In June 2007, the power cuts in Pakistan lasted no more than 3 or 4 hours a day. Today, in extremely hot weather, Pakistanis have to endure without electricity for 8 to 10 hours a day. Industrial production is suffering, exports are down, jobs are being lost, and the national economy is in a
downward spiral. By all indications, the power crisis in Pakistan is getting worse than ever.
Extended Load-shedding:
Extended electricity load shedding in Karachi's five major industrial estates is causing losses in billions of rupees as the production activity has fallen by about 50 per cent. KESC, Karachi's power supply utility, is dealing with with a shortfall of around 700MW against a total demand of 2200MW. Almost all forms of power generation from fossil fuel to hydroelectric to nuclear are down from a year ago. The economy, major exports and overall employment are also down and the daily wage earners are suffering. The government owes over Rs. 10b to the
independent power producers (IPPs) and paying them will help bring them into full operation and ease the crisis at least partially.
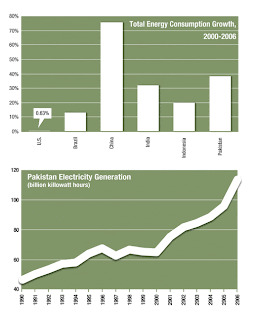 Electricity Demand:
Electricity Demand:
As discussed in an earlier
post, Pakistan's current installed capacity is around 19,845 MW, of which around 20% is hydroelectric. Much of the rest is thermal, fueled primarily by gas and oil.
Pakistan Electric Power Company PEPCO blames independent power producers (IPPs) for the electricity crisis, as they have been able to give PEPCO only 3,800 MW on average out of 5,800 MW of confirmed capacity. Most of the IPPs are running fuel stocks below the required minimum of 21 days. IPPs complain that they are not being paid on time by PEPCO.
Per capita energy consumption of the country is estimated at 14 million Btu, which is about the same as India's but only a fraction of other industrializing economies in the region such as Thailand and Malaysia, according to the US Dept of Energy 2006 report. To put it in perspective, the world average per capita energy use is about 65 million BTUs and the average American consumes 352 million BTUs. With 40% of the Pakistani households that have yet to receive electricity, and only 18% of the households that have access to pipeline gas, the energy sector is expected to play a critical role in economic and social development. With this growth comes higher energy consumption and stronger pressures on the country’s energy resources. At present, natural gas and oil supply the bulk (80 percent) of Pakistan’s energy needs. However, the consumption of those energy sources vastly exceeds the supply. For instance, Pakistan currently produces only 18.3 percent of the oil it consumes, fostering a dependency on imports and that places considerable strain on the country’s financial position. On the other hand, hydro, coal, wind and solar are perhaps underutilized and underdeveloped today, as Pakistan has ample potential to exploit these resources.
Gilani Government's Response:
Neelum-Jhelum hydroelectric project, first formally announced by former Minister Omar Ayub on June 10, 2007, is finally starting in earnest under the PPP government of Prime Minister Yousaf Raza Gilani. This hydro project is expected to add 963MW power generating capacity at a cost US $2.2 billion, according to Business Wire. Prior to this project, the new Pakistani Prime Minister signed a deal with a Chinese company, Dong Fong, for setting up 525 MW thermal power plant with an investment of $450 million at Chichoki Mallian (Sheikhupura). Both of these projects are expected help partially close the 3000 MW gap that exists today between supply and demand in Pakistan.
Renewable Energy Opportunities:
In response to the warnings of energy crisis in Pakistan, President Musharraf's government recognized the need and the potential for renewable alternatives and, in 2006, created Alternative Energy Development Board
to pursue renewable energy. In particular, AEDB is focusing on wind and solar as viable alternatives. AEDB is facilitating setting up of small renewable energy projects in line with government’s policy of promoting the use of renewable energy in the country’s power generation mix, says the board’s chief executive officer Mr Arif Alauddin. AEDB has recently issued Makwind Power Private Ltd (MPPL) a Letter of Intent for the setting up of 50MW wind farm at Nooriabad in Sindh, as part of its efforts to facilitate 700 MW wind energy by 2010.

According to data published by
Miriam Katz of Environmental Peace Review, Pakistan is fortunate to have something many other countries do not, which are high wind speeds near major centers. Near Islamabad, the wind speed is anywhere from 6.2 to 7.4 meters per second (between 13.8 and 16.5 miles per hour). Near Karachi, the range is between 6.2 and 6.9 (between 13.8 and 15.4 miles per hour). Pakistan is also fortunate that in neighboring India, the company
Suzlon manufactures wind turbines, thus decreasing transportation costs. Working with Suzlon, Pakistan can begin to build its own wind-turbine industry and create thousands of new jobs while solving its energy problems. Suzlon turbines start to turn at a speed of 3 meters per second. Vestas, which is one of the world's largest wind turbine manufacturers, has wind turbines that start turning at a speed of 4 meters per second. In addition to Karachi and Islamabad, there are other areas in Pakistan that receive a significant amount of wind.
In only the Balochistan and Sindh provinces, sufficient wind exists to power every coastal village in the country. There also exists a corridor between Gharo and Keti Bandar that alone could produce between 40,000 and 50,000 megawatts of electricity, says Ms. Katz who has studied and written about alternative energy potential in South Asia. Given this surplus potential, Pakistan has much to offer Asia with regards to wind energy. In recent years, the government has completed several projects to demonstrate that wind energy is viable in the country. In Mirpur Sakro, 85 micro turbines have been installed to power 356 homes. In Kund Malir, 40 turbines have been installed, which power 111 homes. The Alternative Energy Development Board (AEDB) has also acquired 18,000 acres for the installation of more wind turbines.
In addition to high wind speeds near major centers as well as the Gharo and Keti Bandar corridor, Pakistan is also very fortunate to have many rivers and lakes. Wind turbines that are situated in or near water enjoy an uninterrupted flow of wind, which virtually guarantees that power will be available all the time. Within towns and cities, wind speeds can often change quickly due to the presence of buildings and other structures, which can damage wind turbines. In addition, many people do not wish for turbines to be sited near cities because of noise, though these problems are often exaggerated. Wind turbines make less noise than an office and people comfortably carry on conversations while standing near them.

As is painfully evident in summers, Pakistan is an exceptionally sunny country. If 0.25% of Balochistan was covered with solar panels with an efficiency of 20%, enough electricity would be generated to cover all of Pakistani demand. In all provinces the
AEDB has created 100 solar homes in order to exploit solar energy.
Solar energy makes much sense for Pakistan for several reasons: firstly, 70% of the population lives in 50,000 villages that are very far away from the national grid, according to a report by the
Solar Energy Research Center (SERC). Connecting these villages to the national grid would be very costly, thus giving each house a solar panel would be cost efficient and would empower people both economically and socially.
Coal Power and Hydroelectricity
In addition to high winds and abundant solar potential, Pakistan has the fifth largest coal deposits in the world. The negative environmental effects of coal burning can be be mitigated by making use of the latest clean coal technologies that limit noxious gas exhaust into the atmosphere.

Pakistan also has some deposits of natural gas in the Potwar Plateau region and near the border between Balochistan and Sindh, but these are likely to disappear within 20 years.
Because of the presence of many rivers and lakes, it makes sense for Pakistan to build dams to support water management and electricity generation projects. However, it must be done with care to avoid damage to the environment or loss of farmland.
Financial and Policy Incentives
Despite the fact that Pakistan is so well endowed with wind and solar potential, only a few projects such as those mentioned above have been completed. One of the reasons why this has occurred is that Pakistan does not have major financial incentives available for those who want to install wind turbines or solar panels. Let us look at the case of India, Pakistan's neighbor. Despite having less potential for wind, India now has the world's fourth largest number of wind turbines installed at 7,093 MW, according to
India: Renewable Energy Market report. Ahead of India are Germany at 21,283 MW, Spain at 13,400 MW and the US at 12,934 MW. In Germany, Spain and India, those who install wind turbines and solar panels are guaranteed a certain rate per kilowatt hour. In India, this varies according to the technology and the area. The
Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, India reports that in most areas, between 2500 and 4800 rupees are guaranteed for solar panels, and for wind turbines, between 250,000 and 300,000 rupees are awarded.
Because of the above incentives, the cost of wind in India is between 2 and 2.5 cents per kilowatt hour while in Pakistan, the cost is 7 cents. In December 2006, President Musharraf announced a national renewable energy policy. This policy means that small projects do not need approval and that any person can put up their own project. However, there are no financial incentives for doing so. At the moment, all renewable energy equipment has no sales or income tax and is free of custom duty, but these incentives are not enough to stimulate major growth in the renewable energy market where ROIs and other financial ratios have a long gestation or breakeven period. In certain situations, such as the textiles and other Karachi industrial units losing production and export opportunities due to power cuts, it may make sense for the owners to join hands and build power generation capacity they can rely on.
Conclusion
In addition to coal and hydro electricity generation,
Miriam Katz argues that it is clear that Pakistan is a suitable country for the installation of wind and solar: due to high winds near cities; the presence of rivers and lakes as well as the availability of wind turbines from nearby India. There are also other reasons for installing renewable energy. It is quite normal for extended power outages to happen on a daily basis in the country, but this cannot continue if the Pakistani economy is to grow. In March 2007, President Musharraf stated that renewable energy should be part of the push to increase energy supplies by 10 to 12 percent every year. The government also set a target of 10 percent of energy to come from renewables by 2015. If the new PPP-led government follows through with aggressive renewable energy push, Pakistan could be an Asian leader in renewable energy given its natural resources of wind and solar as its strategic endowments.
Related Links:
Renewable Energy Businesses in Pakistan
Pakistan Council of Renewable Energy Technology
Pakistan Policy on Renewable Technology
Sugarcane Ethanol Project in Pakistan
Community Based Renewable Energy Project in Pakistan 




.jpg/_jcr_content/renditions/original)

You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network