pandemic"
Incomes of Poorest Pakistanis Growing Faster Than Their Richest Cou...
Can Pakistan Effectively Respond to Coronavirus Outbreak?
How Grim is Pakistan's Social Sector Progress?
Pakistan Fares Marginally Better Than India On Disease Burdens
Trump Picks Muslim-American to Lead Vaccine Effort
Democracy vs Dictatorship in Pakistan
Pakistan Child Health Indicators
Pakistan's Balance of Payments Crisis
Panama Leaks in Pakistan
Conspiracy Theories About Pakistan Elections"
PTI Triumphs Over Corrupt Dynastic Political Parties
Strikingly Similar Narratives of Donald Trump and Nawaz Sharif
Nawaz Sharif's Report Card
Riaz Haq's Youtube Channel
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 16, 2022 at 10:37pm
-
From The Print News Youtube channel:
India’s Forex reserve lose $80 bn in 8 months as RBI defends rupee, quarterly CAD at alarming level
------------
Indias foreign exchange reserves fall to lowest in 23 monthshttps://www.business-standard.com/article/finance/india-s-forex-res...
The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI’s) headline foreign exchange reserves declined by $7.9 billion to $553.11 billion in the week ended September 2, the latest central bank data showed.
The reserves are at their lowest since October 9, 2020, the RBI data showed. Analysts cited the RBI’s defence of the rupee through dollar sales amid a globally strengthening greenback as one of the reasons for the fall in reserves.
Incidentally, during the week that ended September 2, the rupee marked a fresh intraday low of 80.13 per US dollar.
-------------
Why are India's foreign reserves depleting, and what could it mean for the country? - BusinessToday
https://www.businesstoday.in/latest/economy/story/why-are-indias-fo...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 18, 2022 at 4:45pm
-
Strong #US #Dollar Spells Trouble for World #Economy. Its rise being felt in #fuel and #food shortages in #SriLanka, in #Europe’s record #inflation, in #Japan’s exploding #trade deficit, #Pakistan's #IMF bailout and #Bangladesh seeking IMF help https://www.wsj.com/articles/dollars-rise-spells-trouble-for-global... via @WSJ
For the U.S., a stronger dollar means cheaper imports, a tailwind for efforts to contain inflation, and record relative purchasing power for Americans. But the rest of the world is straining under the dollar’s rise.
“I think it’s early days yet,” said Raghuram Rajan, a finance professor at the University of Chicago’s Booth School of Business. When he served as governor of the Reserve Bank of India last decade, he complained loudly about how Fed policy and a strong dollar hit the rest of the world. “We’re going to be in a high-rates regime for some time. The fragilities will build up.”
-------------
The U.S. dollar is experiencing a once-in-a-generation rally, a surge that threatens to exacerbate a slowdown in growth and amplify inflation headaches for global central banks.
The dollar’s role as the primary currency used in global trade and finance means its fluctuations have widespread impacts. The currency’s strength is being felt in the fuel and food shortages in Sri Lanka, in Europe’s record inflation and in Japan’s exploding trade deficit.
This week, investors are closely watching the outcome of the Federal Reserve’s policy meeting for clues about the dollar’s trajectory. The U.S. central bank is expected Wednesday to raise interest rates by at least 0.75 percentage point as it fights inflation—likely fueling further gains in the greenback.
In a worrying sign, attempts from policy makers in China, Japan and Europe to defend their currencies are largely failing in the face of the dollar’s unrelenting rise.
Last week, the dollar steamrolled through a key level against the Chinese yuan, with one dollar buying more than 7 yuan for the first time since 2020. Japanese officials, who had previously stood aside as the yen lost one-fifth of its value this year, began to fret publicly that markets were going too far.
The ICE U.S. Dollar Index, which measures the currency against a basket of its biggest trading partners, has risen more than 14% in 2022, on track for its best year since the index’s launch in 1985. The euro, Japanese yen and British pound have fallen to multidecade lows against the greenback. Emerging-market currencies have been battered: The Egyptian pound has fallen 18%, the Hungarian forint is down 20% and the South African rand has lost 9.4%.
The dollar’s rise this year is being fueled by the Fed’s aggressive interest-rate increases, which have encouraged global investors to pull money out of other markets to invest in higher-yielding U.S. assets. Recent economic data suggest that U.S. inflation remains stubbornly high, strengthening the case for more Fed rate increases and an even stronger dollar.
Dismal economic prospects for the rest of the world are also boosting the greenback. Europe is on the front lines of an economic war with Russia. China is facing its biggest slowdown in years as a multidecade property boom unravels.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 18, 2022 at 4:46pm
-
Strong #US #Dollar Spells Trouble for World #Economy. Its rise being felt in #fuel and #food shortages in #SriLanka, in #Europe’s record #inflation, in #Japan’s exploding #trade deficit, #Pakistan's #IMF bailout and #Bangladesh seeking IMF help https://www.wsj.com/articles/dollars-rise-spells-trouble-for-global... via @WSJ
For the U.S., a stronger dollar means cheaper imports, a tailwind for efforts to contain inflation, and record relative purchasing power for Americans. But the rest of the world is straining under the dollar’s rise.
“I think it’s early days yet,” said Raghuram Rajan, a finance professor at the University of Chicago’s Booth School of Business. When he served as governor of the Reserve Bank of India last decade, he complained loudly about how Fed policy and a strong dollar hit the rest of the world. “We’re going to be in a high-rates regime for some time. The fragilities will build up.”
-------------
-------
On Thursday, the World Bank warned that the global economy was heading toward recession and “a string of financial crises in emerging market and developing economies that would do them lasting harm.”
The stark message adds to concerns that financial pressures are widening for emerging markets outside of well-known weak links such as Sri Lanka and Pakistan that have already sought help from the International Monetary Fund. Serbia became the latest to open talks with the IMF last week.
“Many countries have not been through a cycle of much higher interest rates since the 1990s. There’s a lot of debt out there augmented by the borrowing in the pandemic,” said Mr. Rajan. Stress in emerging markets will widen, he added. “It’s not going to be contained.”
A stronger dollar makes the debts that emerging-market governments and companies have taken out in U.S. dollars more expensive to pay back. Emerging-market governments have $83 billion in U.S. dollar debt coming due by the end of next year, according to data from the Institute of International Finance that covers 32 countries.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 19, 2022 at 1:18pm
-
India’s current account deficit (CAD) likely widened to its highest in nearly a decade in the June 2022 quarter to USD 30.5 billion or 3.6 per cent of GDP, as per a Reuters’ poll of economists held between 9-15 September 2022. Economists opine that soaring global commodity prices and Rupee at 80 contributed to the worsening trade gap and bloating the CAD. Forecasts for CAD ranged between USD 28.5-34.0 billion or 2.4 per cent to 5 per cent of GDP.
https://www.cmie.com/kommon/bin/sr.php?kall=warticle&dt=2022091...'s%20current%20account%20deficit%20(CAD,between%209%2D15%20September%202022.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 30, 2022 at 5:13pm
-
#India central bank chief Das raises interest rates 4th time in 2022, says global #economic outlook remains bleak, with #recession fears mounting & #inflation persisting at “alarmingly high levels”. #Indian forex reserves down $100 billion, #rupee weak. https://www.wsj.com/articles/indias-central-bank-calls-aggressive-m...
India’s central bank raised its key interest rate by half a percentage point, as efforts to rein in inflation and protect an economic recovery have been complicated by its currency’s decline against the U.S. dollar.
On Friday, the Reserve Bank of India raised its overnight lending rate to 5.90% from 5.40%, the fourth increase since it began raising rates following an unscheduled meeting in May, prompted by global inflationary pressures exacerbated by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
RBI Gov. Shaktikanta Das said that having witnessed the major shocks of the coronavirus pandemic and the conflict in Ukraine, the global economy is now in the midst of a third major shock arising from aggressive monetary policy tightening from advanced economies that is having spillover effects on the rest of the world.
“There is nervousness in financial markets with potential consequences for the real economy and financial stability,” Mr. Das said. “The global economy is indeed in the eye of a new storm.”
The pace at which the U.S. Federal Reserve has raised rates, coupled with growing fears of a global recession, have strengthened the dollar and heaped downward pressure on other currencies. The Fed approved its third consecutive interest-rate rise of 0.75 percentage point last week and signaled additional large increases as inflation remains stubbornly high. Central banks around the world continue to tighten their own monetary policy.
The British pound hit its lowest-ever level against the U.S. dollar this week as investors worried about the government’s plans to cut taxes and the Bank of England warned it would raise interest rates as much as needed to hit its inflation targets. The Chinese yuan slid to its weakest level against the dollar in more than a decade, and Japan intervened in the foreign-exchange market for the first time in 24 years to support the yen.
In India, the rupee is down about 9% this year against the dollar. Despite the RBI’s efforts to defend the currency, it slumped in July past 80 rupees per dollar to record lows. That defense has contributed to an almost $100 billion decrease in India’s foreign-exchange reserves over the past year to $545 billion. The RBI also attributes some of that decrease to the change in value of other currencies it holds.
Mr. Das said the global economic outlook remains bleak, with recession fears mounting and inflation persisting at “alarmingly high levels” across multiple jurisdictions.
“Central banks are charting new territory with aggressive rate hikes even if it entails sacrificing growth in the near-term,” he said.
Emerging-market economies in particular, Mr. Das said, are confronting challenges of slowing global growth, elevated food and energy prices, debt distress and sharp currency depreciations. Despite the unsettling global environment, he added, the Indian economy remains resilient.
Robert Carnell, Asia-Pacific chief economist at ING Bank, said a weak rupee was more troublesome from the point of view of imports becoming more expensive rather than from any external debt issue, given India’s debt levels remained relatively low.
Mahesh Vyas, the managing director of the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy, said while the principal objective of the RBI’s currency intervention is to avoid volatility, support for the rupee for any given value is futile.
“Government efforts can delay the slide of the rupee but it cannot stop it,” he said.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on October 28, 2022 at 8:42am
-
#India's #forex reserves drop to $524 billion, the lowest since July 2020. https://www.reuters.com/markets/asia/indias-forex-reserves-drop-low...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 30, 2022 at 7:49am
-
India's current account gap widens to 9-year high
https://www.reuters.com/world/india/indias-current-account-gap-wide...
MUMBAI, Dec 29 (Reuters) - India's current account deficit widened in the July-September quarter as high commodity prices and a weak rupee increased the country's trade gap, data from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) showed on Thursday.
In absolute terms, the current account deficit (CAD) (INCURA=ECI) was $36.40 billion in the second quarter of fiscal year 2022/23, its highest in more than a decade. As a percentage of GDP, it was 4.4%, its highest since the June quarter of 2013.
The CAD was $18.2 billion, or 2.2% of GDP, in the preceding April-June quarter, while the deficit was $9.7 billion, or 1.3% of GDP, in the same quarter a year earlier, the release showed.
In a statement, the RBI linked the widening deficit to the increase of "the merchandise trade deficit to $83.5 billion from $63.0 billion in Q1 2022/23 and an increase in net outgo under investment income".
In its Financial Stability Report released after the data, it said the widened trade deficit reflected "the impact of slowing global demand on exports, even as growth in services exports and remittances remained robust".
The median forecast of 18 economists in a Dec. 5-14 Reuters poll was for a $35.5 billion CAD in the July-September quarter.
The RBI said services exports reported growth of 30.2% on a year-on-year (y-o-y) basis, driven by exports of software, business and travel services, while net services receipts increased sequentially and y-o-y.
Private transfer receipts, mainly representing remittances by Indians employed overseas, rose by 29.7% to $27.4 billion from a year earlier.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on May 16, 2023 at 4:34pm
-
Top 10 Countries that Export the Most Goods and Services (Current US$ millions - World Bank 2020)
https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/exports-by-country
Rank Country Exports (Current US$)
1 China $2,723,250.43
2 United States $2,123,410.00
3 Germany $1,669,993.51
4 Japan $785,365.75
5 United Kingdom $770,478.62
6 France $733,165.40
7 Netherlands $711,504.80
8 Hong Kong (China SAR) $612,566.52
9 Singapore $599,216.28
10 South Korea $596,945.20
Profiles of the world's largest exporters
1. China
Aside from the European Union (which is a collective of many countries), China is the world’s largest exporter. In 2020, China exported an estimated $2.72 trillion worth of goods and services, primarily electronic equipment and machinery such as broadcast equipment, computers, integrated circuits, office machine parts, and telephones. In 2018, China’s exports made up about 10.78% of the global total.
2. United States
The U.S. is the second-largest exporter in the world, with an estimated $2.12 trillion in exports for 2020. The largest exports of the U.S. are crude and refined petroleum; integrated circuits; pharmaceuticals and medical instruments; and aircraft including planes, spacecraft, and helicopters as well as their replacement parts. One of the reasons that the United States lags behind China in exports is the cost of labor. Many goods cannot be produced, manufactured, or assembled in the U.S. for a price comparable to that in China.
3. Germany
Having exported an estimated $1.67 trillion worth of goods and services in 2020, Germany is the world’s third-largest exporter. As one of the most technologically advanced countries in the world, Germany’s main exports include automobiles (BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Audi, Volkswagen), pharmaceuticals (Bayer), aircraft, machinery, electronics, and chemicals. Germany is the third of three countries to have exports exceeding $1 trillion, behind only China and the United States.
4. Japan
Japan’s exports for 2020 were valued at an estimated $785.4 billion. Japan’s major exports include automobiles (Toyota, Honda, Nissan, Mazda, Suzuki, more) and automobile parts, integrated circuits and electronic devices (Nintendo, Panasonic, Sony, and many more). Japan's largest export customers are China, the United States, South Korea, Taiwan, and Hong Kong.
5. United Kingdom
The United Kingdom ranked as the fifth-highest exporter in the world in terms of dollar value in 2020, shipping an estimated $770.5 billion in goods and services to international customers. The U.K.'s top exports include cars (Bentley, Jaguar, Mini, Rolls-Royce, more), gas turbines, gold, medicines, hard liquor, antiques, and crude petroleum (which is often first imported from Norway, then exported to the rest of Europe, as well as China and South Korea).
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on August 31, 2023 at 10:30am
-
From Google Gen AI
India's current account deficit widened to $13.4 billion in Q4FY22, which is 1.5% of GDP. The capital account deficit was $1.7 billion in Q4FY22, which was the first deficit since the Taper Tantrum episode in September 2013.
The current account tracks the flow of imports and exports.
A current account deficit occurs when the inflow of foreign currency from exports is less than the outflow of foreign currency from imports.
The capital account tracks the flow of assets and liabilities.
A capital account deficit occurs when the debit items are more than the credit items. This indicates a net outflow of capital from the country.
The sum of the current and capital accounts is always zero. This means that when a country has a deficit in its current account, it necessarily has a surplus in its capital account and vice versa.
India generally has a capital account surplus because it attracts a large share of foreign investments.
https://prepp.in/news/e-492-capital-account-indian-economy-notes
Comment
- ‹ Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Next ›
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Pak-Saudi Joint Defense: Is Pakistan A Major Power or Bit Player in the Middle East?
The recently signed “Strategic Mutual Defense Agreement” between Saudi Arabia and Pakistan states that “any aggression against either country will be considered an aggression against both”. It is being seen by some geopolitical analysts as the beginning of an "Islamic NATO". Others, such as Indian-American analyst Shadanand Dhume, have dismissed Pakistan as no more than a "bit player"…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on September 27, 2025 at 5:30pm — 7 Comments
Silicon Valley Pakistani-Americans Among Top Donors to Mamdani Campaign
Omer Hasan and Mohammad Javed are the top donors to Zohran Mamdani’s mayoral campaign in New York City, according to media reports. Both are former executives of Silicon Valley technology firm AppLovin. Born and raised in Silicon Valley, Omer is the son of a Pakistani-American couple who are long-time residents of Silicon Valley, California. …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on September 19, 2025 at 9:00am
© 2025 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network