PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network
The Global Social Network
Food Price Hikes Badly Hurting Average Pakistani Consumers
Global food prices are soaring by double digits amid the coronavirus pandemic, according to Bloomberg News. Bloomberg Agriculture Subindex, a measure of key farm goods futures contracts, is up almost 20% since June. It may in part be driven by speculators in the commodities markets. These rapid price rises are hitting the people in Pakistan and the rest of the world hard. In spite of these hikes, Pakistan remains among the least expensive places for food, according recent studies. It is important for Pakistan's federal and provincial governments to rise up to the challenge and relieve the pain inflicted on the average Pakistani consumer.
| Global Agricultural Futures Contracts. Source: Bloomberg |
Global Food Prices:
Global food prices are increasing at least partly due to several nations buying basic food commodities to boost their strategic reserves in the midst of the pandemic. A Bloomberg News report says that "agricultural commodity buyers from Cairo to Islamabad have been on a shopping spree since the Covid-19 pandemic upended supply chains". It may in part be driven by speculators in the commodities markets. Here's an excerpt of the Bloomberg story:
"Agricultural prices have been on the rise as countries stepped up purchases, adding to demand from China and a drought in the Black Sea region. That has helped push the Bloomberg Agriculture Subindex, which measures key farm goods futures contracts, up almost 20% since June. Sugar prices have gained a boost as China replenished stockpiles, said Geovane Consul, chief executive officer of a Brazilian sugar and ethanol joint venture between U.S. agribusiness giant Bunge Ltd. and British oil major BP Plc."
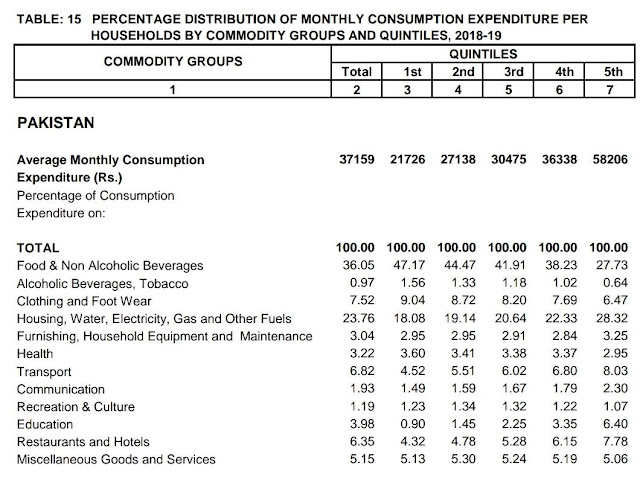 |
| Pakistan Household Expenditure on Food. Source: HIES |
Supply Constraint in Pakistan:
The Pakistan Government estimates final wheat production ended up at 25.5 million tons, slightly above the five-year average of 25.38 million tons, according to Grain Central. While that represented a 1.2 million tons increase on the 24.3 million tons harvested in 2019, it was well short of the government’s target of 27 million tons, forcing Pakistan to import wheat at higher global prices.
Demand for fruits and vegetables is also rising at about 9.5% a year, according to Mordor Intelligence. The supply is falling short of demand, putting pressure on prices.
 |
| Global Food Price Comparison. Source: Bayut |
The food prices have risen 14% for urban and 16.8% for rural areas of Pakistan in the last 12 months, according to Pakistan Bureau of Statistics. In spite of this inflationary trend, the grocery prices in Pakistan remain among the lowest in the world. A comparison by Dubai-based Bayut shows that groceries in Pakistan cost 72.9% less than in the United States. Other least-expensive countries for groceries include Tunisia ( 67% less), Ukraine ( 66.7% less), Egypt (65.6% less) and Kosovo (65.6% less).
Globally, Switzerland sells the most expensive groceries, with prices 79.1% higher than in the U.S. Norway is the second most expensive place to buy groceries, with prices 37.4% more expensive than in the U.S., and Iceland is third most expensive, where food items are 36.6% pricier, according to Bayut.
 |
| Cost of Dining Out. Source: Commodity.com |
Summary:
Global food price hikes have hit average Pakistani hard in spite of the fact that grocery prices in Pakistan remain the lowest the world. Bloomberg Agriculture Subindex, a measure of key farm goods futures contracts, is up almost 20% since June. It may in part be driven by speculators in the commodities markets. World food commodity prices are increasing at least partly due to several nations buying basic food commodities to boost their strategic reserves in the midst of the pandemic. It is important for Pakistan's federal and provincial governments to intervene in the markets to relieve the average Pakistani consumer's pain.
Related Links:
Haq's Musings
South Asia Investor Review
COVID19 in Pakistan: Test Positivity Rate and Deaths Declining
Construction Industry in Pakistan
Pakistan's Pharma Industry Among World's Fastest Growing
Pakistan to Become World's 6th Largest Cement Producer by 2030
Is Pakistan's Response to COVID19 Flawed?
Pakistan's Computer Services Exports Jump 26% Amid COVID19 Lockdown
Coronavirus, Lives and Livelihoods in Pakistan
Vast Majority of Pakistanis Support Imran Khan's Handling of Covid1...
Pakistani-American Woman Featured in Netflix Documentary "Pandemic"
Coronavirus Antibodies Testing in Pakistan
Can Pakistan Effectively Respond to Coronavirus Outbreak?
How Grim is Pakistan's Social Sector Progress?
Pakistan Fares Marginally Better Than India On Disease Burdens
Trump Picks Muslim-American to Lead Vaccine Effort
Democracy vs Dictatorship in Pakistan
Pakistan Child Health Indicators
Pakistan's Balance of Payments Crisis
Panama Leaks in Pakistan
Conspiracy Theories About Pakistan Elections"
PTI Triumphs Over Corrupt Dynastic Political Parties
Strikingly Similar Narratives of Donald Trump and Nawaz Sharif
Nawaz Sharif's Report Card
Riaz Haq's Youtube Channel
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on November 10, 2020 at 10:20am
-
#Pakistan tenders to buy 320,000 tons of #wheat. In last wheat tender on Oct. 16, Pakistan bought about 340,000 tons of wheat. #ImranKhan permitted wheat imports in June to reduce domestic wheat and flour prices amid tight local supplies. #food #inflation https://www.hellenicshippingnews.com/pakistan-tenders-to-buy-320000...
A government agency in Pakistan has issued a new international tender to purchase and import 320,000 tonnes of wheat, European traders said on Monday.
The tender from the Trading Corporation of Pakistan (TCP) closes on Nov. 3.
The wheat can be supplied from optional origins and shipment must be organised so that all the grain arrives in Pakistan by Jan. 31, 2021. The minimum offer is 100,000 tonnes.
The TCP has regularly bought wheat in the global market in past weeks, aiming to improve local supplies and cool prices.
In its last reported wheat tender on Oct. 16, Pakistan is believed to have bought about 340,000 tonnes of wheat.
Pakistan’s government permitted wheat imports in June to reduce domestic wheat and flour prices amid tight local supplies.
Separately, the Pakistan government’s Economic Coordination Committee, its top economic decision-making body, said it had been informed that the TCP should be able to secure 1 million tonnes of wheat through international tender purchases up to January 2021.
The committee will also consider raising the TCP’s mandate for wheat purchases from 1.50 million tonnes to 1.80 million tonnes.
The committee decided too that 300,000 tonnes of wheat should be imported on a government-to-government basis from the Russian federation by another Pakistani state agency, PASSCO.
The committee also approved a request from Pakistan’s Ministry of Food to import another 320,000 tonnes from Russia under a government-to-government scheme either by PASSCO or TCP.
It was decided as well that further tendering of wheat could be stopped and that the TCP could instead use government-to-government deals for additional procurement of wheat.
Because of the arrival of Pakistan’s new crop in March 2021, the committee decided no vessel of imported wheat should be arranged either in the public or private sector beyond February 2021.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 13, 2020 at 1:15pm
-
FAO Food Price Index rises sharply
https://reliefweb.int/report/world/fao-food-price-index-rises-sharply
Global food commodity prices rose to a nearly six-year high in November. FAO also trims its cereal crop forecasts and notes 45 countries need external assistance for food
**3 December 2020, Rome - **Global food commodity prices rose sharply in November to their highest level in nearly six years, according to a benchmark United Nations report released today.
The FAO Food Price Index averaged 105.0 points during the month, up 3.9 percent from October and 6.5 percent higher than its value a year earlier. The monthly increase was the sharpest since July 2012, putting the index at its highest level since December 2014, the Food and Agriculture Organization said.
The FAO Food Price Index tracks changes in the international prices of the most globally traded food commodities. All of its sub-indices rose in November.
The FAO Vegetable Oil Price Index gained a stunning 14.5 percent in the month, led by an ongoing rally in palm oil prices linked to sharp contractions in world inventory levels.
The FAO Cereal Price Index rose 2.5 percent from October and averaged 19.9 percent higher than in November 2019. Wheat export prices rose, linked to reduced harvest prospects in Argentina, as did maize prices on account of lower output expectations in the United States of America and Ukraine as well as large purchases by China. International rice prices held steady during the month.
The FAO Sugar Price Index rose 3.3 percent month-on-month amid growing expectations of a global production shortfall in the upcoming marketing season as unfavorable weather conditions drove weaker crop prospects in the European Union, the Russian Federation and Thailand.
The FAO Dairy Price Index increased 0.9 percent to near an 18-month high, driven largely by firmer butter and cheese prices and surging retail sales in Europe during a seasonal low period for milk production in the region.
The FAO Meat Price Index rose 0.9 percent from October, but it is still 13.7 percent below its value a year ago. Prices of bovine, ovine and pig meats all increased, while those of poultry meat declined.
FAO trims world 2020 cereal output forecast
FAO has further lowered its forecast for global cereal production in 2020, which now stands at 2 742 million tonnes - still a record high and 1.3 percent above the previous year's outturn.
The new forecasts released today with FAO's Cereal Supply and Demand Brief point to world coarse grains production of 1 470 million tonnes, wheat production of 761.7 million tonnes, and rice output of 508.4 million tonnes.
Looking ahead, planting of the northern hemisphere's winter wheat crop is underway and remunerative prices are expected to increase sowings in several major producing countries. However, crop conditions in the United States of America are moderately poorer due to dry weather conditions, influenced by the prevailing La Niña weather phenomenon.
World cereal utilization in 2020/21 is now forecast to rise to 2 744 million tonnes, up 1.9 percent from 2019/20, led by expectations of increasing feed use of maize and sorghum in China as well as a rise in the production of maize-based ethanol in Brazil and the U.S.A.
Worldwide cereal stocks by the close of seasons in 2021 are predicted to decline to 866.4 million tonnes, translating into a global stock-to-use ratio of 30.7 percent - which FAO notes is a five-year low but still a relatively comfortable level.
World trade in cereals in 2020/21 is forecast to rise 3.4 percent from the previous year to 454.6 million tonnes, driven primarily by a faster than expected pace in maize sales by the U.S.A. and continued strong purchases from China.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 13, 2020 at 6:26pm
-
SPI-based weekly inflation falls 0.26pc
https://nation.com.pk/13-Dec-2020/spi-based-weekly-inflation-falls-...
The Sensitive Price Indicator (SPI) based weekly inflation for the week ended on December 10, for the combined consumption group, witnessed nominal decrease of 0.26 percent as compared to the previous week. The SPI for the week under review in the above mentioned group was recorded at 141.04 points against 141.41 points registered in the previous week, according to the latest data of Pakistan Bureau of Statistics (PBS). As compared to the corresponding week of last year, the SPI for the combined consumption group in the week under review witnessed an increase of 8.44 percent. The weekly SPI with base year 2015-16=100 is covering 17 urban centers and 51 essential items for all expenditure groups. The Sensitive Price Indicator for the lowest consumption group up to Rs17,732 witnessed 0.56 percent decrease and went down from 148.29 points in last week to 147.46 points during the week under review. Meanwhile, the SPI for the consumption groups from Rs17,732-22,888, Rs22,889-29,517; Rs29,518-44,175; Rs29,518 to Rs44,175 and above Rs 44,175 per month also decreased by 0.48 percent, 0.38 percent; 0.30 percent and 0.16 percent respectively. During the week, prices of 13 items decreased, 16 items increased while that of 22 items remained constant. The items, which recorded decrease in their average prices, included potatoes, sugar, onions, tomatoes, masoor pulse, gur, wheat flour, mash pulse, rice (Basmati broken), gram pulse, moong pulse, LPG Cylinder and curd. The commodities, which recorded increase in their average prices, included eggs, garlic, vegetable ghee, vegetable ghee, firewood, mustard oil, washing soap, rice (Irri-6/9), beef, bananas, chicken, cooked beef, shirting, cooked beef, cooking oil (lose), mutton, cooked daal. Similarly, the prices of the commodities that observed no change during the week under review included bread, milk (fresh), powdered milk, salt, chilies, tea (packet), tea (prepared), cigarettes, long cltoh, lawn, georgette, gents sandal, gents chappal, ladies sandal, electricity charges, gas charges, energy saver, match box, petrol, diesel, telephone call charges and toilet soap.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 31, 2020 at 4:20pm
-
According to Asif Ahmed, one of the prominent Arthis who also serves as vice chairman of the market committee that manages Karachi Sabzi Mandi, criticism of middlemen is uncalled for. “Arthis take risks, growers don’t. It’s our money that’s at stake. We extend financing to growers when banks look the other way,” Mr Ahmed says.
He denied that Arthis charge ‘exorbitant’ interest rates, although a study published by the State Bank of Pakistan (SBP) in 2014 found out that growers pay a mark-up of almost 50pc on funds they borrow from informal lenders. This mark-up is in addition to their 6-10pc fee that they charge for trading about 90pc of the entire produce that comes to the market.
Muhammad Kashif, a Karachi-based wholesaler, says growers are ‘captive customers’ of Arthis. “Sabzi Mandi is off-limits to independent growers. They can’t bring their produce inside the Mandi without involving an Arthi. The only way for growers to cut out the Arthi is to become one by setting up shop,” he says.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on December 31, 2020 at 4:21pm
-
PAKISTAN FRUITS AND VEGETABLES MARKET - GROWTH, TRENDS, AND FORECAST (2020 - 2025)
https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/pakistan-fruits...
PAKISTAN FRUITS AND VEGETABLES MARKET - GROWTH, TRENDS, AND FORECAST (2020 - 2025)
Pakistan Fruit and Vegetable market is segmented on the basis of Production, Consumption and Trade in terms of Import and Export of Fruits and Vegetables. Some of the major fruits and vegetables produced in Pakistan are mangoes, oranges, apples, onions, tomatoes, carrots and watermelons among others.
Fruits and Vegetables Market in Pakistan is expected to register a CAGR of 5.9% during the forecast period of (2020-2025). Pakistan has a wide range of agro-climatic conditions which is allowing the country to produce a wide variety of tropical and sub-tropical fruits and vegetables. According to FAO, Fruits accounts for 9 million tons in 2018. Mangoes with the highest production of 2.3 million metric tons followed by oranges with the production of 1.5 million metric tons. Similarly, vegetable production accounts for 5.4 million tons where 40% of production is only attributed to onions with 2.1 million tons of production followed by tomatoes, carrots, and turnip. According to the Pakistan Bureau of Statistics, in 2018 Pakistan exported 768,200 metric tons of fruit worth of USD 415 million.
-
Comment by Riaz Haq on May 26, 2022 at 7:35am
-
A Heat Wave’s Lamented Victim: The Mango, India’s King of Fruits
Blistering spring temperatures have devastated crops of the country’s most beloved fruit. “The soul of a farmer shudders at seeing these fruitless trees,” one grower said.
https://www.nytimes.com/2022/05/25/world/asia/india-heat-wave-mango...India is the world’s largest mango producer, accounting for nearly 50 percent of the global crop. Much of it is consumed domestically, but the country exports tens of millions of dollars’ worth of mangoes each year to the United Arab Emirates, Britain, Germany and the United States. Over the past decade, India has been trying to penetrate markets in other European Union countries as well.
In the past, export growth has been limited by the higher costs of Indian mangoes compared with those from countries like Brazil, Peru, Israel and Pakistan. India has been striving to increase productivity, which would lower costs.
Even before the extreme heat, India’s mango exports had been badly damaged by the supply chain disruptions of the pandemic, with shipments abroad shrinking by almost 50 percent last year. India’s top export organization had hoped for a big turnaround this year as the Indian and U.S. governments eased trade rules.
Comment
Twitter Feed
Live Traffic Feed
Sponsored Links
South Asia Investor Review
Investor Information Blog
Haq's Musings
Riaz Haq's Current Affairs Blog
Please Bookmark This Page!
Blog Posts
Pak-Saudi Joint Defense: Is Pakistan A Major Power or Bit Player in the Middle East?
The recently signed “Strategic Mutual Defense Agreement” between Saudi Arabia and Pakistan states that “any aggression against either country will be considered an aggression against both”. It is being seen by some geopolitical analysts as the beginning of an "Islamic NATO". Others, such as Indian-American analyst Shadanand Dhume, have dismissed Pakistan as no more than a "bit player"…
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on September 27, 2025 at 5:30pm — 5 Comments
Silicon Valley Pakistani-Americans Among Top Donors to Mamdani Campaign
Omer Hasan and Mohammad Javed are the top donors to Zohran Mamdani’s mayoral campaign in New York City, according to media reports. Both are former executives of Silicon Valley technology firm AppLovin. Born and raised in Silicon Valley, Omer is the son of a Pakistani-American couple who are long-time residents of Silicon Valley, California. …
ContinuePosted by Riaz Haq on September 19, 2025 at 9:00am
© 2025 Created by Riaz Haq.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network to add comments!
Join PakAlumni Worldwide: The Global Social Network