PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
Why Does India Lag So Far Behind China?
Indian mainstream media headlines suggest that Pakistan's current troubles are becoming a cause for celebration and smugness across the border. Hindu Nationalists, in particular, are singing the praises of Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi and some Pakistani analysts have joined this chorus. This display of triumphalism and effusive praise of India beg the following questions: Why are Indians so obsessed with Pakistan? Why do Indians choose to compare themselves with much smaller Pakistan rather than to their peer China? Why does India lag so far behind China when the two countries are equal in terms of population and number of consumers, the main draw for investors worldwide? Obviously, comparison with China does not reflect well on Hindu Nationalists because it deflates their bubble.
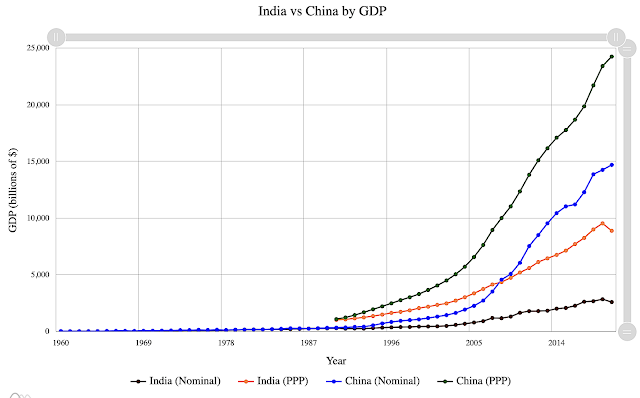 |
| Comparing China and India GDPs. Source: Statistics Times |
 |
| Top Patent Filing Nations in 2021. Source: WIPO.Int |
 |
| India's Weighting in MSCI EM Index Smaller Than Taiwan's. Source: N... |
The US Commerce Department is actively promoting India Inc to become an alternative to China in the West's global supply chain. US Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo recently told Jim Cramer on CNBC’s “Mad Money” that she will visit India in March with a handful of U.S. CEOs to discuss an alliance between the two nations on manufacturing semiconductor chips. “It’s a large population. (A) lot of workers, skilled workers, English speakers, a democratic country, rule of law,” she said.
India's unsettled land border with China will most likely continue to be a source of growing tension that could easily escalate into a broader, more intense war, as New Delhi is seen by Beijing as aligning itself with Washington.
In a recent Op Ed in Global Times, considered a mouthpiece of the Beijing government, Professor Guo Bingyun has warned New Delhi that India "will be the biggest victim" of the US proxy war against China. Below is a quote from it:
"Inducing some countries to become US' proxies has been Washington's tactic to maintain its world hegemony since the end of WWII. It does not care about the gains and losses of these proxies. The Russia-Ukraine conflict is a proxy war instigated by the US. The US ignores Ukraine's ultimate fate, but by doing so, the US can realize the expansion of NATO, further control the EU, erode the strategic advantages of Western European countries in climate politics and safeguard the interests of US energy groups. It is killing four birds with one stone......If another armed conflict between China and India over the border issue breaks out, the US and its allies will be the biggest beneficiaries, while India will be the biggest victim. Since the Cold War, proxies have always been the biggest victims in the end".
Related Links:
Do Indian Aircraft Carriers Pose a Threat to Pakistan's Security?
Can Washington Trust Modi as a Key Ally Against China?
Ukraine Resists Russia Alone: A Tale of West's Broken Promises
Ukraine's Lesson For Pakistan: Never Give Up Nuclear Weapons
AUKUS: An Anglo Alliance Against China?
Russia Sanction: India Profiting From Selling Russian Oil
Indian Diplomat on Pakistan's "Resilience", "Strategic CPEC"
Vast Majority of Indians Believe Nuclear War Against Pakistan is "W...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 8, 2023 at 8:25am
-
Chris Kay
@christopherkay
The more India tries to ramp up production, the more it depends on China for components and raw materials, report
@vrishtibeniwal
https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2023-06-08/modi-s-make-in-i...
https://twitter.com/christopherkay/status/1666641446869544960?s=20
----------------
Fun Zoo Toys is an Indian manufacturing success story. The maker of heart-shaped cushions and “Little Ganesha” dolls started out as a family business in 1979 and has grown to be one of the nation’s major manufacturers of fluffy toys.
Sales doubled after Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Made-in-India push saw import duties on toys ramped up from 20% to 70% over three years to 2023. But that’s just half of the story: the production surge to meet those sales wouldn’t have been possible without raw materials like metallic pins, integrated circuits and LEDs imported from China.
--------------
The Make in India dream keeps colliding with the Chinese reality
Read more at:
https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/policy/the-make-i...
Last month, External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar said Indian businesses need to stop looking for a "China fix", while terming the Make in India programme a strategic statement to spur the country's manufacturing.
Jaishankar was voicing the general sentiment that China's cheap imports de-industrialise India, take away millions of jobs and keep it dependent on China, therefore India's trade imbalance with China calls for more local manufacturing. India's trade gap with China widened to $83.2 billion in the last fiscal as against $72.91 billion in 2021-22. Exports to China dipped by about 28 per cent to $15.32 billion in 2022-23, while imports rose by 4.16 per cent to $98.51 billion in the last fiscal.
The solar dilemma
India's solar industry is an example of how India faces a complex challenge to fulfill its Make in India ambition. India might cut its import duties on solar panels to half, Reuters has reported recently. The renewable energy ministry has held talks with the finance ministry to approve its request to cut the import tax on solar panels from 40% to 20%,
India's nascent solar modules industry, which has been growing in the shelter of high tariffs, dread such a steep cut in import duties. The duty cut will deliver a blow to India's ambition of quickly expanding local production.
But local plants can’t keep up with rising demand and India must import solar modules to fill the gap. India is aiming to install 280 gigawatts of solar generation by 2030, compared to about 64 gigawatts now, as it overhauls its coal-dominated power grid, according to news agency Blomberg. That would require the addition of 27 gigawatts of capacity every year for the rest of the decade — more than double the volume installed last year.
While its local industry can't meet the rising demand, India must import more solar modules. But that imperils its nascent domestic industry which must grow to support the solar energy targets. “Such volatile changes in government policy show that businesses can’t be dependent on policy support,” Vinay Rustagi, MD at Bridge To India, a renewable energy consulting firm, told Bloomberg recently. “It’s a dampener for domestic manufacturing prospects.”
The China conundrum
Even when India tries to become more self-reliant by increasing local manufacturing capacity, it still has to depend on China for critical intermediate inputs. Take the case of Apple's iPhones made in India by Tata. Almost 90% components used for Apple phones by Tata are sourced from Mainland China, even as Apple looks to shift manufacturing to India, ET has reported recently. Items such as brackets, industrial glues, screws, mesh, pressure sensitive adhesives and metal parts are all shipped from China as per Apple’s instructions.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 8, 2023 at 8:26am
-
The Make in India dream keeps colliding with the Chinese reality
The China conundrum
Even when India tries to become more self-reliant by increasing local manufacturing capacity, it still has to depend on China for critical intermediate inputs. Take the case of Apple's iPhones made in India by Tata. Almost 90% components used for Apple phones by Tata are sourced from Mainland China, even as Apple looks to shift manufacturing to India, ET has reported recently. Items such as brackets, industrial glues, screws, mesh, pressure sensitive adhesives and metal parts are all shipped from China as per Apple’s instructions.
Only Apple’s old-time vendors such as Foxconn, Pegatron and Wistron manufacture “end-to-end” phones in India. In FY23, India accounted for 5% of iPhone’s total global production and exported phones worth $5 billion, a near four-fold surge compared with a year ago.
Localisation of manufacturing, the domestic value addition, however, can't happen before manufacturing achieves critical mass. Till then, India will have to depend on China for imports of intermediate goods. If you add to it the import of finished items where India cannot compromise growth, such as in the solar sector, it indicates a heavy reliance on China. It means India's project to become self-reliant in manufacturing must depend on imports from China, at least initially.
Many electric two-wheeler companies cornering subsidies, aimed at promoting domestic manufacturing to meet the ambitious green mobility goals, from the government without fulfilling the localisation requirements is a case in point. Many parts are imported from China due to lack of sufficient local manufacturing.
What are the prospects?
Global supply chains are not easy to shift from countries where they got embedded in a vast local manufacturing ecosystem. The countries trying to do that must develop comparable ecosystems which can't happen overnight. Meanwhile, they will have to depend on imports from China. Tariffs alone can't help local industries.
But India's concerted push for self-reliance in manufacturing, powered by hefty production-linked incentives, is not without results. India's imports of electronic goods such as laptops, personal computers, integrated circuits and solar cells from China declined during 2022-23, according to a report by economic think tank Global Trade Research Initiative (GTRI). The fall in imports is notable in electronic items where the incentives scheme is operational. Import of medical equipment declined 13.6 per cent to $2.2 billion last fiscal year as compared to 2021-22. Similarly, import of solar cells, parts, diodes slumped 70.9 per cent to $1.9 billion in 2022-23.
However, import of lithium-ion batteries surged about 96 per cent to $2.2 billion last fiscal year. India's green mobility goals will only increase these imports steeply. For India to keep its growth steady, meet its energy goals and expand its manufacturing base, the Make in India must be supported by Make in China.
Read more at:
https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/policy/the-make-i...
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 11, 2023 at 12:19pm
-
‘Things not going well’: Six die in #India within months. The deaths have led to criticisms of Project #Cheetah, a £4.8m international scheme that involved moving 20 animals from #Africa to India’s Kuno National Park earlier this year. #Modi #BJP
https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2023/jun/11/things-not-goin...
A controversial attempt to reintroduce cheetahs to the wild has suffered a major setback after three adults and three cubs died over the past eight months.
The deaths have led to criticisms of Project Cheetah, a £4.8m international scheme that involved moving 20 animals from Africa to India’s Kuno National Park earlier this year. Some conservationists say not enough space was reserved for the cheetahs while others complained that the project was set up too hastily.
However, project scientists insisted that several fatalities were to be expected at the start of the project, and forecast that the death toll would stabilise in the near future.
“If you are going to reintroduce an animal to the wild, you have to do it very carefully,” said Professor Sarah Durant, of the Zoological Society of London. “And it is clear that things are not going well. The programme seems rushed.”
Cheetahs are the world’s fastest land animals and can run at speeds of up to 65mph. There are five subspecies and all have suffered major drops in numbers caused by climate change, hunting by humans and habitat destruction. As a result, surviving populations of East African, South African and Northeast African cheetahs are now vulnerable, according to the International Union for the Conservation of Nature. The other two – the Northwest African cheetah and the Asiatic cheetah – are critically endangered.
India’s own population of cheetahs – made up of the Asiatic subspecies – was wiped out last century, with the last documented native animals being shot by Maharajah Ramanuj Singh Deo in 1947. The Asian cheetah now survives only in Iran.
By contrast, there are about 6,500 African cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus), and there have been successes in restoring numbers in semi-managed wildlife reserves in South Africa. With the eradication of its own cheetahs, India launched efforts to re-establish a population using the Southern African cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus jubatus). However, these moves were blocked, initially, by the Indian supreme court, where it was argued that because it was not a native species, its introduction broke international conservation regulations.
In 2020, the court’s ruling was overturned and Project Cheetah was launched with considerable fanfare, including support from the Indian prime minister, Narendra Modi. The first animals – eight cheetahs that had been relocated from Namibia – arrived at Kuno last September, and 12 more were moved from South Africa in February.
However, by late May this year, three of the Kuno cheetahs and three newborn cubs had died . Two adults succumbed to organ failure and a third was killed in a violent mating encounter. The cause of the deaths of the cubs is unclear at present. While cubs in the wild have poor survival rates owing to predation from lions and hyenas, those born in protected reserves have high survival rates.
The deaths of the three adults were not unexpected given the high stress of relocation, said Adrian Tordiffe, a veterinarian at South Africa’s University of Pretoria and a consultant for the project, in the journal Nature. “The fact that we had multiple deaths occurring in a short space of time is not unusual in the sense that it’s the high-risk period. Once things stabilise, that will plateau.”
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 23, 2023 at 11:30am
-
See new Tweets
Conversation
Derek J. Grossman
@DerekJGrossman
Me: "What the US is really looking for is access to India, in the case of a conflict against China. The hope is that over time, as we continue our security cooperation, India will kind of bend a little bit, to be more flexible and maybe allow us access...
https://twitter.com/DerekJGrossman/status/1672282612554162176?s=20
Why the US is selling India so many weapons
Prime Minister Modi visits the White House, and arms deals follow.
By Jonathan Guyer
https://www.vox.com/world-politics/2023/6/23/23770369/why-us-sellin...
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi arrived in Washington for a state visit this week. Beyond the black-tie dinner at the White House and a speech to Congress, there have been a lot of arms deals.
Jets, drones, cyber capabilities, and more.
It’s a significant list, and builds on an expanding military partnership. The US has partnered with India more and more in response to China’s rise, seeing New Delhi as a valuable counterweight. This is happening as India advances grievous human rights abuses against minorities, against journalists, and against political critics — all in contradiction of America’s stated values.
And yet this week, the White House is promoting a “next generation defense partnership” with India. This includes the co-production of cutting-edge technologies like jet engines and semiconductors, the prospect of new arms sales, and agreements that would allow the US to have its navy ships repaired in India. The country will also purchase 31 advanced drones from General Atomics in a deal that will cost some $3 billion. And the Pentagon and the Indian Ministry of Defense have established a new military-tech incubator called INDUS-X.
Experts point out that India under Modi increasingly does not share American values, and some of the advanced military technologies that the US is providing the country could be used against dissidents or journalists.
“If we’re just going to go full-on countering China with India as a realist approach to things, that can come back and bite us,” says Derek Grossman, a defense analyst at the RAND Corporation. “Because, as we saw during the Cold War, a lot of the dictators or semi-authoritarian regimes that we cozied up with, they were not our friends in the long run.”
US-India defense cooperation, very briefly explained
India built a relationship with the Soviet Union during the Cold War, and to this day, most of the Indian military’s weapons come from Russia. It wasn’t until the mid-2000s that India started buying arms from the United States, growing from around nothing in 2008 to $8 billion of US sales to the country by 2013, and to $20 billion in 2020.
Now, the new agreements will help create capacities for India as an arms producer. The Pentagon’s top Asia official, Ely Ratner, says the US was helping modernize the Indian military. The US Embassy in New Delhi described an initiative to “fast-track technology cooperation and co-production in areas such as air combat and land mobility systems, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance, munitions, and the undersea domain.”
India wants to manufacture military and aerospace products. In this respect, the prospective General Electric engine deal represents a major change. Export controls and trade regulations have previously been a challenge for forging advanced production lines in India. “Engine technology is pretty sensitive,” says Vikram Singh of the United States Institute of Peace and the consulting firm WestExec Advisors. “This is a big, ambitious agenda.”
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 23, 2023 at 11:31am
-
Why the US is selling India so many weapons
Prime Minister Modi visits the White House, and arms deals follow.
By Jonathan Guyer
https://www.vox.com/world-politics/2023/6/23/23770369/why-us-sellin...
Both countries are eyeing China’s growing military and technological prowess, and the US is particularly concerned about the perceived threat of a Chinese invasion of Taiwan.
But Grossman, who previously spent a decade working on China policy at the Pentagon, says that the US goal of bolstering India’s defense is less about creating a partner who would actively participate in any US-China confrontation and actually more about India providing safe harbor on the continent. “What the United States is really looking for is access to India, in the case of a conflict against China,” he told me. “But the hope is that over time, as we continue our security cooperation, India will kind of bend a little bit, to be more flexible and maybe allow us access at certain times to certain places that can help us conduct operations.”
The US Navy established ship repair agreements with India that would enable the US to service its boats in Indian shipyards, with more agreements forthcoming, according to the White House. Grossman also emphasized that, in 2020, US Navy aircraft refueled on India’s base in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. “They’re letting us do that in peacetime; why wouldn’t they let us do that when the stakes are much higher?” he said.
But even beyond the democratic issues, there are limits to how close this partnership could get in the near term. India remains non-aligned: It hasn’t taken a side in the Ukraine war, nor signed on to the sanctions against Russia. While India is a member of the “Quad,” an informal partnership with the US, Japan, and Australia, it is not a treaty ally of the United States. Grossman said that many in the Defense Department would like to see the US move toward a formal alliance with India.
That would be messy, notably because Pakistan is India’s prime rival and Pakistan is a close partner of the United States. Both countries have nuclear weapons, so if the US were to establish a treaty with India, the dynamics of a potential India-Pakistan conflict would be staggeringly complex for the US and dangerous for the world.
Nevertheless, the US military partnership with India has become a pillar of the Biden administration’s policy toward Asia. Interestingly, the US goes out of its way to not say it has anything to do with China, although analysts uniformly agree that it’s all about China. “The strategic environment that we’re facing in the Indo-Pacific challenges to peace and stability, I think those have animated a sense of Indian purpose more generally,” a senior US official, speaking on the condition of anonymity, told reporters.
The defense sector, unsurprisingly, is thrilled. Just ask the Asia Group, a consulting firm that advises clients like General Electric, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, and Raytheon and was founded by Kurt Campbell, who’s now the Biden White House’s point person on Asia policy.
Campbell’s former firm says the time is now to invest in India. “Companies that postpone entry or expansion in India might miss opportunities to maximize their long-term returns,” Gopal Nadadur, an Asia Group executive based in India, wrote recently. “Defense and aerospace companies like Airbus, Boeing, Dassault, General Electric, General Atomics, Raytheon Technologies and Pratt & Whitney have boosted their engineering and manufacturing operations in India.”
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on June 23, 2023 at 11:31am
-
Why the US is selling India so many weapons
Prime Minister Modi visits the White House, and arms deals follow.
By Jonathan Guyer
https://www.vox.com/world-politics/2023/6/23/23770369/why-us-sellin...
Will defense innovation make Asia safer?
Bringing in military-tech startups and investment firms has been a core strategy of the Pentagon in recent years, and that’s also now going to play a part in the US-India relationship. On Wednesday, the Chamber of Commerce hosted what it called an “innovation bridge” — the INDUS-X event.
US and Indian startups that focus on the military, aerospace, and satellites attended, alongside venture capital firms and major defense contractors like Raytheon and Boeing. The proceedings were sponsored by General Atomics, Lockheed Martin, and one of the big Indian companies, Mahindra Defence. The INDUS-X joint initiative will be “a catalyst for India to achieve its target of $5 billion in defense exports by 2025 and for India to diversify its defense supply chain,” according to the Chamber.
One of the keynote speakers, Secretary of the Air Force Frank Kendall, told attendees that he expected “huge growth,” in the two countries’ defense partnership, “the hockey stick curve that all entrepreneurs dream of.”
Participants did not directly discuss China, according to Pushan Das of the US-India Business Council, but it was the impetus for the gathering. “The reason why we’re doing all of this — the reason why there is the US-India defense-industry road map — it is because both countries have a common threat. They face a common challenge,” he told me. “And that’s pushing the defense relationship forward.”
But the focus on business interests has often meant that less attention has been paid in the commercial community to how increased military production and surveillance technologies in India could embolden Modi.
Modi is a Hindu nationalist leader who journalist Fareed Zakaria says is responsible for the decay of Indian democracy. His attacks on political rivals, the press, and minorities call into question the strategic benefits of growing military cooperation with the country. To cite a recent example, India arrested Vivek Raghuvanshi, a contributor to the US-based outlet Defense Times, in May.
Senior Biden administration officials told a press conference that raising human rights concerns would be part of President Biden’s private conversations with Modi, but declined to provide specificity. Human rights concerns did not come up in the conversations at INDUS-X, according to Das, and Air Force Secretary Kendall did not raise them in his remarks.
Singh, who worked in the Obama Pentagon, says that pragmatism is necessary to counter China. “We look at Prime Minister Modi, like a lot of other complicated partners, be it in Southeast Asia, like Vietnam or Thailand, or in Europe, like Poland, or Hungary, or Turkey,” he told me. “But I think we’ve reached a point where American leaders are able to talk to Indian leaders about these sorts of concerns.”
There’s also another risk of flooding India with arms that Campbell, who served in the Obama State Department, warned of in his 2016 book The Pivot: The Future of American Statecraft in Asia.
“China and India both remain under 2 percent of GDP for defense spending, while, for comparison, between 2009 and 2013, US Defense spending averaged 4.4 percent of GDP,” he wrote. “If Asian powers were to devote the same proportion to defense spending as the United States, the region would quickly become even more dangerous.”
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 5, 2023 at 7:21am
-
India’s GDP gap with US, China is widening alarmingly
Claims and speculations about the US going into a recession and India being an economic bright star are highly exaggerated
by SUBHASH CHANDRA GARG, Ex Finance Secretary of India
https://www.deccanherald.com/amp/opinion/india-s-gdp-gap-with-us-ch...
The International Monetary Fund (IMF)’s GDP database shows that the world GDP crossed $100 trillion, in current US dollars, in 2022: it was for the first time ever. The global GDP was about $34 trillion at the turn of the century. This milestone is momentous: global GDP trebled in 20 years.
In 2019, a year before Covid-19 pandemic, global GDP was a little over $87 trillion, with the United States’s GDP amounting to $21.38 trillion, China’s amounting to $14.34 trillion, and India’s GDP amounting to $2.84 trillion.
Off late there is a lot of brouhaha about the US economy falling into recession, whereas India registering world-beating GDP growth. The facts, however, are not sanguine.
For 2022, three years after all the Covid-19 disruptions, the US GDP has grown to $25.46 trillion, China’s GDP to $18.1 trillion, and India’s GDP to $3.39 trillion.
The US and China have added GDP of $4.08 trillion and $3.76 trillion respectively in these three years. At the same time, India could add only $0.55 trillion. Both the US and China have added more than India’s 2022-23 GDP ($3.39 trillion) during this period.
Given this, are we ratcheting up our GDP growth to catch up with the US and China, or is India’s GDP gap with the US and China widening uncomfortably?
Double depreciation of rupee
We all see INR-USD in terms of nominal exchange rates. Roughly Rs 69 equalled $1 on December 31, 2019. On December 31, 2022, it required nearly Rs 83 to get $1. The INR depreciated by about Rs 14 (or 20 per cent) in these three years. The nominal GDP, though boosted by Indian inflation, is reduced by INR’s depreciation.
There is another factor — the US inflation — the effect of which, however, usually gets missed out. The US’s real GDP growth is worked out after adjusting the USD for inflation. The US’s GDP was $21.38 trillion in 2019. If we were to account the inflation adjusted real US growth, a contraction by -2.8 per cent would bring down the US’s real GDP to $20.78 trillion in 2020, the 5.9 per cent growth in 2021 will take it to $22.01 trillion, and the 2.1 per cent growth in 2022 will make real US GDP amount to $22.47 trillion. This, however, is not done. The US’s GDP is stated by the IMF in current US dollars.
Therefore, to compare apples with apples to assess India’s relative performance, India’s GDP of $2.67 trillion (in 2020-21), $3.15 trillion (in 2021-22) and $3.39 trillion (in 2022-23) needs to be juxtaposed against the US’s nominal GDP of $21.06 trillion (in 2020), $23.06 trillion (in 2021) and $25.46 trillion (in 2022) and not the inflation adjusted real GDP.
Measuring the US’s GDP in current dollars dramatically transforms its low GDP growth during 2019-2022 from 1.67 per cent in real terms to a quite high growth of 5.99 per cent. India’s GDP growth at 6.08 per cent during this period looks impressive against the US’s real GDP growth of 1.67 per cent, but not so great compared to the 5.99 per cent growth in current US dollars.
The Chinese yuan did not depreciate much against the US dollar during this period, thereby delivering a robust GDP growth of 8.07 per cent per annum — which is much higher than India’s growth.
The truth is, not catching up, but the GDP gap is only widening.
A bright spot?
A few days back, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, in a boast-like now-deleted post, termed India a bright star again having become a $3.75 trillion economy — the fifth largest.
The IMF has projected India’s GDP to grow to $3.75 trillion in 2023-24. There are nine months still to go in FY 2023-24. Let us look at IMF’s numbers to see how bright is India’s star shining.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 5, 2023 at 7:22am
-
India’s GDP gap with US, China is widening alarmingly
Claims and speculations about the US going into a recession and India being an economic bright star are highly exaggerated
by SUBHASH CHANDRA GARG, Ex Finance Secretary of India
https://www.deccanherald.com/amp/opinion/india-s-gdp-gap-with-us-ch...
India’s GDP, in current US dollars, was $1.86 trillion in 2013-14; it grew to $3.39 trillion in 2022-23. Our annual compounded GDP growth for the period 2013-2022 turns out to be 6.9 per cent; and is at 5.85 per cent during the four years between 2018-19 and 2022-23.
India’s annual compounded GDP growth from 1990-91, the year after the economic reforms began, to 2013-14, the year before the Narendra Modi-led Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) came to power, was 7.81 per cent over a 23-year period. It might not please Sitaraman to know that India’s compounded dollar GDP growth between 2003-04 ($0.52 trillion) and 2013-14 ($1.86 trillion) was much higher at 13.59 per cent!
Against this backdrop, India’s last 4-year GDP growth of 5.85 per cent does not look exceptionally bright.
Tough policy reforms
There is an unnecessary attempt from various quarters to claim and project that the economic performance under this government has been exceptional, whereas the facts are quite on the contrary.
Instead of this misleading projection, it will do India’s economic prospects good if the focus is on real and tough policy reforms to raise the GDP growth to levels of 8-10 per cent per annum for the next 20-25 years to make India a real bright star and to serve the people well.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 6, 2023 at 7:58am
-
The West needs to get real about India | The Strategist
https://www.aspistrategist.org.au/the-west-needs-to-get-real-about-...
by John McCarthy, ex Australian Ambassador to India
The first is that India’s economic promise—particularly as an eventual rival to China—is overblown.
Doubts about the extent of India’s promise have been around for a couple of decades—in fact, ever since some commentators started suggesting that India would one day outstrip China.
These doubts were cogently expressed by Harvard academic Graham Allison in a recent essay in Foreign Policy. Allison, inter alia, suggested that we need to reflect on several ‘inconvenient truths’:
We have been wrong in the past about the pace of the rise of India—namely in the early 1990s and the middle of the first decade of this century.
India’s economy is much smaller than China’s—and the gap has increased, not decreased. In the early 2000s, China’s GDP was two to three times as large as India’s. It is now roughly five times as large.
India has been falling behind in the development of science and technology to power economic growth. China spends 2% of GDP on research and development, compared with India’s 0.7%. On artificial intelligence, the figures are startling. For example, China holds 65% of AI patents, while India holds just 3%.
China’s workforce is more productive than India’s. The quality of their respective workforces is affected by poverty and nutrition levels. As one example, according to the 2022 UN State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World report, 16.3% of India’s population was undernourished in 2019–2021 compared with less than 2.5% of China’s population.
The second argument is that India’s worldview is quite different to that of most Western countries.
India rightly sees itself as a force in international affairs. It aspires to be a powerful pole in a multipolar world. It adheres to a doctrine of strategic autonomy. It is guided by what it thinks is best for India, not by alliances or what others want of it.
India’s China-driven strategic congruence with the US is not the same as a quasi-alliance relationship. India doesn’t operate within a framework of mutual obligation. It doesn’t expect others to come to its aid and it won’t join someone else’s war.
In a recent Foreign Affairs article entitled ‘America’s bad bet on India’, an American academic of Indian origin, Ashley Tellis, argues that New Delhi would never involve itself in any US confrontation with China that did not threaten its own security.
The Tellis piece has weight because he was a main intellectual force behind the ‘nuclear deal’ concluded in 2008.
Moreover, India will differ radically from the West on some questions. True, as the Ukraine war has progressed, India has put some daylight between itself and Russia. But it declines to impose sanctions on Moscow. Both countries benefit from Russia’s sales of oil to India.
And never a proponent of the Western-inspired liberal international order, India is also a leader of the disparate—but re-energised—global south, effectively the developing world.
The third argument is that the west’s line that its relationship with India is based on shared democratic values does not hold up.
In a recent interview with the Financial Times, Biden’s national security adviser, Jake Sullivan, said he saw the long-term trajectory of the US-India relationship as being ‘built on the notion that democracies with shared value systems should be able to work together both to nurture their own democracies internally and to fight for shared values globally’. Come off it, Mr Sullivan!
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on July 6, 2023 at 10:02am
-
Will India Surpass China to Become the Next Superpower?
Four inconvenient truths make this scenario unlikely.
https://foreignpolicy.com/2023/06/24/india-china-biden-modi-summit-...
by Prof Graham Allison, Harvard's Kennedy School of Government
First, analysts have been wrong about India’s rise in the past. In the 1990s, analysts trumpeted a growing, youthful Indian population that would drive economic liberalization to create an “economic miracle.” One of the United States’ most thoughtful India analysts, journalist Fareed Zakaria, noted in a recent column in the Washington Post that he found himself caught up in the second wave of this euphoria in 2006, when the World Economic Forum in Davos heralded India as the “world’s fastest-growing free market democracy” and the then-Indian trade minister said that India’s economy would shortly surpass China’s. Although India’s economy did grow, Zakaria points out that these predictions didn’t come true.
Second, despite India’s extraordinary growth over the past two years—when India joined the club of the world’s five largest economies—India’s economy has remained much smaller than China’s. In the early 2000s, China’s manufacturing, exports, and GDP were about two to three times larger than India’s. Now, China’s economy is about five times larger, with a GDP of $17.7 trillion versus India’s GDP of $3.2 trillion.
Third, India has been falling behind in the race to develop science and technology to power economic growth. China graduates nearly twice as many STEM students as India. China spends 2 percent of its GDP on research and development, while India spends 0.7 percent. Four of the world’s 20 biggest tech companies by revenue are Chinese; none are based in India. China produces over half of the world’s 5G infrastructure, India just 1 percent. TikTok and similar apps created in China are now global leaders, but India has yet to create a tech product that has gone global. When it comes to producing artificial intelligence (AI), China is the only global rival to the United States. China’s SenseTime AI model recently beat OpenAI’s GPT on key technical performance measures; India has no entry in this race. China holds 65 percent of the world’s AI patents, compared with India’s 3 percent. China’s AI firms have received $95 billion in private investment from 2013 through 2022 versus India’s $7 billion. And top-tier AI researchers hail primarily from China, the United States, and Europe, while India lags behind.
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Improved US-Pakistan Ties: F-1 Visas For Pakistani Students Soaring
The F-1 visas for Pakistani students are soaring amid a global decline, according to the US government data. The US visas granted to Pakistani students climbed 44.3% in the first half of Fiscal Year 2025 (October 2024 to March 2025) with warming relations between the governments of the two countries. The number of visas granted to Indian students declined 44.5%, compared to 20% fewer US visas given to students globally in this period. The number of US visas granted to Pakistani…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on October 19, 2025 at 10:00am — 1 Comment
Major Hindu American Group Distances Itself From Modi's India
"We are not proxies for India in the US", wrote Suhag Shukla, co-founder and executive director of the Hindu American Foundation (HAF) in a recent article for The Print, an Indian media outlet. This was written in response to Indian diplomat-politician Shashi Tharoor's criticism that the Indian-American diaspora was largely silent on the Trump administration policies hurting India. …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on October 11, 2025 at 2:00pm
© 2025 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()

You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network