PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
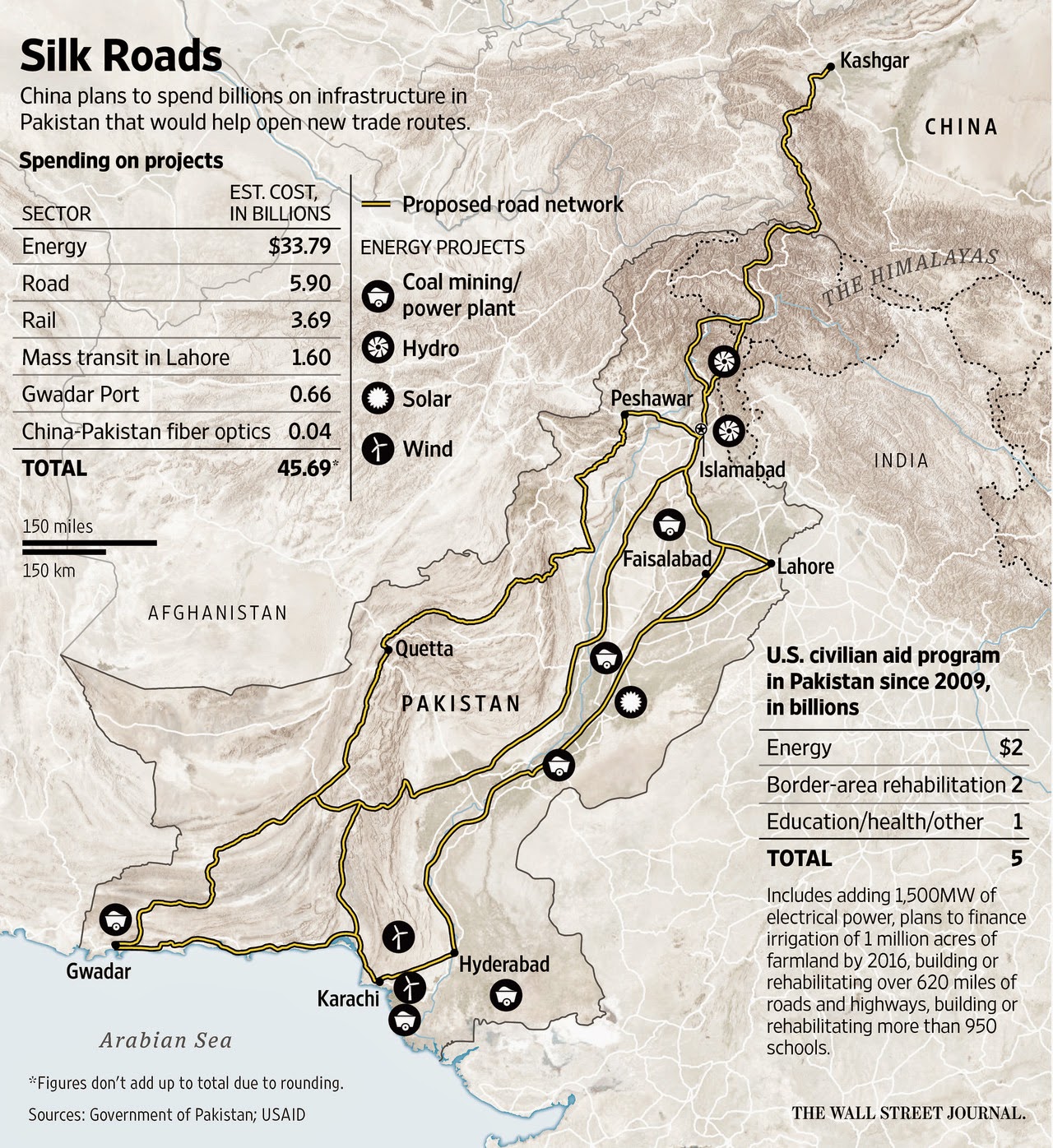
Can CPEC Make Pakistani Manufacturing More Competitive?
In addition to a basic sense of security, the cost of production and availability of required skills are essential for making manufacturing competitive. Cost has several components: labor cost and abundant, cheap energy and infrastructure. Skill comes from education and training infrastructure. Will CPEC (China-Pakistan Economic Corridor) help Pakistan achieve competitiveness on these fronts?
Abundant, Cheap Energy:
Costs rise dramatically if expensive plant and equipment are not fully utilized due to lack of gas and electricity. It is hard for a manufacturer to be competitive if its factories lie idle for many hours a day due to load-shedding as has been the case in Pakistan for many years.
Transport Infrastructure:
Manufacturers rely heavily on efficient supply chains. They need required parts delivered on time to continue to operate. Others who depend on their output need to have their orders filled on a just-in-time (JIT) basis. All of this not possible without reliable transport infrastructure over roads, rails, air and sea.
Skilled Labor:
Energy and infrastructure are necessary but not sufficient to be competitive. Availably of skilled labor is just as important. If the education and training infrastructure does not supply the required skills, then it's not possible for an economy to be competitive.
China Pakistan Economic Corridor:
Can China Pakistan Economic Corridor deliver energy, transport infrastructure and skilled labor to improve Pakistani economy's competitiveness? It appears that the first two will be in good shape after CPEC projects are completed. However, significant questions remain with regard to the education and vocational training infrastructure to build the required skilled labor pool.
Summary:
Abundant, cheap energy, transport infrastructure and availability of skilled labor are essential for improving Pakistan's manufacturing competitiveness. It appears that the first two will be in good shape after CPEC projects are completed. However, significant questions remain with regard to the education and training infrastructure to build the required skilled labor pool.
Related Links:
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 25, 2017 at 4:47pm
-
China has stopped being a low labor country many years ago, he noted, adding that Apple entered China because of the advancement of people's skills.
Tim Cook, CEO of Apple at the 2017 Fortune Global Forum /CGTN Photo
Talking about Apple's operations in China, Cook said the company holds 15 percent of the country's smartphone market, but noted that the focus is to produce the best products.
He also noted that there are two million app developers in China who are contributing to the app store, and "these are inspiring entrepreneurs."
Cook also attempted to set the record straight about the misconception that Apple products are "designed in California, and manufactured in China."
"The truth is the process engineering and process developments that are associated with our products require innovation itself, not only on the products the way it is made."
Cook also elaborated on the concept of humanity within the realm of technology, which he touched upon a couple of days ago at the fourth World Internet Conference.
He said Apple stands at the intersection of technology and liberal arts, with users at the center. He maintained that a great user experience should be the focus, and noted that in a world where tech can do anything, developers should put humanity at the center of their creations.
http://www.ecns.cn/voices/2017/12-07/283543.shtml
https://www.facebook.com/FortuneMagazine/videos/10155596353037949/
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 7, 2018 at 4:57pm
-
CPEC With Virtues Blessed Pakistan With Bountiful Harvest In 2017 [ANALYSIS]
http://www.valuewalk.com/2018/01/cpec-virtues-blessed-pakistan-boun...
Discussing the energy sector under CPEC, there were 16 projects prioritized with the total capacity of 10,400MW as well as 8 actively promoted projects. Year 2017 has witnessed the operationalization of 2x660MW Sahiwal Coal-Fired Power Plant, 50MW Dawood Wind Farm and 50MW Sachal Wind Farm. Near to completion are the 900MW Quaid-e-Azam Solar Park in Bahawalpur (90% work has been done) and 100MW Jhimpir Wind Farm. 2x660MW Port Qasim Coal-fired Power Plant, 4x330MW Engro Thar Coal-fired Power Plant and Surfice Mine in Block II of Thar Coal Field, 720MW Karot Hydro-Power Project, and 873MW Suki Kinari Hydropower Project are under construction.
Year 2017 has witnessed the seventy percent completion of the two infrastructure projects; KKH PhaseII(Havelian- Thakot Section),120 km, Karachi-Lahore Motorway (Sukkur-Multan Section),392 km. Rest of the infrastructure projects are working on their pace while the spine of the CPEC Railway Line ML-1’s complete feasibility report has been compiled up for the further progress. An efficient and fast transportation network is vital importance for the economic development.
In the area of industrial cooperation under CPEC, there are six projects under construction and year 2018 will be witnessing their destiny. China has advantages in experience, technology, financing and industrial capacity, while Pakistan enjoys favorable conditions in resources, labor forces and market. By carrying out industrial cooperation, both sides will achieve mutual complementarity and win-win results.
Year 2017 marked a landmark achievement for Pakistan as Federal Minister Ahsan Iqbal said that CPEC Long Term Plan would be public on 18th of December, 2017 which would further add the prospects for more inclusive research of this mega project. Simultaneously, there are bright prospects to jack up the developments in various sectors which include agriculture, information technology. This demonstrates the success of this meeting and the willingness of China to diversify its cooperation under the CPEC project. In this backdrop, the harmony between the provincial and federal governments is required and they should work enthusiastically for the inclusion of more projects under CPEC and to complete the ongoing projects. It can be hoped that the end result would be productive and the project will be able to proceed. The continuity of the meetings of Joint Cooperation Committee since 2013 to Nov 2017 shows the evaluation and progress of work on the ongoing projects under CPEC. 7th JCC has further deepened mutual cooperation between the two countries under the framework of CPEC and would pave a clear way for Pakistan to enter the phase of Industrial Cooperation.
----
CPEC has helped Pakistan to mitigate the chronic energy crises which have negative impacts on the economic growth of Pakistan. This energy shortage has hampered the industrial production and the businesses were closed down because of the interrupted supply of energy. CPEC project has played a significant role in this regard whereas WAPDA and KESC failed to resolve this problem of energy shortage. CPEC energy projects based on the wind, solar, coal and hydro power would create the generation of 16,400 MW.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 21, 2022 at 10:24am
-
Muneeb Sikander
@MuneebASikander
1/2 Pak Flood hit rural economyWork produces things of value and transforms physical world in ways to make life better and survival possible.
But without organised and purposeful productive action, i.e., work, not possible for most people asis at the base of economic order
https://twitter.com/MuneebASikander/status/1572606162939289601?s=20...----------------
2/2 Flood hit rural areas
Agrarian to agriculture/livestock based or limited workshop industry. Limited Agri TFP + 15.4 million at poverty risk
1. Need for agri TFP improvement
2., Need to diversify economic base by Proto-industrialization,https://www.stlouisfed.org/publications/regional-economist/second-q...
https://twitter.com/MuneebASikander/status/1572606221076819970?s=20...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 21, 2022 at 10:42am
-
How to Jump-Start Industrialization in Sub-Saharan Africa
May 27, 2021
By Yi Wen , Iris Arbogast
https://www.stlouisfed.org/publications/regional-economist/second-q...
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Most sub-Saharan nations have such low per capita incomes that it would take decades of double-digit growth to attain U.S. living standards.
Nations that industrialize successfully often begin with small-scale efforts and progress to mass-producing heavy industrial goods.
African countries could follow this development pattern with government-provided infrastructure and other support.
When considering income disparities across nations, the differences often can be striking, particularly for nations in the sub-Saharan region of Africa. Per capita income in many poor countries like these is 30 to 50 times smaller than in the U.S. In sub-Saharan Africa, 38 of 48 countries had gross national income (GNI) per capita levels below $2,300 in 2019, while GNI per capita was $65,850 in the U.S., according to data from the World Bank’s World Development Indicators database.
Generations of economists have studied economic development and given policy suggestions to officials in poor countries in Africa and elsewhere, but the disparities remain. To catch up to U.S. living standards, they would need to grow at about 11% per year for 40 to 50 years—an almost impossible standard that only China has come close to achieving in recent history.
The New Stage Theory of Development
The commonality between successful Asian countries’ industrialization (such as China’s rapid rise in the past 40 years) and successful European nations’ industrialization (such as the British Industrial Revolution in the 18th* and 19th centuries) is that these economies all went through three key stages during their industrialization, according to the New Stage Theory of Development (NST):1
Proto-industrialization, which features massive numbers of workshops in rural areas with small-scale production of basic consumer goods for long-distance trade
A first industrial revolution, which features mass production of labor-intensive, light consumer goods for domestic and international markets
A second industrial revolution, which features mass production of capital-intensive, heavy industrial goods
The first stage is very important but has been largely ignored by development economists. During this initial stage, rural farmers or poor households in urban areas use their free time to manufacture simple products and engage in long-distance trade. This raises their income and nurtures the formation of an increasingly unified market and primitive production networks, while developing entrepreneurship and labor skills. 2
During the second stage, large-scale factory systems become prevalent for light industries such as textiles, processed food, toys and furniture. This mass-production stage is labor-intensive, export oriented and benefits from poor countries’ comparative advantage in cheap labor. Mass production in the second stage is profitable only because proto-industrialization has created a large enough market and distribution networks for consumer goods.
Finally, the expansion of light industry in the second stage facilitates the formation of a large enough market for heavy industrial goods—such as means of transportation, energy, steel and heavy equipment. This is not only because the income of workers needs to be high enough to purchase big-ticket items such as automobiles, but because mass production of heavy industrial goods is profitable only after the second stage creates a mass-production chain to support their demand. 3
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on September 21, 2022 at 10:43am
-
How to Jump-Start Industrialization in Sub-Saharan Africa
May 27, 2021
By Yi Wen , Iris Arbogast
https://www.stlouisfed.org/publications/regional-economist/second-q...
In some newly emerging Asian economies, such as Vietnam and Bangladesh, about 30% of rural households were participating in nonfarm wage employment in the early- to mid-2000s (29% in 2002 in Vietnam and 35% in 2005 in Bangladesh). Rates of nonfarm wage employment in poor African countries, such as Ethiopia, Ghana, Malawi and Nigeria, remain between 5% and 18%.
In 2019, the GNI per capita in Bangladesh and Vietnam was $1,940 and $2,590, respectively. GNI per capita was $850 in Ethiopia, $2,220 in Ghana, $380 in Malawi and $2,030 in Nigeria. Although GNI per capita in Nigeria and Ghana is relatively high for the region, these economies are more dependent on income from oil and other natural resources than Bangladesh and Vietnam, according to data from the World Bank’s Development Indicators.
On the other hand, when China engaged in full-fledged proto-industrialization in the 1980s and kick-started its first industrial revolution around the early 1990s, the number of village workers as a fraction of the total rural labor force increased greatly. These workers went from 9% of the labor force in 1978 to 23% by 1988, and then increased to 30% by 2000.5
The Chinese experience in recent decades and the British industrial revolution in the 17th and 18th centuries imply that proto-industries must reach 40% to 50% of total agricultural value added—or about 25% to 30% of total rural labor force in their employment share—to spark a full-fledged first industrial revolution, or to render mass production of light consumer goods profitable and internationally competitive. 6
Based on this criterion, Vietnam and Bangladesh should possess the market conditions for supporting mass-production technologies in light industries like textiles. Indeed, these two countries are currently the largest clothing exporters after China, according to data from the World Trade Organization. But countries such as Ethiopia, Ghana, Malawi and Nigeria do not appear ready to support mass-production technologies in light industries, since their textile and clothing exports are very low.
Policy Implications for Africa
Based on the New Stage Theory of Development, we have a few policy suggestions for countries where rural manufacturing is not yet prevalent. Policymakers should provide every means possible to enhance proto-industrialization, which will help their countries embark on a healthy path of economic development.
The goal is to absorb as many rural households as possible into small-scale manufacturing workshops to increase their income and create a primitive supply chain and a disciplined labor force. This is one of the critical steps for nurturing a mass market to support full-fledged mass-production in light industries.
Governments should provide the necessary infrastructure and social capital to allow farmers to organize themselves into firms and send their goods to distant markets. Part of the income earned could be used to support government initiatives such as building local roads and canals, which reduce transportation costs and are a better use of resources than large projects like high-speed trains—which are better suited to the second industrial revolution stage.
Successfully creating proto-industrial supply chains, commercial distribution networks and competition between proto-industrial firms would eventually help give rise to large firms that mass produce light industrial goods such as textiles. A nation can also be more likely to attract large foreign firms that outsource their labor-intensive manufacturing industries by using subsidization policies such as providing ports, roads and free land as incentives.
* This article has been updated to correct the start of British industrialization.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 25, 2022 at 7:04pm
-
ADB CAREC Energy Report
https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/850111/carec-en...
Electricity Generation
Pakistan’s electricity sector has a total installed capacity of 34.5 GW, with thermal generation dominating
the power mix, having a share of 66% (National Transmission and Despatch Company 2020). Gas-fired
plants are the main source of power, having an installed capacity of almost 9.3 GW, while oil-fired power
plants have 6.5 GW installed capacity and coal-fired plants have 4.6 GW. Since the regulatory framework
allowed independent power producers to develop generation projects, multiple new thermal power
plants were constructed. As the country’s oil and natural gas reserves are diminishing, further growth in
alternative energy sources is needed.
Historically, hydropower was one of the main sources of electricity generation in Pakistan. The total
hydropower resource potential is estimated at 60 GW (Faizi 2020). However, with the expansion of
thermal power, its share in electricity has declined significantly and currently holds a 29% share of total
installed capacity. The country has 30 hydropower plants in operation, with a total installed capacity
of 9.9 GW, including 17 categorized as major hydropower and 13 as small hydropower units operating
mainly as a run-of-river units. The three main projects are Tarbela Dam (4.8 GW installed capacity),
Ghazi–Barotha (1.4 GW), and Mangla Dam (1.1 GW). Tarbela and Mangla dams, commissioned in the
1970s, are considered the main contributors to hydropower generation. To enhance the quality and
reliability of supply, Mangla Dam is planned for refurbishment, and Tarbela Dam for extension.
Pakistan’s first nuclear power plant, Karachi Nuclear Power Plant (KANUPP), began operations in 1970,
with a capacity of 100 megawatts (MW). Since then, nuclear power generation has experienced active
growth, and current capacity is 2.5 GW. Cross-country cooperation is a cornerstone of Pakistan’s strategy
to reach its goal of 8,800 MW of nuclear installed capacity by 2030. Currently, one new reactor of
1,100 MW is being built.
The country’s renewable energy potential has been realized to only a limited extent. The theoretical
potential of total wind energy is estimated at 340 GW, with the southern wind corridors being the most
auspicious—the Gharo–Keti Bandar wind corridor has over 50 GW of potential alone. However, only
around 1.1 GW of wind energy capacity is currently in operation. Likewise, solar power has tremendous
potential—as high as 2,900 GW, only about 0.4 GW of which is installed as of 2021. Although projects such
as the Quaid-e-Azam Solar Park (0.4 GW capacity) were successfully implemented, the lack of political
commitment, land availability, and the lower performance of outdated PV plants installed earlier are among
the reasons for limited development of renewable energy. Additional potential solutions include offshore
wind, floating solar PV in existing hydropower reservoirs, and wind farms near hydropower plants with
integration into existing grid infrastructure.
Power generation during fiscal year 2020 reached 121,691 GWh: 32% by hydroelectric plants, 57% by
thermal plants, 8% by nuclear plants, and 3% by renewable energy power plants.
Transmission and Distribution
Pakistan’s power T&D system is suffering from significant energy losses and disruptions. In 2020, 19.8%
of energy was lost during its transmission, distribution, and delivery to end consumers. Among the
10 distribution companies, losses vary greatly from 9% to 39% (NEPRA 2020). On average, the country
experienced 81 interruptions (system average interruption frequency index) lasting nearly 5,300 minutes
(system average interruption duration index) in 2020. The poor performance can be attributed to a
variety of factors, including poor technical conditions, insufficient collection rate of accounts receivable,
and issues with circular debt present in the country.
Pakistan had 7,470 kilometers (km) of 500 kilovolts (kV) and 11,281 km of 220 kV T&D lines in 2020.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 25, 2022 at 7:05pm
-
ADB CAREC Energy Report
https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/850111/carec-en...
Transmission and Distribution
Pakistan’s power T&D system is suffering from significant energy losses and disruptions. In 2020, 19.8%
of energy was lost during its transmission, distribution, and delivery to end consumers. Among the
10 distribution companies, losses vary greatly from 9% to 39% (NEPRA 2020). On average, the country
experienced 81 interruptions (system average interruption frequency index) lasting nearly 5,300 minutes
(system average interruption duration index) in 2020. The poor performance can be attributed to a
variety of factors, including poor technical conditions, insufficient collection rate of accounts receivable,
and issues with circular debt present in the country.
Pakistan had 7,470 kilometers (km) of 500 kilovolts (kV) and 11,281 km of 220 kV T&D lines in 2020.
Distribution companies are responsible for T&D activities below 132 kV. Importantly, only 74% of Pakistan’s
population is connected to the power grid. With high electricity losses and frequent outages, Pakistan is
planning to introduce advanced grid management infrastructure and metering. Advanced conductors and
other smart grid upgrades could help reduce T&D losses.
There are two operators in Pakistan’s natural gas T&D system: Sui Northern Gas Pipelines Limited
(SNGPL), covering the central and northern regions of the country; and Sui Southern Gas Company
Limited (SSGCL), covering the southern regions. Total grid losses accounted for nearly 17% by SSGCL and
11% by SNGPL in 2020. According to estimates, average leakage rate is 4.9 leaks per km for SSGCL, and
2.2 leaks per km for SNGPL (for comparison, this value equals 0.2 in Germany and 0.4 in Massachusetts, on
average). The gas pipeline systems require a major overhaul and modernization to increase the efficiency
of transportation and to reduce leakages.
Comment
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Can Pakistan's JF-17 Become Developing World's Most Widely Deployed Fighter Jet?
Worldwide demand for the JF-17 fighter jet, jointly developed by Pakistan Aeronautical Complex (PAC) and China’s Chengdu Aircraft Industry Group (CAIG), is surging. It is attracting buyers in Africa, Asia and the Middle East. At just $40 million a piece, it is a combat-proven flying machine with no western political strings attached. It has enormous potential as the lowest-cost 4.5…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on February 4, 2026 at 8:00pm
EU-India Trade Deal: "Uncapped" Mass Migration of Indians?
The European Union (EU) and India have recently agreed to a trade deal which includes an MOU to allow “an uncapped mobility for Indian students”, according to officials, allowing Indians greater ease to travel, study and work across EU states. India's largest and most valuable export to the world is its people who last year sent $135 billion in remittances to their home country. Going by the numbers, the Indian economy is a tiny fraction of the European Union economy. Indians make up 17.8%…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on January 28, 2026 at 11:00am — 10 Comments
© 2026 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network