PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
India's Economy Grew Only 0.2% Annually in the Last Two Years
The Indian government has reported an 8.4% jump in economic growth in the July-to-September period compared with a contraction of 7.4% for the same period a year earlier. The average GDP growth in India over the last two years has averaged just 0.2% per year. The news appears to indicate strong recovery after a big economic hit suffered from the COVID pandemic since early 2020. Pakistan's economy fared relatively better during the pandemic. Pakistan's GDP rose 0.5% in 2020 and 3.9% in 2021. As a result, Pakistan now fares better than India on multiple indices including Hanke Misery Index, World Happiness Index, Food Affordability Index and World Hunger Index.
India's Economy:
Welcoming the news, renowned Indian economist Kaushik Basu tweeted: "India's growth of 8.4% over Jul-Sep is welcome news. But it'll be injustice to India if we don't recognize, when this happens after -7.4% growth, it means an annual growth of 0.2% over 2 years. This is way below India's potential. India has fundamental strength to do much better".
 |
| Indian Economist Kaushik Basu's Tweet |
Indian-American Nobel Laureate economist Abhijit Banerjee, too, spoke out in agreement. He said, "I think that we (Indians) are in a moment of great pain. The economy is still well below as against what it was in 2019". "We don't know how much below, but it is substantially below. And I am not blaming anybody, I am just saying", he added.
India's Rising Public Debt:
India's debt to gdp ratio is nearing 90%, the highest in the South Asia region. It has risen by 17% in the last two years, the most of any emerging economy. By contrast, Pakistan's debt to GDP ratio has increased by a mere 1.6% to 87.2% from 2019 to 2020.
 |
| India's Rising Debt. Source: Business Standard |
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has projected the Indian government debt, including that of the center and the states, to rise to a record 90.6% of gross domestic product (GDP) during 2021-22 against 89.6% in the previous year. By contrast, the percentage of Pakistan's public debt to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) including debt from the International Monetary Fund, and external and domestic debt has fallen from 87.6% in Fiscal Year (FY) 2019-20 to 83.5% in FY 2020-21.
Hanke's Misery Index:
Pakistanis are less miserable than Indians in the economic sphere, according to the Hanke Annual Misery Index (HAMI) published in early 2021 by Professor Steve Hanke. With India ranked 49th worst and Pakistan ranked 39th worst, both countries find themselves among the most miserable third of the 156 nations ranked. Hanke teaches Applied Economics at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland. Hanke explains it as follows: "In the economic sphere, misery tends to flow from high inflation, steep borrowing costs, and unemployment. The surefire way to mitigate that misery is through economic growth. All else being equal, happiness tends to blossom when growth is strong, inflation and interest rates are low, and jobs are plentiful". Several key global indices, including misery index, happiness index, hunger index, food affordability index, labor force participation rate, ILO’s minimum wage data, all show that people in Pakistan are better off than their counterparts in India. The rankings for the two South Asian nations are supported by other indices such as the World Bank Labor Participation data, International Labor Organization Global Wage Report, World Happiness Report, Food Affordability Index and Global Hunger Index.
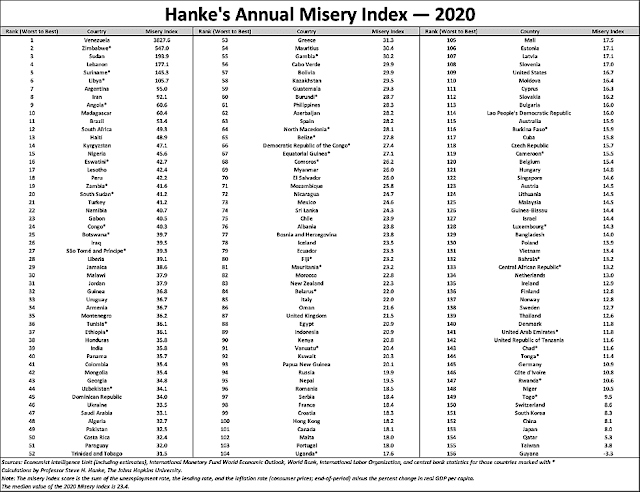 |
| Hanke's Annual Misery Index 2021. Source: National Review |
Employment and Wages:
Labor force participation rate in Pakistan is slightly above 50% during this period, indicating about a 2% drop in 2020. Even before COVID pandemic, there was a steep decline in labor force participation rate in India. It fell from 52% in 2014 to 47% in 2020.
 |
| Labor Force Participation Rates in Pakistan (Top), India (bottom). ... |
The International Labor Organization (ILO) Global Wage Report 2021 indicates that the minimum wage in Pakistan is the highest in South Asia region. Pakistan's minimum monthly wage of US$491 in terms of purchasing power parity while the minimum wage in India is $215. The minimum wage in Pakistan is the highest in developing nations in Asia Pacific, including Bangladesh, India, China and Vietnam, according to the International Labor Organization.
 |
| Monthly Minimum Wages Comparison. Source: ILO |
Global Food Security:
 |
| History of Inflation in Pakistan. Source: Statista |
 |
| Hunger Trends in South Asia. Source: Global Hunger Index |
Amid the COVID19 pandemic, Pakistan's World Happiness ranking has dropped from 66 (score 5.693) among 153 nations last year to 105 (score 4.934) among 149 nations ranked this year. Neighboring India is ranked 139 and Afghanistan is last at 149. Nepal is ranked 87, Bangladesh 101, Pakistan 105, Myanmar126 and Sri Lanka129. Finland retained the top spot for happiness and the United States ranks 19th.
 |
| Pakistan Happiness Index Trend 2013-2021 |
One of the key reasons for decline of happiness in Pakistan is that the country was forced to significantly devalue its currency as part of the IMF bailout it needed to deal with a severe balance-of-payments crisis. The rupee devaluation sparked inflation, particularly food and energy inflation. Global food prices also soared by double digits amid the coronavirus pandemic, according to Bloomberg News. Bloomberg Agriculture Subindex, a measure of key farm goods futures contracts, is up almost 20% since June. It may in part be driven by speculators in the commodities markets. These rapid price rises have hit the people in Pakistan and the rest of the world hard. In spite of these hikes, Pakistan remains among the least expensive places for food, according to recent studies. It is important for Pakistan's federal and provincial governments to rise up to the challenge and relieve the pain inflicted on the average Pakistani consumer.
Pakistan's Real GDP:
Vehicles and home appliance ownership data analyzed by Dr. Jawaid Abdul Ghani of Karachi School of Business Leadership suggests that the officially reported GDP significantly understates Pakistan's actual GDP. Indeed, many economists believe that Pakistan’s economy is at least double the size that is officially reported in the government's Economic Surveys. The GDP has not been rebased in more than a decade. It was last rebased in 2005-6 while India’s was rebased in 2011 and Bangladesh’s in 2013. Just rebasing the Pakistani economy will result in at least 50% increase in official GDP. A research paper by economists Ali Kemal and Ahmad Waqar Qasim of PIDE (Pakistan Institute of Development Economics) estimated in 2012 that the Pakistani economy’s size then was around $400 billion. All they did was look at the consumption data to reach their conclusion. They used the data reported in regular PSLM (Pakistan Social and Living Standard Measurements) surveys on actual living standards. They found that a huge chunk of the country's economy is undocumented.
Pakistan's service sector which contributes more than 50% of the country's GDP is mostly cash-based and least documented. There is a lot of currency in circulation. According to the State Bank of Pakistan (SBP), the currency in circulation has increased to Rs. 7.4 trillion by the end of the financial year 2020-21, up from Rs 6.7 trillion in the last financial year, a double-digit growth of 10.4% year-on-year. Currency in circulation (CIC), as percent of M2 money supply and currency-to-deposit ratio, has been increasing over the last few years. The CIC/M2 ratio is now close to 30%. The average CIC/M2 ratio in FY18-21 was measured at 28%, up from 22% in FY10-15. This 1.2 trillion rupee increase could have generated undocumented GDP of Rs 3.1 trillion at the historic velocity of 2.6, according to a report in The Business Recorder. In comparison to Bangladesh (CIC/M2 at 13%), Pakistan’s cash economy is double the size. Even a casual observer can see that the living standards in Pakistan are higher than those in Bangladesh and India.
Related Links:
Haq's Musings
South Asia Investor Review
Pakistan Among World's Largest Food Producers
Food in Pakistan 2nd Cheapest in the World
Pakistan's Pharma Industry Among World's Fastest Growing
Pakistan to Become World's 6th Largest Cement Producer by 2030
Pakistan's 2012 GDP Estimated at $401 Billion
Pakistan's Computer Services Exports Jump 26% Amid COVID19 Lockdown
Coronavirus, Lives and Livelihoods in Pakistan
Vast Majority of Pakistanis Support Imran Khan's Handling of Covid1...
Pakistani-American Woman Featured in Netflix Documentary "Pandemic"
Incomes of Poorest Pakistanis Growing Faster Than Their Richest Cou...
Can Pakistan Effectively Respond to Coronavirus Outbreak?
How Grim is Pakistan's Social Sector Progress?
Pakistan Fares Marginally Better Than India On Disease Burdens
Trump Picks Muslim-American to Lead Vaccine Effort
Democracy vs Dictatorship in Pakistan
Pakistan Child Health Indicators
Pakistan's Balance of Payments Crisis
Panama Leaks in Pakistan
Conspiracy Theories About Pakistan Elections"
PTI Triumphs Over Corrupt Dynastic Political Parties
Strikingly Similar Narratives of Donald Trump and Nawaz Sharif
Nawaz Sharif's Report Card
Riaz Haq's Youtube Channel
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 8, 2021 at 6:42pm
-
India runs perennial trade deficits. Unlike China's, India's US$ reserves are not built by trade surpluses. India is heavily dependent on foreign debt and direct and portfolio investments for its US$ reserves.
As long the West sees India as a useful counterweight to China, the western money will continue to flow into India.
Here are a couple of excerpts from The Hindu Businessline on this subject:
https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/opinion/the-flip-side-to-build...
"Ample reserves are a source of comfort, but there are costs in managing them as well as risks due to debt and hot money flows"
"In BoP parlance, capital flows include equity flows (mainly foreign direct investment and portfolio investment) and debt flows (essentially consist of external commercial borrowing or ECB, NRI deposits, trade credit and portfolio debt investment). As per the IIP, debt liabilities account for nearly 48 per cent and carry the risk of debt service (repayment and interest payment). Portfolio equity investments are known as “hot” money or speculative money and as on March 2021, these flows accounted for 23 per cent of total liabilities. Thus, the forex reserves build-up has the potential risks of growing debt liabilities and facing the vagaries of “hot” money"
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 14, 2021 at 1:59pm
-
Budget 2021-22: Minimum wage increased from Rs17,500 to Rs20,000
Salaries and pensions increased by 10%
https://www.samaa.tv/money/2021/06/budget-2021-22-minimum-wage-incr...
The government has increased the minimum wage from Rs17,500 per month to Rs. 20,000.
Federal Finance Minister Shaukat Tarin on Friday presented the budget for the next financial year 2021-22.
Introducing the budget, the Finance Minister said that low-income earners have been affected more by inflation. In order to reduce the burden of inflation, the minimum wage has been increased from Rs. 17,500 to Rs20,000 per month.
The finance minister said that the salaries of government employees are being increased by 10% and the pensions of retired employees will be increased by 10% from July 1.
--------------
In purchasing power parity terms, one PPP US$ is equal to about PKR 40.
So Rs 20,000 per month minimum wage translates to $500 in PPP terms.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 28, 2021 at 7:21am
-
#India's #economy growing fast but problems remain: November inflation 14.23%. #Fuel and #energy prices rose nearly 40% last month. Urban #unemployment – most of the better-paying jobs are in cities – has been moving up since September and is now above 9%. https://aje.io/ytyan4
That will not be easy, say experts. The pandemic has devastated India’s micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs), which contribute 30 percent of the nation’s GDP as well as half of the country’s exports and represent 95 percent of its manufacturing units.
The government of Prime Minister Narendra Modi told Parliament in December that a survey it had conducted suggested that 9 percent of all MSMEs had shut down because of COVID-19. And that might be just the tip of the iceberg. In May, another survey of more than 6,000 MSMEs and startups found that 59 percent were planning to shut shop, scale down or sell before the end of 2021.
----------Baldev Kumar threw his head back and laughed at the mention of India’s resurgent GDP growth. The country’s economy clocked an 8.4-percent uptick between July and September compared with the same period last year. India’s Home Minister Amit Shah has boasted that the country might emerge as the world’s fastest-growing economy in 2022.
Kumar could not care less.
As far as he was concerned, the crumpled receipt in his hand told a different story: The tomatoes, onions and okra he had just bought cost nearly twice as much as they did in early November. The 47-year-old mechanic had lost his job at the start of the pandemic. The auto parts store he then joined shut shop earlier this year. Now working at a car showroom in the Bengaluru neighbourhood of Domlur, he is worried he might soon be laid off as auto sales remain low across India.
He has put plans for his daughter’s wedding on hold, unsure whether he can foot the bill. He used to take a bus to work. Now he walks the five-kilometre (three-mile) distance to save a few rupees. “I don’t know which India that’s in,” he said, referring to the GDP figures. “The India I live in is struggling.”
Kumar wasn’t exaggerating – even if Shah’s prognosis turns out to be correct.
Asia’s third-largest economy is indeed growing again, and faster than most major nations. Its stock market indices, such as the Sensex and Nifty, are at levels that are significantly higher than at the start of 2021 – despite a stumble in recent weeks. But many economists are warning that these indicators, while welcome, mask a worrying challenge – some describe it as a crisis – that India confronts as it enters 2022.
November saw inflation rise by 14.23 percent, building on a pattern of double-digit increases that have hit India for several months now. Fuel and energy prices rose nearly 40 percent last month. Urban unemployment – most of the better-paying jobs are in cities – has been moving up since September and is now above 9 percent, according to the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy, an independent think-tank. “Inflation hits the poor the most,” said Jayati Ghosh, a leading development economist at New Delhi’s Jawaharlal Nehru University.
All of this is impacting demand: Government data shows that private consumption between April and September of 2021 was 7.7 percent lower than in 2019-2020. The economic recovery from the pandemic has so far been driven by demand from well-to-do sections of Indian society, said Sabyasachi Kar, who holds the RBI Chair at the Institute of Economic Growth. “The real challenge will start in 2022,” he told Al Jazeera. “We’ll need demand from poorer sections of society to also pick up in order to sustain growth.”
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 23, 2022 at 11:22am
-
India's economy has some bright spots, a number of very dark stains: Raghuram RajanRajan said that one way to expand budgetary resources is through asset sales, including parts of government enterprises and surplus government land
Read more at: https://www.deccanherald.com/national/indias-economy-has-some-brigh...
The Indian economy has "some bright spots and a number of very dark stains" and the government should target its spending "carefully" so that there are no huge deficits, noted economist and former RBI Governor Raghuram Rajan said on Sunday. Known for his frank views, Rajan also said the government needs to do more to prevent a K-shaped recovery of the economy hit by the coronavirus pandemic. Generally, a K-shaped recovery will reflect a situation where technology and large capital firms recover at a far faster rate than small businesses and industries that have been significantly impacted by the pandemic. "My greater worry about the economy is the scarring to the middle class, the small and medium sector, and our children's minds, all of which will come into play after an initial rebound due to pent up demand. One symptom of all this is weak consumption growth, especially for mass consumption goods," Rajan told PTI in an e-mail interview.
Rajan, currently a Professor at the University of Chicago Booth School of Business, noted that as always, the economy has some bright spots and a number of very dark stains. "The bright spots are the health of large firms, the roaring business the IT and IT-enabled sectors are doing, including the emergence of unicorns in a number of areas, and the strength of some parts of the financial sector," he said. On the other hand, "dark stains" are the extent of unemployment and low buying power, especially amongst the lower middle-class, the financial stress small and medium-sized firms are experiencing, "including the very tepid credit growth, and the tragic state of our schooling". Rajan opined that Omicron is a setback, both medically and in terms of economic activity but cautioned the government on the possibility of a K-shaped economic recovery. "We need to do more to prevent a K shaped recovery, as well as a possible lowering of our medium-term growth potential," he said.
--------
Regarding the rising inflationary trends, Rajan said inflation is a concern in every country, and it would be hard for India to be an exception. According to him, announcing a credible target for the country's consolidated debt over the next five years coupled with the setting up of an independent fiscal council to opine on the quality of the budget would be very useful steps. "If these moves are seen as credible, the debt markets may be willing to accept a higher temporary deficit," he said.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on February 25, 2022 at 7:38am
-
Why 7% growth is miracle and 5% reality for India's economy - Times of India
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/for-ind...
------------5% growth amid de-globalisation to be significant achievement for India, says Ruchir Sharma
https://www.cnbctv18.com/economy/oil-breaches-100-for-first-time-si...
Morgan Stanley Chief Global Strategist Ruchir Sharma on Saturday said if the Indian economy grows at 5 percent in the era of deglobalization, then it will be a significant achievement.
Addressing the FICCI Annual Convention, Sharma further said India hastily passed agriculture and labour reforms during the COVID-19 pandemic.
"Our expectations have to be realistic...if we can grow at more than 5 percent in a year, that is a significant achievement," he said.
Sharma also noted that it is no longer feasible in the world of deglobalisation to grow at 7 percent as exports cannot grow at 20 percent or 30 percent in a year, which was good in an era of globalisation.
"So, for an economy like India's, the growth rate of 5 percent will be pretty credible even in this era where I think emerging economies, in general, will make some sort of a comeback," he added.
Sharma pointed out that there were about 100 economies that were growing at 7 percent or more in 2007.
"That has never happened in the history of the global economy. In the last decade, only 10 economies in the world have grown 7 percent or more in any year," he said.
Sharma also argued that if the population growth of a country is slowing, then that country can't grow at the same pace as it did in the past.
According to the RBI, the Indian economy is likely to contract by 7.5 percent, in 2020-21.
He also pointed out that intra regional trade is the lowest in South Asia compared to any subregion of the world.
Sharma pointed out that India has seen a slight increase in exports since 2010.
"The last decade was a lost decade for emerging economies. The only economy to have gained in the global share in the last decade was China," he noted.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on March 10, 2022 at 10:08am
-
#Mumbai #FII Exodus: Foreign investors selling #Indian shares at a rate of $1 billion a day as #India's stocks plummet. Pace picks up after a record $2.9 billion withdrawn last week. #Modi #BJP #Hindutva #economy #Russia #Ukraine https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2022-03-10/a-billion-dollar...
India’s $3.2 trillion stock market is witnessing an unprecedented foreign selloff as the surge in oil prices fuels worries of an inflation shock in the major energy-importing nation.
While global funds have been net sellers of local equities since the start of October, when the benchmark S&P BSE Sensex hit an all-time high, the pace of outflows has intensified since the start of the war in Ukraine. India relies on imports to meet about 85% of its oil needs.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on March 27, 2022 at 7:08am
-
#India's 2022 #GDP Growth Cut to 4.6% Due to #Ukraine War. India will face restraints on several fronts: #energy access & prices, primary commodity bottlenecks, reflexes from #trade sanctions, #food #inflation, tightening policies & financial instability.
https://thewire.in/economy/indias-2022-gdp-growth-downgraded-to-4-6...
United Nations: India’s projected economic growth for 2022 has been downgraded by over 2% to 4.6% by the United Nations, a decrease attributed to the ongoing war in Ukraine, with New Delhi expected to face restraints on energy access and prices, reflexes from trade sanctions, food inflation, tightening policies and financial instability, according to a UN report released on Thursday.
The UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) report downgraded its global economic growth projection for 2022 to 2.6% from 3.6% due to shocks from the Ukraine war and changes in macroeconomic policies that put developing countries particularly at risk.
The report said while Russia will experience a deep recession this year, significant slowdowns in growth are expected in parts of Western Europe and Central, South and South-East Asia.
India was forecast to grow at 6.7% in 2022 and this projection has been downgraded to 4.6% by UNCTAD.
The report said as some of the other economies in South and Western Asia may gain some benefits from fast growth of demand and prices of energy, they will be hampered by the adversities in primary commodity markets, especially food inflation, and will be further hit by inherent financial instabilities.
India in particular will face restraints on several fronts: energy access and prices, primary commodity bottlenecks, reflexes from trade sanctions, food inflation, tightening policies and financial instability, it said.
The report has downgraded the GDP growth of the US from 3% to 2.4%. China will also see growth decrease to 4.8% from 5.7%. The report projects a deep recession for Russia, with growth decelerating from 2.3% to -7.3%.
The report said the Russian economy faces stringent external constraints imposed by the sanctions.
While Russia is still exporting oil and gas, and will therefore see compensating increases of revenue due to high prices, sanctions severely limit the use of foreign exchange earnings for the purchase of imports or debt servicing.
Russia will experience severe shortages of a wide range of imported goods, high inflation and a substantially devalued currency. While the state will likely act to cushion the shock and limit unemployment and the fall of household incomes, its capacity is limited.
Trade with China and some other partners will continue, but they will not be able to provide substitutes for the wide range of imported goods that the Russian Federation currently cannot access. Assuming the sanctions remain in place through 2022, even if the fighting in Ukraine ends, Russia will experience a severe recession, it said.
The report noted that a number of developing country central banks also engaged in quantitative easing: active purchasing of bonds in the open market.
A small number of developing country central banks engaged in private sector bond purchases, but public bond buying was more widespread: the central banks of India, Thailand, Colombia and South Africa, among others, engaged in public bond purchases.
In the global monetary hierarchy, the place of a national currency today is determined less by the size of its domestic production base than by the size of its domestic financial sector.
The currencies of Brazil, Russia, India and China account for no more than 3.5% of the $6.6 trillion daily turnover in the forex markets, a ratio barely one-tenth of the United States dollar’s 44%, it said.
UNCTAD said the ongoing war in Ukraine is likely to reinforce the monetary tightening trend in advanced countries following similar moves that began in late 2021 in several developing countries due to inflationary pressures, with expenditure cuts also anticipated in upcoming budgets.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 1, 2022 at 7:35am
-
Ritesh Kumar Singh
@RiteshEconomist
We shouldn't get carried away by 13.5% #GDPgrowth in Q1 FY2022/23.
Q1FY2020/21: INR 35.5 trillion
Q1FY2022/23: INR 36.85 trillion
The increase in 3 years: INR 1.35 trillion or 3.9% in 3 years.
#economy #India #IndiaAt75
@EconomicTimes
https://twitter.com/RiteshEconomist/status/1564989770966523905?s=20...
--------
Q1 GDP growth misses estimates despite low base; govt spending subdued
13.5% expansion in June QTR despite low base; GVA at basic prices up 12.7%
https://www.business-standard.com/article/economy-policy/q1-gdp-gro...
Keeping the two pandemic years of 2020 and 2021 out, Q1 real GDP in 2022-23 is only 3.8 per cent higher than in the equivalent quarter of 2019-20. Gross value added (GVA) at basic prices grew at 12.7 per cent in the June quarter while nominal GDP was up 26.7 per cent, reflecting elevated inflationary pressures in the economy.
Growth in private final consumption expenditure, or private spending, grew at a robust 25.9 per cent with pent-up demand kicking in as consumers felt confident to spend. Government spending, however, grew only 1.3 per cent, signalling that both the Central and state governments kept their expenditure in check during the quarter.
Gross fixed capital formation (GFCF), which represents investment demand in the economy, grew at a robust 20.1 per cent. However, compared to the pre-pandemic period of FY20, GFCF grew only 6.7 per cent.
On the supply side, manufacturing grew by a disappointing 4.8 per cent. Despite 25.7 per cent growth in trade, hotel, transport services, the sector, with the highest contribution to GDP, is still 15.5 per cent below the pre-pandemic level of the equivalent quarter in FY20.
The labour-intensive construction sector grew 16.8 per cent but it is barely above the pre-pandemic level, growing 1.2 per cent.
Madhavi Arora, lead economist, Emkay Global Financial Services, said. “We maintain growth may remain at 7 per cent for the year, albeit with downside risks. Going ahead, even as recovery in domestic economic activity is yet to be broad-based, global drags in the form of still elevated prices, shrinking corporate profitability, demand-curbing monetary policies and diminishing global growth prospects weigh on the growth outlook.”
Nikhil Gupta, chief economist of Motilal Oswal, said assuming no change in projections by the RBI for the rest of the year, the first-quarter data suggested the central bank’s FY23 growth forecast would be revised to 6.7 per cent from 7.2 per cent.
The RBI expected 16.2 per cent growth in Q1, with 6.2, 4.1, and 4 per cent growth in the subsequent quarters.
Aurodeep Nandi, India economist and vice-president at Nomura, said even if one were to discount the low base, this marked a stellar rise in sequential momentum with post-pandemic tailwinds lifting GDP growth in the June quarter.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 12, 2022 at 9:42am
-
India's Economic Situation 'Bleak'; We Know the Issue but Not the Solution: Pronab Sen
In an interview with Karan Thapar, the country's former chief statistician said that India will miss the RBI's target of 7.2% growth for this financial year and that it'll come around 6-6.5%.
https://thewire.in/video/watch-indias-economic-situation-bleak-we-k...
In an interview where he paints a bleak and disturbing picture of the state of the economy, India’s former chief statistician professor Pronab Sen has said that we can identify the problems that are retarding growth but we don’t know how to tackle them.
Worse, professor Sen says he is not sure if the government has diagnosed the problems because it has not spoken about them and its silence can be variously interpreted. Consequently, he says that India will miss the RBI’s target of 7.2% growth for this financial year and that it will growth will only come in somewhere around 6-6.5%.
However, he points out, in real terms growth will actually be just 4% which, he adds, is at least 2.5% below the growth India needs to create jobs for its population. This means, professor Sen points out, we can boast of being the fastest growing economy but it’s equally true that we are considerably falling short of the rate of growth we need (6.57%) to create sufficient jobs for our people which, in turn, will boost consumption and spending and create incentives for investment.
In these circumstances, professor Sen said that first quarter growth of FY23 at 13.5% is clearly disappointing.
In a 42-minute interview to Karan Thapar for The Wire, professor Sen, who is currently the country director of the International Growth Centre, identified two critical areas where the Indian economy faces serious problems about which we are not sure what we should do.
The first is the MSME sector which, he added, has undoubtedly shrunk in size over the last two years. The problem is not a question of encouraging and helping existing MSMEs so much as creating the environment for new MSMEs to emerge. The specific problem is that the informal credit line on which they depend has dried up and we don’t know how to revive that credit line. The government does not have a clear way of doing so.
And, the problem afflicting MSMEs, professor Sen says, is the reason why manufacturing has only grown year-on-year by 4.8% and why joblessness and unemployment are an increasing concern. Most jobs are created by MSMEs or the wider unorganised sector and that seems to have stopped or, at least, is not happening in sufficient measure.
The second problem professor Sen identified is the critical services sector of trade, hotel, transport, communication and broadcasting services, which represent 30.5% of employment but is still 15.5% below pre-pandemic levels. Once again, he said we don’t know what we need to do to boost this sector back to pre-pandemic levels. He pointed out that many MSMEs work in this sector and its future is, therefore, directly linked to MSMEs.
Professor Sen also pointed out that the global situation will not be of much help to India. Interest rates are likely to remain high and exports, which have been a support to the economy until recently, will face problems in markets like Europe and America and, therefore, fail to provide the boost to growth they have previously given. However, he believes oil prices could come down.
He believes India is clearly locked into a K-shaped recovery and the arms of the K are moving further and further apart.
Whilst scoffing at commentators and newspapers that have called for broad-based reforms, without identifying what they would be, professor Sen said that the key reform needed would be credit lines that would service MSMEs and provide funds for new MSMEs to start up.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 19, 2022 at 8:41pm
-
Kaushik Basu
@kaushikcbasu
Over 2020-22 India's annual GDP growth is 0.43%. This places India in the middle of the world's growth table. What's worrying is that a decade ago India was in the top 3. Also youth unemployment at 28.3% is the highest in decades. So the growth that's happening is all at the top.
https://twitter.com/kaushikcbasu/status/1571866854800461826?s=20&am...
Comment
- ‹ Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Next ›
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Has Pakistan Destroyed India's S-400 Air Defense System at Adampur?
Pakistan claims its air force (PAF) has destroyed India's high-value Russian-made S-400 air defense system (ADS) located at the Indian Air Force (IAF) Adampur air base. India has rejected this claim and posted pictures of Prime Minister Narendra Modi posing in front of its S-400 rocket launchers in Adampur. Meanwhile, there are reports that an Indian S-400 operator, named Rambabu Kumar Singh, was killed at about the time Pakistan claims to have hit it. Pakistan is believed to have targeted…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on May 21, 2025 at 4:00pm — 2 Comments
Pakistan Downs India's French Rafale Fighter Jets in History's Largest Aerial Battle
Pakistan Air Force (PAF) pilots flying Chinese-made J10C fighter jets shot down at least two Indian Air Force's French-made Rafale jets in history's largest ever aerial battle involving over 100 combat aircraft on both sides, according to multiple media reports. India had 72 warplanes on the attack and Pakistan responded with 42 of its own, according to Pakistani military. The Indian government has not yet acknowledged its losses but senior French and US intelligence officials have …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on May 9, 2025 at 11:00am — 32 Comments
© 2025 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network