PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
Pakistan Ranks Among World's Top 3 Nations For New Hydroelectric Capacity Added in 2018
Pakistan ranked third in the world by adding nearly 2,500 MW of hydropower in 2018, according to Hydropower Status Report 2019. China added the most capacity with the installation of 8,540 megawatts, followed by Brazil (3,866 MW), Pakistan (2,487 MW), Turkey (1,085 MW), Angola (668 MW), Tajikistan (605 MW), Ecuador (556 MW), India (535 MW), Norway (419 MW) and Canada (401 MW).
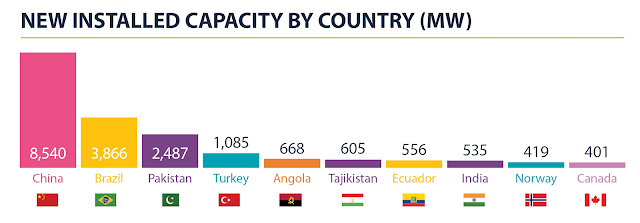 |
| New Installed Hydroelectric Power Capacity in 2018. Source: Hydrowo... |
Pakistan's Water and Power Development Authority (WAPDA) says commissioning of the 108-MW Golen Gol 2, 1,410-MW Tarbela 4th Extension and 969-MW Neelum Jhelum hydropower projects in 2018 boosted its hydroelectric generating capacity of 9,389 MW, an increase of 36% in just one year, according to Hydro Review. Hydropower now makes up about 28% of the total installed capacity of 33,836 MW as of February, 2019. WAPDA reports contributing 25.63 billion units of hydroelectricity to the national grid during the year, “despite the fact that water flows in 2018 remained historically low.” This contribution “greatly helped the country in meeting electricity needs and lowering the electricity tariff for the consumers.”
| Top 20 Countries by Newly Installed Hydropower Capacity. Source: IHA |
Pakistan has the potential to generate 59,000 MW of hydropower, according to studies conducted by the nation's Water and Power Development Authority (WAPDA). Currently, it's generating only 9,389 MW of hydroelectric power, about 16% of the estimated potential. Media reports indicate that China is prepared to finance and build another 40,000MW capacity as part of the development of the Northern Indus Cascade region which begins in Skardu in Gilgit-Baltistan and runs through to Tarbela, the site of Pakistan’s biggest dam, in Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa province.
 |
| Pakistan Power Generation Fuel Mix. Source: Third Pole |
One of the ways Pakistan can help reduce carbon emissions is by realizing its full hydroelectric potential by building more dams. The development of the Northern Indus Cascade region to generate 40,000MW of hydropower is a significant part of this effort.
Haq's Musings
South Asia Investor Review
Recurring Cycles of Drought and Floods in Pakistan
Pakistan's Response to Climate Change
Massive Oil and Gas Discovery in Pakistan: Hype vs Reality
Renewable Energy for Pakistan
Digital BRI: China and Pakistan Building Fiber, 5G Networks
LNG Imports in Pakistan
Growing Water Scarcity in Pakistan
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor
Ownership of Appliances and Vehicles in Pakistan
CPEC Transforming Pakistan
Pakistan's $20 Billion Tourism Industry Boom
Riaz Haq's YouTube Channel
PakAlumni Social Network
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 25, 2022 at 7:03pm
-
Until about a decade ago, the Jhimpir region in Sindh was a dry, barren stretch of land, inhabited by nomadic tribes. Today, it is home to hundreds of mammoth rotating blades in about two dozen wind farms.
https://www.dawn.com/news/1722458
Around 90 kilometres from Karachi, Jhimpir is the heartland of the country’s largest ‘wind corridor’, which has the potential to produce 11,000 megawatts (MW) of clean energy.
Among early investors was the China Three Gorges Corporation, a Chinese state-owned power company, operating under an investment holding company, China Three Gorges South Asia Investment Limited.
The company has funded and built three wind projects with a combined capacity of nearly 150 MW. The first of these began construction in 2012.
The latter two projects, completed in 2018, were funded under the China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), an integral part of Beijing’s flagship multibillion-dollar Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
In an official statement following Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif’s visit to China on Nov 1-2, the premier reaffirmed the importance of CPEC to Pakistan’s development.
For the time being, renewables represent only a small portion of Pakistan’s power generation mix. Of a total of 43,775 MW, installed capacity for wind and solar represent around 4.2 per cent (1,831 MW) and 1.4pc (630 MW) respectively, according to the National Electric Power Regulatory Authority’s State of Industry 2022 report.
In terms of CPEC, the November 2022 joint statement from China and Pakistan listed oil and gas as among the “priority areas of CPEC cooperation”.
But a recent shift in the direction of Chinese investment may be hugely significant for the country’s energy future, and the climate.
The shift from coal?
In the years before the launch of CPEC in 2015, Pakistan was desperate to end its long, crippling power shortages.
The country was keen to develop its untapped indigenous coal in Thar desert, but multilateral financial institutions were not interested. Along came China in 2013, with an offer to lend massive amounts for infrastructure development and coal mining.
Details of the financing deals are a closely guarded secret, but multiple Chinese-funded coal projects followed. Eight completed or under-construction coal projects are listed as part of CPEC, totalling 6,900 MW, which include four on Thar coal.
Then in 2021, after growing pressure on China — currently the world’s biggest polluter — to curb its greenhouse gas emissions, Beijing announced it would not build new coal-fired power plants overseas, and would increase support for low-carbon energy.
In December 2020, Pakistan announced that it would not build any new power projects that depend on imported coal, and pledged that by 2030, 60pc of its energy will come from clean and renewable sources.
The government has since scrapped a number of potential coal projects, including a 300 MW plant at the Chinese-controlled Gwadar sea port in Balochistan. Reportedly, it is to be replaced by a solar plant.
‘Greening’ CPEC
As Beijing tries to rebrand the BRI as an eco-friendly initiative, Chinese officials have promoted the idea of a ‘green’ CPEC. But Hina Aslam, research fellow at the Sustainable Development Policy Institute (SDPI), a think tank in Islamabad, points out that “in the energy sector, it has meant a greater focus on hydro rather than wind and solar”.
Besides wind energy in Jhimpir, China Three Gorges Corporation is investing heavily in what it is globally known for: hydropower (the company is behind the Three Gorges Dam in China, the world’s biggest power station).
In June 2022, it completed a 720 MW project in Karot in northern side of the country.
Work is advancing on a 1,124 MW hydropower plant near Muzaffarabad, and a third 640 MW project has recently been approved in Mahl. The same company is behind both projects.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 25, 2022 at 7:05pm
-
Put together, China Three Gorges aims to produce 2,500 MW of renewable energy in Pakistan, mostly through hydro. The Pakistan government – like many others – includes hydropower under the umbrella of renewable energy, but this is disputed by many environmentalists due to the often high environmental, social and financial costs of hydropower, including disruption of important riverine ecosystems. In Pakistan, dams are also politically contentious and a source of discord between upstream and downstream provinces. Yet, both Beijing and Islamabad appear keen to pursue hydropower.
But there are huge challenges facing Pakistan’s shift to renewable energy. “A lack of consistency in policy has been the biggest issue,” says Noman Sohail, senior business manager at China Three Gorges South Asia Investment Ltd.
“Arranging lenders and finance for renewable projects is not a problem. But it’s disorienting when policies are reversed, tariffs renegotiated and unpaid capacity payments allowed to pile up.”
Growing popularity of solar
There is one form of renewable energy in particular that presents immense potential for Pakistan, but which has seen little investment to date: solar. A World Bank study in 2020 urged Pakistan to urgently expand solar and wind “to at least 30 per cent of electricity generation capacity by 2030, equivalent to around 24,000 MW”.
As of 2022, the proportion is 5.6pc according to the National Electric Power Regulatory Authority’s State of Industry 2022 report.
Pakistan’s slow take-up of solar energy is evident from the fact that of the 21 energy projects completed or in development under CPEC, only one is solar: the 1,000 MW Quaid-i-Azam Solar Park in Cholistan Desert, Punjab, built by Chinese company Zonergy.
This project, promoted as one of the world’s biggest solar parks, was meant to be completed by 2017. But only 40pc of this capacity has been implemented so far.
Suleman Rehman, chief executive of Burj Capital, a Dubai-based investment company focused on renewable energy in Pakistan, says that regardless of the government’s apparent lack of focus, the demand for affordable solar power is growing exponentially.
“The competition is getting intense. More and more local players are coming up every month. Installing a 4MW solar project is no longer a big deal for us,” says Rehman.
According to Rehman, the private sector is not waiting for policymakers to facilitate the energy transition. Those who can are turning to the solar option. That explains the recent proliferation of rooftop photovoltaic panels in big cities, as well as in off-grid villages across the country.
The solar future
Costly fuel imports have already had a crippling effect on Pakistan’s economy. This year, the volatility of global energy prices, exacerbated by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, took a damaging toll on Pakistan’s foreign exchange reserves. The country was on the verge of a default before the International Monetary Fund agreed to step in to help it stay afloat.
In an attempt to reduce dependence on imported fuel, on 1 September 2022 Prime Minister Shahbaz Sharif announced the rapid deployment of 10,000 MW of solar power in the country. But details of how this will be achieved, and by when, are sketchy.
The plan reportedly involves transitioning all public sector buildings to solar power. The proposal also encourages power plants running on coal, oil and gas to partially shift to solar power.
China will have a crucial role to play if this shift to solar is to happen, says Rehman, though it may come in a different form than the mega-projects seen under CPEC.
“China will still have a big role because they are producing the cheapest [solar] equipment worldwide. But I really hope the government won’t put this under CPEC because that would put local players at a disadvantage,” says Rehman.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on January 5, 2023 at 2:14pm
-
Gwadar Pro Official
@Gwadar_Pro
China state-affiliated media
The Chinese company is working 24 hours a day according to three shifts on Dasu Hydropower Project. After the completion of Dasu Dam project, 4320 MW electricity will be generated. Thousands of employment opportunities have already been created on the project.
https://twitter.com/Gwadar_Pro/status/1610941378862940160?s=20&...
-----------
Wapda, KP districts sign deal to build transmission line
https://www.dawn.com/news/1726085
The Water and Power Development Authority (Wapda) and a united jirga from three districts in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa’s Kohistan region signed an agreement on Monday to facilitate the construction of a transmission line for evacuation of 4,300 megawatts electricity to be generated by Dasu dam and other hydropower projects.
The “Confidence-Building Measures’ Agreement (CBMA) was signed between Wapda, the administration of Hazara division, and notables from the three districts — Upper Kohistan, Lower Kohistan and Kolai Palas Kohistan.
Under the agreement, Wapda committed to implementing development schemes — to be selected through a yet to be conducted field survey — as CBMs under its Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in consultation with the civil administrations and the locals, Wapda said in a statement.
“Most importantly, this agreement will pave the way for smooth execution and completion of long-delayed 132kV transmission line from Duber hydel power station to Dasu, direly needed for stable supply of electricity during peak construction period of Dasu project,” it added.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on March 6, 2023 at 4:06pm
-
POWERCHINA Celebrates 10th Anniversary of CPEC: Committed to Bringing Pakistan Forward for Green and Sustainable Development
https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20230306005420/en/POWERCHINA...
This year will see the 10th anniversary of the China-proposed Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and the 10th anniversary of the launch of the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC). As one of the key enterprises participating in the construction of the CPEC, POWERCHINA has been active in various fields such as energy, electricity, water management, and infrastructure investment in Pakistan since it entered the Pakistani market as early as 1987.
Over the past 36 years, POWERCHINA has completed the 103 projects in Pakistan, including the first roller-compacted concrete (RCC) dam in Pakistan – the Gomal Zam Dam multipurpose project, and the first mainstream hydropower station on the Indus River – the Ghazi-Barotha Hydropower Project, the largest installed hydropower station – the Tarbela 4th & 5th Extension Hydropower Project, and the largest wind farm – the Tricon Boston 150 MW Wind Power Project.
In the past ten years, among the first 20 energy and infrastructure projects of the CPEC, POWERCHINA has participated in the investment and construction of 11 projects. POWERCHINA has consolidated the traditional power business, and continued to contribute to the development of new energy and other fields. Pakistan's largest hydropower hub project currently being constructed by POWERCHINA, the Diamer Basha Dam Project, will become the tallest and largest RCC dam in the world, and is expected to provide Pakistan with 18.1 billion KWh of clean electricity every year. As the project progresses, it is expected to provide more than 20,000 job opportunities, which is considered as one of the many positive effects of the project by Nadeem Ilyas, a Pakistani engineer of the project.
As one of the leading enterprises in China, POWERCHINA has carried out high-quality clean energy project construction and operation in accordance with international standards, and is committed to improving Pakistan's infrastructure conditions and alleviating local power shortages. It has not only made important contributions to the sustainable development of Pakistan, but also played a key role in the development of CPEC.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on April 7, 2023 at 7:54am
-
Saudi Arabia signs $240m loan agreement to support Mohmand Dam
https://www.dawn.com/news/1746406/saudi-arabia-signs-240m-loan-agre...
The statement noted that the project is expected to enhance water and food security, and improve the standard of living for people in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, where almost 80 per cent of the population resides in rural areas, boosting the region’s socioeconomic development by creating employment opportunities and reducing poverty levels.
It added that by using renewable energy sources, the project will generate 800 MW of electricity production capacity, contributing to Pakistan’s energy security. In addition, the storage of 1.6 million cubic meters of water will support sustainable agricultural practices, enable irrigation of 6,773 hectares of new land, and increase the total cropping area from 1,517 hectares to 9,227 hectares in the province, facilitating agricultural activities.
Co-financed by the SFD, OPEC, Islamic Development Bank, and the Kuwait Fund for Arab Economic Development, the project aligns with SDG-2 (Food Security), SDG-6 (Clean Water), and SDG-7 (Clean Energy) and embodies SDG-17 (Partnerships for the Goals).
During the agreement signing ceremony, the CEO of SFD said this initiative is an extension of the fund’s continued support for development projects and programmes in Pakistan since its inception. He also highlighted the significance of joint cooperation between development funds, as evidenced by this project.
For his part, Dr Niaz expressed his sincere appreciation and gratitude to the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for its unwavering support towards the development sector in Pakistan through the SFD.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on August 16, 2024 at 8:39pm
-
First unit of CPEC's Suki Kinari hydropower project connected to grid in Pakistan - International Water Power
https://www.waterpowermagazine.com/news/first-unit-of-cpecs-suki-ki...
The first unit of the Suki Kinari Hydropower Project in northwest Pakistan was successfully connected to the national grid on Monday, marking a significant milestone in the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) initiative.
The project, located in the Mansehra district of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, is being developed by China Energy Construction Overseas Investment Company Ltd. Once fully operational, the 884MW plant will generate approximately 3.21 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity annually, supplying affordable clean energy to over 1 million households.
Suki Kinari is expected to play a key role in addressing Pakistan’s electricity shortfall, reducing coal consumption, and lowering carbon dioxide emissions by an estimated 2.52 million tons per year. Construction began in January 2017, and the facility is scheduled to become fully operational later this year.
At the heart of the Suki Kinari project are four Pelton turbine generators, each with a capacity of 221MW, collectively contributing to the total capacity of 884MW. The hydropower plant boasts a maximum net head of 922.72m and a minimum head of 845.76m.
The reservoir’s operating parameters are set with a maximum level of 2233m and a minimum level of 2223m, holding a storage capacity of 10.37 million m3 below the minimum operating level. The project also features an underground powerhouse located approximately 400m deep and a tailrace tunnel extending about 1583m.
CPEC, launched in 2013 as part of China’s Belt and Road Initiative, focuses on enhancing energy, transportation, and industrial infrastructure in Pakistan. The successful connection of the Suki Kinari project’s first unit to the grid is seen as a critical step toward its commercial operation.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on February 18, 2025 at 10:07am
-
World Bank set to approve $1bn loan for Dasu project expansion
https://www.geo.tv/latest/588799-world-bank-set-to-approve-1bn-loan...
Official reveals cost of phase I shot up by 190.1% to Rs1,700bn.
Rise attributed to various factors such including in land acquisition.
After erection of stage II, Dasu project would generate 4,320 MWs.
The World Bank (WB) is set to issue a fresh $1 billion loan for the first phase of the Dasu hydropower project, following the approval of a revised PC-1 with updated completion timelines, The News reported on Monday.
A senior official of the Economic Affairs Division (EAD) revealed that cost of the first stage of the project has shot up by 190.1% to Rs1,700 billion from Rs586 billion.
The increase in the cost is attributed mainly to a delay in land acquisition, security concerns and an increase of US dollar value by 178%.
“The project of stage I would generate 2,160 MWs. However, after erecting stage II of the project, it would generate 4,320 MWs. Dasu Hydropower Project is a run-river project on the Indus River located seven kilometres upstream of Dasu Town, District Kohistan (Upper), Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
"The site is 74km downstream of the proposed Diamer Bhasha Dam site and 345km from Islamabad. The project will generate 4,320 MWs (12 Units @ 360 MW each) hydroelectric power with annual energy of 21,445 GWh and will be developed in two stages (Stage I and II).
"Stage I will generate 2,160 MW (06 Units @ 360MW each) with annual energy of 12,222 GWh. Stage I will be completed in five years. The WB has already given the loan of $588 million and also extended the guarantee leverage for generating $460 million from the international market.”
However, under the new financing for the project, out of $1 billion, $800 million loan is of International Development Association (IDA) and $200 million will be extended under the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD).
Out of the IDA loan, Pakistan will attain $435 million at zero interest rate, $365 million at 5.83% interest rate, and get $200 million under IBRD at 6.13% interest rate.
"We have prepared the revised PC-1 of the project at the cost of Rs1,700 billion and will send it within a couple of days to the Planning Commission for its approval. After that, Water and Power Development Authority (Wapda) and WB will formally sign the $1 billion (loan)," the Ministry of Water Resources confirmed.
The land acquisition for the dam project was to be completed by 2014, but the process finished in 2021-22. Another reason for the escalating cost is the appreciation of US dollar by 178% to Rs278 from Rs100.
"The project was earlier scheduled to get completed by 2023-24 which would now be completed by 2027-28. The Economic Affairs Division has played a pivotal role in diverting the bank’s loan to the project of paramount importance. The WB has already extended $1 billion loan to Pakistan in other heads, but it was not being spent. This is why the loan has been re-purposed and diverted to the Dasu Dam with the approval of the executive board of the bank," added the ministry.
Comment
- ‹ Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Next ›
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Earth Day: Pakistan's Progress Toward Low-Carbon Economy
Pakistan celebrates Earth Day on April 22 every year by organizing various events sponsored by the government and non-government organizations to raise awareness of the issues faced by the earth. Today it is being observed with a range of initiatives, including pledges for zero waste, commitments to sustainable practices, and community-based actions to protect the planet. Pakistan contributes less than 1% of global carbon emissions, but it is among the countries considered most vulnerable to…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on April 22, 2025 at 5:00pm
International Schools: Pakistan Ranks Among Top 5 Countries in the World
Pakistan ranks among the top 5 nations in terms of international schools offering schooling based on International Baccalaureate (IB) and IGCSE (Cambridge) curricula. China leads with 1,000 international schools, followed by India (900), UAE (784), Pakistan (598) and Brazil (415). The medium of instruction in these schools is English. …
Posted by Riaz Haq on April 19, 2025 at 8:00am
© 2025 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network