PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
Even with the run-up (in KSE-100), Andrew Brudenell, manager of the HSBC Frontier
Markets fund (HSFAX) in London, says Pakistan is one of the cheapest
markets he follows, at about seven times earnings. He notes that
earnings growth has kept pace with the market. The firms, he adds, are
typically cash-rich, boast strong return on equity levels in the 20%
range, and pay good dividends. In Pakistan, the informal, cash-based economy for goods and services is larger than the formal economy. Barron's, November 17, 2012
Growing gap between dismal official economic statistics and consumption boom coupled with strong corporate profits in Pakistan is a challenge for many analysts around the world. Most believe that Pakistan's GDP is, in fact, much larger and growing faster than the government data indicates.
Informal Economy Estimates:
M. Ali Kemal and Ahmed Waqar Qasim, economists at Pakistan Institute of Development Economics (PIDE), have published their research on estimates of the size of Pakistan's informal or underground economy.
Kemal and Qasim explore several published different approaches for sizing Pakistan's underground economy and settle on a combination of PSLM (Pakistan Social and Living Standards Measurement) consumption data and mis-invoicing of exports and imports to conclude that the country's "informal economy was 91% of the formal economy in 2007-08". Here are the figures offered by the authors for 2007-8:
1) Formal Economy: Rs. 10,242 billion= $170 billion (using Rs.60 to a US dollar)
2) Informal Economy: Rs. 9,365 billion = $156 billion
3) Total Economy (Sum of 1 & 2): Rs. 19,608 billion = $326 billion
Assuming that the ratio of formal and informal economy remained the same in 2011-12, here are the figures for Pakistan's total economy as of the end of last fiscal year which ended in June, 2012 :
1) Formal Economy: $210 billion
2) Informal Economy: $191 billion
3) Total Economy: $401 billion
 |
| Hypermart Lahore |
Naween Mangi of Businessweek in her piece titled "The Secret Strength of Pakistan's Economy" described how Pakistan's informal cash-based economy evades government's radar, illustrating it with the story
of a tire repair shop owner Muhammad Nasir. Nasir steals water and
electricity from utility companies, receives cash from his customers in
return for his services and issues no receipts, pays cash for his cable
TV connection, and pays off corrupt police and utility officials and
local politicians instead of paying utility bills and taxes.
Karachi Stock Market:
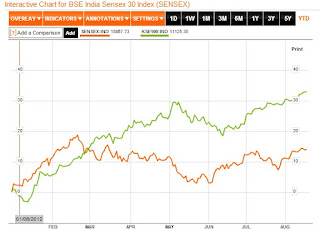 |
| Comparing Karachi and Mumbai Share Indexes |
A string of strong earnings announcements by Karachi Stock Exchange
listed companies and the Central Bank's 1.5% rate cut have helped the KSE-100 index exceed 16,000 level, a gain of 42.1% (33.2% in US dollar terms) year to date. In spite of this run-up in KSE-100, Andrew Brudenell, manager of the HSBC Frontier
Markets fund (HSFAX) in London, remains bullish on Pakistani equities, according to Barron's. Pakistan is one of the cheapest
markets he follows, at about seven times earnings. He notes that
earnings growth has kept pace with the market. The firms, he adds, are
typically cash-rich, boast strong return on equity levels in the 20%
range, and pay good dividends.
Conclusion:
While Pakistan's public finances remain shaky, it appears that the country's economy is in fact healthier than what the official figures show. It also seems that the national debt is much less of a problem given the debt-to-GDP ratio of just 30% when informal economy is fully comprehended. Even a small but serious effort to collect more taxes can make a big dent in budget deficits. My hope is that increasing share of the informal economy will become documented with the rising use
of technology. Bringing a small slice of it in the tax net will make a
significant positive difference for public finances in the coming years.
Related Links:
Haq's Musings
Investment Analysts Bullish on Pakistan
Precise Estimates of Pakistan's Informal Economy
Pak Consumer Boom Fuels Underground Economy
Rural Consumption Boom in Pakistan
Pakistan's Tax Evasion Fosters Aid Dependence
Poll Finds Pakistanis Happier Than Neighbors
Pakistan's Rural Economy Booming
Pakistan Car Sales Up 61%
Resilient Pakistan Defies Doomsayers
Land For Landless Women in Pakistan
Pakistan's Circular Debt and Load-shedding
Hypermart Pakistan


Riaz Haq
Although Pakistani startups posted a 36% decline in third quarter (July-September) of calendar year 2022 compared to the previous quarter, the financial technology (fintech) showed rising graph during the same period.
https://www.nation.com.pk/10-Nov-2022/unbanked-population-helping-p...
According to the data of Invest2Innovate (i2i), a startups consultancy firm, six out of the 14 deals that took place in Q3 2022 were fintech startups, compared to two deals of e-commerce startups. Fintech startups raised $38 million which is 58% of total funding ($65 million) in Q3 2022, compared to e-commerce startups that raised 19% of total funding. The i2i data shows that in Q3 2022, fintech raised 37.1% higher than what it raised in Q2 2022 ($27.7 million). Similarly, in Q2 2022, the total investment of fintech was 63% higher compared to what it raised in Q1 2022 ($17 million).
Sumbal Qureshi, a fintech consultant, told WealthPK that political situation has an impact on the economic situation of the country due to which a lot of foreign fintech companies have held back their initiatives. This situation is also a challenge for local fintech firms. The unusual growth is just because the existing fintechs and more established companies are trying to survive at the moment. They are trying to overcome the situation by continuing to invest in the fintech sector.
Imran Jattala, a well-known IT expert, told WealthPK that 5% of the world’s unbanked population lives in Pakistan. About 18,000 people are crossing the age of 18 every day in Pakistan, and unbanked population and those under 18 use fintech for their financial affairs. So fintech and digital banking is going to thrive despite a decrease in startup funding.
According to data of Pakistan Telecommunication Authority (PTA), over the years, branchless/mobile banking has shown tremendous growth based on the telco-banks-fintech nexus, contributing significantly to financial inclusion. The m-banking network has expanded to over 534,460 m-banking agents and 74.6 million m-wallet accounts. This network enabled more than 2.2 billion annual transactions worth over Rs8 trillion in 2021. Despite these developments, cash still dominates economic activities and there is scant use of electronic payments, especially by micro and small retailers. Cash is the predominant payment method in Pakistan as it is considered ‘safe’ by the majority of retailers and suppliers. Many wages and salaries are also paid through cash.
The importance and usage of electronic banking and alternative delivery channels has increased during the post-Covid-19 period. Realising this, the State Bank of Pakistan further incentivised the use of digital financial channels by instructing banks to waive all inter-bank and intra-bank charges on digital transactions. This resulted in a substantial annual increase of 206% in inter-bank transfers and 122% in intra-bank transfers through internet banking. For mobile banking, the impact was even higher, with a three-fold increase in mobile banking inter-bank transfers from Rs765 billion in FY 2020 to Rs2.346 trillion in FY 2021.
Dec 30, 2022
Riaz Haq
How Informal Sector Affects the Formal Economy in Pakistan? A Lesson for Developing Countries
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/2277978719898975
There have been multiple estimates for the informal sector of Pakistan (Ahmed & Ahmed, 1995; Ahmed & Hussain, 2008; Arby et al., 2010; Aslam, 1998; Gulzar, Junaid, & Haider, 2010; Iqbal, Qureshi, & Mahmood, 1998; Kemal, 2003; Kemal, 2007; Kemal & Qasim, 2012; Kiani, Ahmed, & Zaman, 2015; Mughal, Schneider, & Hayat, 2018; Shabsigh, 1995; Yasmin & Rauf, 2003), yet most of the studies are limited to measuring the informal sector only. However, Shabsigh (1995) explored the relationship between fiscal deficit and informal sector, while Yasmin and Rauf (2003) and Kemal (2007) attempted to explore the nexus between informal and formal sectors. The estimates of the first author were based on simple ordinary least squares (OLS) without accounting for cointegration among variables. On the other hand, Kemal (2007) used vector autoregression (VAR), and his results showed unidirectional causality from informal sector to nominal GDP. Further, they used Johansen Cointegration test and Error correction model to conclude that shadow economy has a positive effect on the formal sector in short- as well as long run. We, however, argue that the effect of the informal sector on official economy may be of asymmetric in nature in the long and short run, emanating from two contrasting propositions:
1.
First, the informal sector, being more dynamic and extensive, is considered a safe haven for informal employment and production activities stemming from its capacity to avoid the bureaucracy and legalities. This may be supporting the economic activity in the long run when the income and savings from the informal sector are spent on consumption goods being produced by the formal economy. Furthermore, countries with relatively high incidence of poverty and weak social welfare institutions may use the informal sector as a substitute for social security.
2.
On the contrary, informality is a burden on exchequer, particularly when it comes to revenue collection in the short run; hence, it restrains the formal economic activity by raising the cost of being formal; that is, taxpayers have to bear the cost of tax evaders. Lower tax collection implies less expenditure on public utilities and lower productivity and economic growth.
The above contrasting propositions also seek strength from Khan, Khwaja, and Olken (2015) who used an experimental study on performance-based incentives to tax officials in Pakistan. Although they showed that the tax revenue increased, however, bribe requests also increased by 30 per cent, which depicts a clear burden on economic growth in the short run. Therefore, we hypothesize that the informal sector may affect the formal economy positively in the long run and negatively in the short run.
Dec 31, 2022
Riaz Haq
Pakistan’s Real Economy Is Near $1 Trillion, Says Finance Minister Aurangzeb
https://propakistani.pk/2025/10/10/pakistans-real-economy-is-near-1...
Speaking at a business session organized for the visiting Saudi business delegation at the Overseas Investors Chamber of Commerce and Industry (OICCI) in Karachi, Aurangzeb said the Prime Minister is personally leading two key reform tracks — tax reforms and Pakistan’s digital transformation toward a cashless economy.
“Pakistan’s recorded economy stands at US$411 billion, but nearly half remains undocumented,” the minister said. “The real size of our economy is closer to a trillion dollars.”
He added that digitization and documentation would be pivotal in broadening the tax base and improving fiscal stability.
Aurangzeb reaffirmed that Pakistan’s economic growth must be driven by the private sector, with the government providing an enabling ecosystem for business and investment. He said macroeconomic stability had been restored, with all three major global rating agencies aligned for the first time in several years.
Referring briefly to the recently approved Pakistan–Saudi Arabia Security Pact, the minister said the agreement reflects growing confidence between the two countries and paves the way for deeper economic collaboration.
He also noted that Pakistan is in a constructive phase of talks with the IMF, with only a few pending matters before a likely staff-level agreement in Washington.
Aurangzeb said the government is focused on converting stabilization into growth by promoting exports, improving energy efficiency, and accelerating digital transformation. “We are now in a phase where reform, documentation, and investment must go hand in hand,” he remarked.
on Sunday