PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
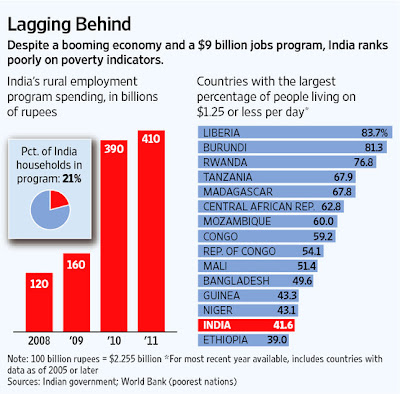
World Bank Finds Indians Poorer Than Pakistanis
A new multi-dimensional measure of poverty confirms that there is grinding poverty in resurgent India. It highlights the fact that just eight Indian states account for more poor people than the 26 poorest African countries combined, according to media reports. The Indian states, including Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh , Orissa, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal, have 421 million "poor" people, compared to 410 million poor in the poorest African countries.

Developed at Oxford University, the Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) goes beyond income poverty based on $1.25 or $2 a day income levels. It measures a range of "deprivations" at household levels, such as schooling, nutrition, and access to health, clean water, electricity and sanitation. According to Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI) country briefings 2010, 55% of Indians and 51% of Pakistanis are poor.

OPHI 2010 country briefings on India and Pakistan contain the following comparisons of multi-dimensional (MPI) and income poverty figures:
India
MPI= 55%,Under$1.25=42%,Under$2=76%,India_BPL=29%
Pakistan
MPI=51%,Under$1.25=23%,Under$2=60%,Pakistan_BPL=33%
Lesotho MPI=48%,Under$1.25=43%,Under$2=62%,Lesotho_BPL=68%
Haiti MPI=57%,Under$1.25=55%,Under$2=72%,Haiti_BPL=NA
China
MPI=12%,Under$1.25=16%,Under$2=36%,China_BPL=3%
Among other South Asian nations, MPI index measures poverty in Bangladesh at 58 per cent and 65 per cent in Nepal.
 |
| Source: Where Are the Poor and Where Are the Poorest? |
While OPHI's MPI is a significant improvement over the simplistic income level criterion for assessing poverty, it appears that the MPI index gives nearly three quarters of the weight to child mortality and school enrollment, and just over a quarter of the weight to a combination of critical factors such as access to electricity, sanitation and clean drinking water which are essential for proper learning environment, increased human productivity and healthy living.
South Asians face a massive challenge in overcoming pervasive poverty that makes the region look worse than the poorest of the poor nations of sub-Saharan Africa.
Just think about the South Asian situation in terms of Maslow's hierarchy of needs. Over 76% of Indians and 60% of Pakistanis living on less than $2 a day are busy struggling at the bottom of the pyramid to satisfy their basic physiological needs. They have no time or to think about freedom and democracy which belong near the top of Maslow's pyramid. It will take a lot more than the usual rhetoric of freedom, democracy and human rights to help them. It will take serious and focused effort to improve their situation through better governance and greater spending on human development. Real progress will not happen as long as South Asians hang the petty thieves and elect great ones to high offices.
Here is a video clip about grinding poverty in resurgent India:
Related Links:
Haq's Musings
South Asia Slipping in Human Development
OPHI Country Briefing: Pakistan
OPHI Country Briefing: India
Slumdog Inspires India's "Big Switch"
Mumbai's Slumdog Millionaire
Poverty Tours in India, Brazil and South Africa
South Asia's War on Hunger Takes Back Seat
British TV Accused of Making "Poverty Porn"
Orangi is Not Dharavi
Bollywood and Hollywood Mix Up Combos
Grinding Poverty in Resurgent India
Slumdog Is No Hit in India
Pakistani Children's Plight
UNESCO Education For All Report 2010
India's Arms Build-up: Guns Versus Bread
South Asia Slipping in Human Development
World Hunger Index 2009
Challenges of 2010-2020 in South Asia
India and Pakistan Contrasted 2010
Food, Clothing and Shelter in India and Pakistan
Introduction to Defense Economics
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on April 19, 2013 at 10:48am
-
Here's an excerpt of a World Bank report released recently:
while the extreme poor in SSA represented only 11 percent of the world’s total in 1981, they now account for more than a third of the world’s extreme poor (figure 3). India contributes another third (up from 22 percent in 1981) and China comes next contributing 13 percent (down from 43 percent in 1981).
http://www.worldbank.org/content/dam/Worldbank/document/State_of_th...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 5, 2013 at 7:16pm
-
Here's The Economist on ending poverty:
IN HIS inaugural address in 1949 Harry Truman said that “more than half the people in the world are living in conditions approaching misery. For the first time in history, humanity possesses the knowledge and skill to relieve the suffering of those people.” It has taken much longer than Truman hoped, but the world has lately been making extraordinary progress in lifting people out of extreme poverty. Between 1990 and 2010, their number fell by half as a share of the total population in developing countries, from 43% to 21%—a reduction of almost 1 billion people.
--------
Starting this week and continuing over the next year or so, the UN’s usual Who’s Who of politicians and officials from governments and international agencies will meet to draw up a new list of targets to replace the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), which were set in September 2000 and expire in 2015. Governments should adopt as their main new goal the aim of reducing by another billion the number of people in extreme poverty by 2030.Nobody in the developed world comes remotely close to the poverty level that $1.25 a day represents. America’s poverty line is $63 a day for a family of four. In the richer parts of the emerging world $4 a day is the poverty barrier. But poverty’s scourge is fiercest below $1.25 (the average of the 15 poorest countries’ own poverty lines, measured in 2005 dollars and adjusted for differences in purchasing power): people below that level live lives that are poor, nasty, brutish and short. They lack not just education, health care, proper clothing and shelter—which most people in most of the world take for granted—but even enough food for physical and mental health. Raising people above that level of wretchedness is not a sufficient ambition for a prosperous planet, but it is a necessary one.
The world’s achievement in the field of poverty reduction is, by almost any measure, impressive. Although many of the original MDGs—such as cutting maternal mortality by three-quarters and child mortality by two-thirds—will not be met, the aim of halving global poverty between 1990 and 2015 was achieved five years early.
The MDGs may have helped marginally, by creating a yardstick for measuring progress, and by focusing minds on the evil of poverty. Most of the credit, however, must go to capitalism and free trade, for they enable economies to grow—and it was growth, principally, that has eased destitution.
Poverty rates started to collapse towards the end of the 20th century largely because developing-country growth accelerated, from an average annual rate of 4.3% in 1960-2000 to 6% in 2000-10. Around two-thirds of poverty reduction within a country comes from growth. Greater equality also helps, contributing the other third. A 1% increase in incomes in the most unequal countries produces a mere 0.6% reduction in poverty; in the most equal countries, it yields a 4.3% cut.
China (which has never shown any interest in MDGs) is responsible for three-quarters of the achievement. Its economy has been growing so fast that, even though inequality is rising fast, extreme poverty is disappearing. China pulled 680m people out of misery in 1981-2010, and reduced its extreme-poverty rate from 84% in 1980 to 10% now.
That is one reason why (as the briefing explains) it will be harder to take a billion more people out of extreme poverty in the next 20 years than it was to take almost a billion out in the past 20. Poorer governance in India and Africa, the next two targets, means that China’s experience is unlikely to be swiftly replicated there......
http://www.economist.com/news/leaders/21578665-nearly-1-billion-peo...
Comment
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Pakistani International Students Flocking to European Universities
Recent data shows that there are nearly 10,000 Pakistani students attending colleges and universities in Germany. This figure is second only to the United Kingdom which issued over 35,000 student visas to Pakistanis in 2024. The second most popular destination for Pakistani students is Australia which is hosting nearly 24,000 students from Pakistan as of 2023, according to the ICEF…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on July 15, 2025 at 9:00am
Pakistani Prosthetics Startup Aiding Gaza's Child Amputees
While the Israeli weapons supplied by the "civilized" West are destroying the lives and limbs of thousands of Gaza's innocent children, a Pakistani startup is trying to provide them with free custom-made prostheses, according to media reports. The Karachi-based startup Bioniks was founded in 2016 and has sold prosthetics that use AI and 3D scanning for custom designs. …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on July 8, 2025 at 9:30pm
© 2025 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network