PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
China and US Battle For Influence in Pakistan
Top US and Chinese diplomats have visited Pakistan to meet with the country's new prime minister Mr. Imran Khan within days of his assuming office. The US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo was the first to call on Prime Minister Imran Khan in Islamabad. Pompeo's visit was soon followed by a three-day visit by Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi. What is at stake in the battle between China and the United States in Pakistan is the prize of global superpower status, according to the US-based Wall Street Journal.
There is a lot of speculation in the western media about the objectives of Pakistan policies being pursued by the two great powers and their impact on the US-China competition for world dominance. Such speculations have centered on the debt related to China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) and the US leverage in potential IMF bailout of Pakistan.
American business publication Wall Street Journal has produced a short video explaining how its staff sees what it describes as "US-China conflict brewing in Pakistan". What is at stake in the battle between China and the United States in Pakistan is the prize of global superpower status. Here are the key points it makes:
1. The US-China conflict brewing in Pakistan is about global dominance sought by the two great powers.
2. If China succeeds, it could become the new center of global trade. If the US wins, it could frustrate China's push to become a global power. The impact of it will be felt around the world for decades.
3. China has already surpassed the United States as the world's biggest exporter of goods and services.
4. The biggest project in China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) in which China is investing heavily and providing massive loans.
5. China could use the infrastructure built in Pakistan under CPEC to gain access to the Indian Ocean and supplant the United States in Pakistan.
6. CPEC-related spending is sinking Pakistan deeper in debt to China. It could force Pakistan to seek $8 billion to $12 billion bailout by IMF where US is the biggest shareholder with veto power.
7. US does not want the IMF bailout money to be used to repay Chinese debt. Not bailing out Pakistan is not an option because it could cost US an important ally in the region.
8. US could, however, use IMF bailout to limit what Pakistan can borrow from China. Such a condition will achieve the US objective of significantly slowing down CPEC and BRI.
9. Pakistan's dilemma is that it needs both the infrastructure improvements financed by China and the IMF bailout to ease pressure on its dwindling foreign exchange reserves.
10. Whoever wins in Pakistan will become the number one global superpower.
Can US "Spend Them (Chinese) Into Oblivion"? |
Here's the Wall Street Journal video:
Related Links:
Can Pakistan Avoid Recurring Balance of Payment Crisis?
Pakistan Economy Hobbled By Underinvestment
Can Indian Economy Survive Without Western Capital Inflows?
Pakistan-China-Russia Vs India-Japan-US
Chinese Yuan to Replace US $ as Reserve Currency?
Remittances From Overseas Pakistanis
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on March 9, 2023 at 7:48am
-
China is right about US containment | Financial Times
By Edward Luce
https://www.ft.com/content/bc6685c1-6f17-4e9e-aaaa-922083c06e70
But encircling Beijing is not a viable long-term strategy
Here is a thought experiment. If Taiwan did not exist, would the US and China still be at loggerheads? My hunch is yes. Antagonism between top dogs and rising powers is part of the human story. The follow-up is whether such tensions would persist if China were a democracy rather than a one-party state. That is harder to say but it is not obvious that an elected Chinese government would feel any less resentful of the US-led global order. It is also hard to imagine the circumstances in which America would willingly share the limelight.
All of which suggests that loose talk of a US-China conflict is no longer far-fetched. Countries do not easily change their spots: China is the middle kingdom wanting redress for the age of western humiliation; America is the dangerous nation seeking monsters to destroy. Both are playing to type. The question is whether global stability can survive either of them insisting that they must succeed. The likeliest alternative to today’s US-China stand-off is not a kumbaya meeting-of-minds, but war. This week, Xi Jinping went further than before in naming America as the force behind the “containment”, “encirclement” and “suppression” of China. Though his rhetoric was provocative, it was not technically wrong. President Joe Biden is still officially committed to trying to co-operate with China. But Biden was as easily blown off course last month as a weather balloon. Washington’s panic over what is after all 19th-century technology prompted Antony Blinken, the US secretary of state, to cancel a Beijing trip that was to pave the way for a Biden-Xi summit. Washington groupthink drove Biden’s overreaction. The consensus is now so hawkish that it is liable to see any outreach to China as weakness. As the historian Max Boot points out, bipartisanship is not always a good thing.
Some of America’s worst blunders — the 1964 Gulf of Tonkin resolution that led to the Vietnam war, or the 2002 Iraq war resolution — were bipartisan. So is the new House committee on China, which its chair, Mike Gallagher, says will “contrast the Chinese Communist party’s techno-totalitarian state with the Free World”. It is probably safe to say he will not be on the hunt for contradictory evidence.
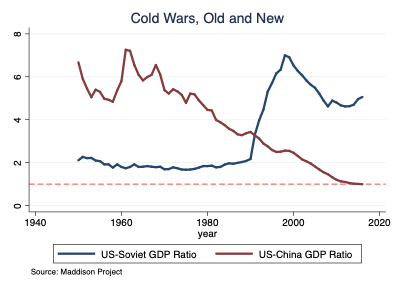
A big difference between today’s cold war and the original one is that China is not exporting revolution. From Cuba to Angola and Korea to Ethiopia, the Soviet Union underwrote leftwing insurgencies worldwide.
The original idea of containment, laid out in George Kennan’s 1947 Foreign Affairs essay, The Sources of Soviet Conduct, was more modest than the undeclared containment that is now US policy. Kennan’s advice was twofold: to stop the expansion of the Soviet empire; and to shore up western democracy. He counselled against the use of force. With patience and skill the USSR would fold, which is what eventually happened.
Today’s approach is containment-plus. When Xi talks of “suppression”, he means America’s ban on advanced semiconductor exports to China. Since high-end chips are used for both civil and military purposes, the US has grounds for denying China the means to upgrade its military. But the collateral effect is to limit China’s economic development.
There is no easy way round this. One possible side-effect will be to accelerate Xi’s drive for “made in China” technology. The Chinese president has also explicitly declared Beijing’s goal of dominating artificial intelligence by 2030, which is another way of saying that China wants to set the rules.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on March 9, 2023 at 7:49am
-
China is right about US containment | Financial Times
By Edward Luce
https://www.ft.com/content/bc6685c1-6f17-4e9e-aaaa-922083c06e70
But encircling Beijing is not a viable long-term strategy
The one positive feature of today’s cold war compared with the last one — China and America’s economic interdependence — is thus something Biden wants to undo. Decoupling is taking on an air of inevitability. When Xi refers to “encirclement”, he is thinking about America’s deepening ties to China’s neighbours. Again, Xi mostly has himself to blame.
Japan’s shift to a more normal military stance, which includes a doubling of its defence spending, probably worries China the most. But America’s growing closeness to the Philippines and India, and the Aukus nuclear submarine deal with Australia and the UK, are also part of the picture. Add in increased US arms transfers to Taiwan and the ingredients for Chinese paranoia are ripe. How does this end?
This is where a study of Kennan would pay dividends. There is no endgame to today’s cold war. Unlike the USSR, which was an empire in disguise, China inhabits historic boundaries and is never likely to dissolve. The US needs a strategy to cope with a China that will always be there.
If you took a snap poll in Washington and asked: one, are the US and China in a cold war; and two, how does the US win it, the answer to the first would be an easy “yes”; the second would elicit a long pause. Betting on China’s submission is not a strategy.
Here is another way to look at it. The US still holds more of the cards. It has plenty of allies, a global system that it designed, better technology and younger demographics. China’s growth is slowing and its society is ageing faster. The case for US resolve and patience is stronger today than it was when Kennan was around. Self-confident powers should not be afraid to talk.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on March 23, 2023 at 7:50am
-
A Threshold Alliance: The China-Pakistan Military Relationship
Wednesday, March 22, 2023 / BY: Sameer P. Lalwani, Ph.D.
https://www.usip.org/publications/2023/03/threshold-alliance-china-...
Geopolitical shifts in South Asia over the past decade, driven by sharper US-China competition, a precipitous decline in China-India relations, and the 2021 withdrawal of US forces from Afghanistan, have pushed the Chinese and Pakistani militaries closer together. The countries’ armies and navies are increasingly sharing equipment, engaging in more sophisticated joint exercises, and interacting more closely through staff and officer exchanges. Yet, as this report concludes, a full China-Pakistan alliance is not inevitable, as Chinese missteps and other sources of friction could slow its consummation.
Summary
Despite China’s eschewal of formal alliances, the China-Pakistan military partnership has deepened significantly over the past decade, approaching a threshold alliance. The trajectory toward a military alliance is not, however, inevitable.
China is Pakistan’s most important defense partner since the end of the Cold War. Beijing has become the leading supplier of Pakistan’s conventional weapons and strategic platforms and the dominant supplier of Pakistan’s higher-end offensive strike capabilities.
China’s military diplomacy with Pakistan quantitatively and qualitatively rivals its military partnership with Russia. China and Pakistan have accelerated the tempo of joint military exercises, which are growing in complexity and interoperability. Increasingly compatible arms supply chains and networked communications systems could allow the countries to aggregate their defense capabilities.
The prospects for China projecting military power over the Indian Ocean from Pakistan’s Western coast are growing. Chinese basing has meaningful support within Pakistan’s strategic circles. The material and political obstacles to upgrading naval access into wartime contingency basing appear to be surmountable and diminishing over time.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on March 28, 2023 at 7:51am
-
Beijing’s opponents ‘may not allow’ alliance with Pakistan
https://www.dawn.com/news/1744608
WASHINGTON: Pakistan and China are engaged in a “threshold alliance” but Beijing’s opponents, particularly the US, may prevent it from becoming a fully-fledged alliance, says a recent US report.
The report titled The Future of the China-Pakistan Military Relationship describes the current status of the China-Pakistan relationship as “a threshold alliance,” but argues that it may not lead to a fully-fledged future alliance, “potentially due to China’s own missteps, or due to opponents’ active measures to arrest the relationship”.
The author, Sameer P. Lalwani, works for the US Institute of Peace (USIP), a federal institution with a Congressional mandate.
The report notes that in 2015, analysts forecast a decline in the China-Pakistan military ties, citing various reasons. But the same year, President Xi Jinping visited Pakistan and introduced CPEC as a “flagship” project and announced sale of eight submarines to Pakistan.
Now, in less than a decade, the China-Pakistan military relationship has “advanced from an episodic partnership to a threshold alliance”, the author argues.
The document claims that Pakistan’s major defence equipment is “increasingly sourced from China, especially the higher-end combat strike and power projection capabilities; and Pakistan continues to retire older US- and European-origin platforms”. But, more is needed for this threshold relationship to become a fully-fledged one. One indicator would be Beijing granting Pakistan more military aid and access to sensitive systems such as the J-20 stealth fighter or nuclear-powered attack submarines.
The other indication would be their militaries adopting a joint peacetime mission “to back each other in the event of a China-India or Pakistan-India border crisis”.
A final signal might be the Chinese Navy deploying maritime reconnaissance assets in Gwadar, it says.
The report, however, notes that both civilian and military leaders have “explicitly denied that Pakistan is drifting into Beijing’s camp and have eschewed pressures forcing them to choose between relations with China and the West”.
According to the report, in China’s and Pakistan’s current political and security environment, there are several points of friction that could slow or reverse the current trajectory of their military relationship.
Politically, China’s treatment of the Uyghurs, a Turkic Muslim minority, in Xinjiang Province could hinder its ties with Pakistan by causing public dissent.
Moreover, China is growing weary of injecting cash into Pakistan’s economy or actively started pursuing economic and military investment in Iran at Pakistan’s expense.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 14, 2023 at 7:57am
-
Pakistan: Don’t ask us to choose between the US and China
https://www.politico.eu/article/pakistan-choose-us-china-global-pow...
Pakistan’s Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs Hina Rabbani Khar tells POLITICO emergence of two rival global power blocs is a threat.
Pakistan has enough problems — including escalating attacks by Taliban insurgents and a spiraling economic crisis — without the added headache of a new Cold War between China and the U.S.
In an interview with POLITICO, Pakistan’s Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs Hina Rabbani Khar insisted Islamabad had no appetite to pick a side in the growing global rivalry between Washington and Beijing.
As a nuclear-armed heavyweight of 250 million people, Pakistan is one of the most closely watched front-line states in the contest for strategic influence in Asia. While Pakistan’s old Cold War partner Washington is increasingly turning its focus to cooperation with Islamabad’s arch-foe India, China has swooped in to extend its sway in Pakistan — particularly through giant infrastructure projects.
Khar insisted, however, that Islamabad was worried about the repercussions of an all-out rupture between the U.S. and China, which would present Pakistan with an unpalatably binary strategic choice. “We are highly threatened by this notion of splitting the world into two blocs,” Khar said on a visit to Brussels. “We are very concerned about this decoupling … Anything that splits the world further.”
She added: “We have a history of being in a close, collaborative mode with the U.S. We have no intention of leaving that. Pakistan also has the reality of being in a close, collaborative mode with China, and until China suddenly came to everyone’s threat perception, that was always the case.”
It’s clear why Pakistan still sees advantages to walking the strategic tightrope between the U.S. and China. Although U.S. officials have expressed frustration over Pakistan’s historic ties to the Taliban in Afghanistan — and have rowed back on military aid — Washington is still a significant military partner. Last year, the U.S. State Department approved the potential sale of $450 million worth of equipment to maintain Pakistan’s F-16 fighter jets.
Simultaneously, Beijing is pledging to deepen military cooperation with Pakistan — partly to outflank the common enemy in India — and is delivering frigates to the Pakistani navy. China is also building roads, railways, hospitals and energy networks in its western neighbor. While these Chinese investments have boosted the country’s economic development, there are also downsides to going all in with China, with Beijing’s critics arguing that Pakistan has become overly indebted and financially dependent on China.
Khar grabbed headlines in April when a leaked memo appeared in the Wall Street Journal in which she was cited as warning that Pakistan’s instinct to preserve its partnership with the U.S. would harm what she deemed the country’s “real strategic” partnership with China.
She declined to comment on that leak, but took a more bullish line on continued American power in her interview in Brussels, saying the U.S. was unnecessarily fearful and defensive about being toppled from its plinth of global leadership, which she argued remained vital in areas such as healthcare, technology, trade and combating climate change.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 14, 2023 at 7:59am
-
Pakistan: Don’t ask us to choose between the US and China
https://www.politico.eu/article/pakistan-choose-us-china-global-pow...
“I don’t think the leadership role is being contested, until they start making other people question it by being reactive,” she said. “I believe that the West underestimates the value of its ideals, soft power,” she added, stressing Washington’s role as the world’s standard setter. China biggest selling point for Pakistan, she explained, was an economic model for lifting a huge population out of poverty.
Leverage — and the lack of it — in Kabul
Khar’s sharpest criticism of U.S. policy centered on Afghanistan, where she said restrictions intended to hobble the Taliban were backfiring, causing a humanitarian and security crisis, pushing many Afghans to “criminal activities, narcotics strategy and smuggling.”
A weakened Afghanistan is causing increased security problems for Pakistan, and the Taliban in Kabul are widely seen as supporting an expanding terror campaign waged by the Pakistani Taliban. Ironically, given the long history of Pakistan’s engagement with the Afghan Taliban, Islamabad is finding it difficult to exercise its influence and secure Kabul’s help in reining in the latest insurgency wave.
When the Afghan Taliban seized power in Kabul in 2021, Pakistan’s then Prime Minister Imran Khan celebrated their victory against “[American] slavery” and spy chief Faiz Hameed made a visit to Kabul and cheerily predicted “everything will be O.K.” Khar, who took office last year, said Khan had reacted “rather immaturely” and argued her government always knew “the leverage was over-projected.”
While the violence has put Pakistan’s soldiers and police on the front line of the fight against the Taliban at home, Khar said Islamabad was taking a highly diplomatic approach in seeking to win round the Taliban in Afghanistan, pursuing political engagement and focusing on economic development — rather than strong-arm tactics.
“Threatening anyone normally gets you worse results than the ones you started with. Even when it is exceptionally difficult to engage at a point when you think your red lines have not been taken seriously, we will still try the route of engagement.”
She firmly rejected the idea that any other country — either the U.S. or China — could play a role in helping Pakistan defeat the Taliban with military deployments. “When it comes to boots on the ground, we would welcome no one,” she said.
Pakistan is seeking bailout cash from the International Monetary Fund as the economy is hammered by blazing inflation and collapsing reserves. When asked whether she reckoned Washington was holding back on supporting Pakistan, partly to test whether China would step up and play a bigger role in ensuring the country’s stability, Khar replied: “I would be very unhappy if that were the case.”
No to navies
When it came to Europe’s role in the Indo-Pacific region, she was wary of the naval dimensions of EU plans, an element favored by France. She was particularly hostile to any vision of an Indo-Pacific strategy that was dedicated to trying to contain Chinese power in tandem with working with India.
One of the leading fears of the U.S. has long been that China could use its investments in the port of Gwadar to build a naval foothold there, a move that would inflame tensions with India, and allow Beijing to project greater power in the Indian Ocean.
Khar said Europe should tread carefully in calibrating its plan for the region.
“I would be very concerned if it is exclusively or predominantly a military-based strategy, which will then confirm it is a containment strategy, it must not be a containment strategy,” she said of the EU’s Indo-Pacific agenda.
“[If it’s] a containment strategy of a certain country, which then courts a certain country that is a very belligerent neighbor to Pakistan, then instead of stabilizing the region, it is endangering the region.”
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 29, 2023 at 7:28pm
-
China's top-ranking diplomat told Japan and South Korea their people can dye their hair blonde and make their noses sharper but that they'll 'never become Westerners,' urging them to work with Beijing instead
https://www.businessinsider.in/politics/world/news/chinas-top-ranki...
China's top diplomat Wang Yi reminded Japanese and South Koreans of their ethnicity.
He said they can "never become Westerners," calling for closer cooperation between their nations.
China's highest-ranking diplomat urged Japan and South Korea to cooperate more closely with Beijing, saying they can change their looks but will "never become Westerners."
"It doesn't matter how much you dye your hair blonde, how sharp you make your nose, you'll never become Europeans or Americans. You'll never become Westerners," Wang Yi told South Korean and Japanese guests at a conference in Qingdao on Monday.
"We have to know where our roots are," the diplomat said, according to a recording of the conversation shared by Chinese media.
Most Europeans and Americans aren't able to tell Chinese, Japanese, or Korean people apart, Wang added.
Wang, who was speaking at the annual International Forum for Trilateral Cooperation, said the three nations should raise a "clear signal" that they want to work together, adding that they should resist a "Cold War mentality" and push back against "bullying and hegemony."
The diplomat's comments come amid rocky US-China relations over Taiwan, chip restrictions, and accusations of Beijing spying on the US with a balloon. Tensions continued to sour in June as President Joe Biden called Chinese leader Xi Jinping a "dictator," as State Secretary Antony Blinken visited Beijing to ease the relationship between both nations.
South Korea and Japan, close US allies, have recently publicly aligned with Washington on several hot-button issues, releasing joint statements with the White House on Taiwan in the last two years. Both nations have also conducted high-profile military drills with the US this year.
Washington has sought to curb China's growing influence in the rest of Asia, as Beijing pursues closer ties with countries like Cambodia, Laos, and Myanmar.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 7, 2023 at 9:23am
-
EIU (Economic Intelligence Unit)report
China Going Global Investment Index 2023
This year’s edition of the China Going Global Investment Index ranks 80 economies across nearly 200 indicators to identify opportunities and risk for Chinese firms and investors looking to expand globally.
A decade since Xi Jinping’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) launched in 2013, Chinese firms have become formidable investors globally, and the flow of overseas investment is set to increase over the next decade.
Comment
- ‹ Previous
- 1
- …
- 6
- 7
- 8
- Next ›
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Silicon Valley Pakistani-Americans Among Top Donors to Mamdani Campaign
Omer Hasan and Mohammad Javed are the top donors to Zohran Mamdani’s mayoral campaign in New York City, according to media reports. Both are former executives of Silicon Valley technology firm AppLovin. Born and raised in Silicon Valley, Omer is the son of a Pakistani-American couple who are long-time residents of Silicon Valley, California. …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on September 19, 2025 at 9:00am
Modi's Hindutva: Has BJP's Politics Hurt India's International Image?
The Indian cricket team's crass behavior after defeating the Pakistani team at the Asia Cup 2025 group encounter has raised eyebrows among sports fans around the world. Not only did Suryakumar Yadav, the Indian team captain, refuse to do the customary handshake before and after the match in Dubai but he also made controversial statements linking the match with the recent India-Pakistan conflict. “A few things in life are above sportsman’s spirit ......We stand with all the victims of the …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on September 15, 2025 at 7:00pm — 1 Comment
© 2025 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()

You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network